Набор мандлеброта в C / C ++ с использованием графики
Опубликовано: 4 Марта, 2022
Фракталы
Фрактал - это бесконечный узор. Фракталы - это бесконечно сложные модели, которые самоподобны в разных масштабах. Они создаются путем повторения простого процесса снова и снова в непрерывном цикле обратной связи. Математически фракталы можно объяснить следующим образом.
Defining Mandlebrot
The Mandelbrot set is the set of complex numbers c for which the function 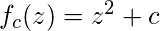 does not diverge when iterated from z=0, i.e., for which the sequence
does not diverge when iterated from z=0, i.e., for which the sequence 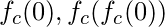 , etc., remains bounded in absolute value. In simple words, Mandelbrot set is a particular set of complex numbers which has a highly convoluted fractal boundary when plotted.
, etc., remains bounded in absolute value. In simple words, Mandelbrot set is a particular set of complex numbers which has a highly convoluted fractal boundary when plotted.

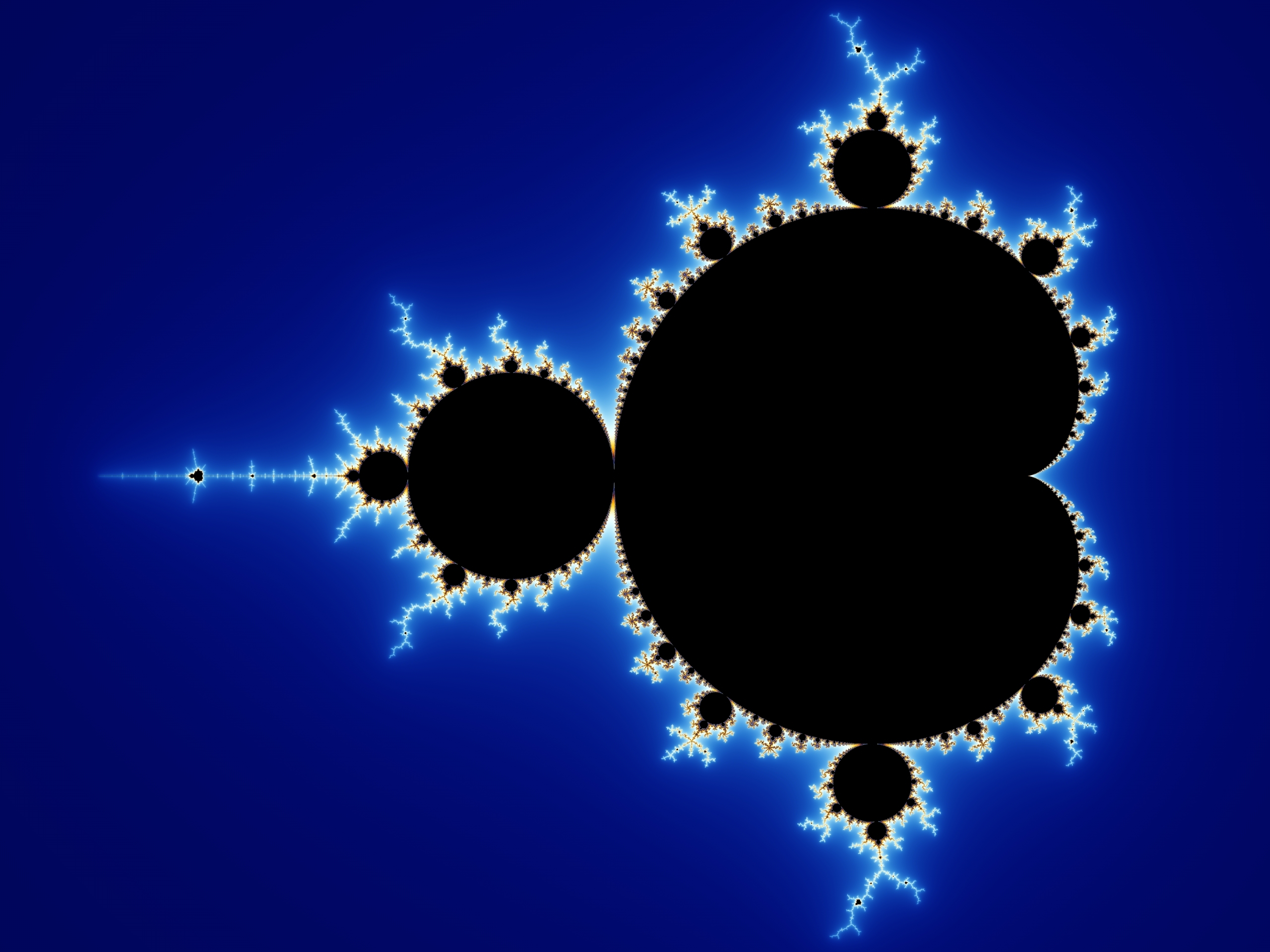
Implementation
#include <complex.h>#include <tgmath.h>#include <winbgim.h> // Defining the size of the screen.#define Y 1080#define X 1920 // Recursive function to provide the iterative every 100th// f^n (0) for every pixel on the screen.int Mandle(double _Complex c, double _Complex t = 0, int counter = 0){ // To eliminate out of bound values. if (cabs(t) > 4) { putpixel(creal(c) * Y / 2 + X / 2, cimag(c) * Y / 2 + Y / 2, COLOR(128 - 128 * cabs(t) / cabs(c), 128 - 128 * cabs(t) / cabs(c), 128 - 128 * cabs(t) / cabs(c))); return 0; } // To put about the end of the fractal, // the higher the value of the counter, // The more accurate the fractal is generated, // however, higher values cause // more processing time. if (counter == 100) { putpixel(creal((c)) * Y / 2 + X / 2, cimag((c)) * Y / 2 + Y / 2, COLOR(255 * (cabs((t * t)) / cabs((t - c) * c)), 0, 0)); return 0; } // recursively calling Mandle with increased counter // and passing the value of the squares of t into it. Mandle(c, cpow(t, 2) + c, counter + 1); return 0;} int MandleSet(){ // Calling Mandle function for every // point on the screen. for (double x = -2; x < 2; x += 0.0015) { for (double y = -1; y < 1; y += 0.0015) { double _Complex temp = x + y * _Complex_I; Mandle(temp); } } return 0;} int main(){ initwindow(X, Y); MandleSet(); getch(); closegraph(); return 0;} |
Output
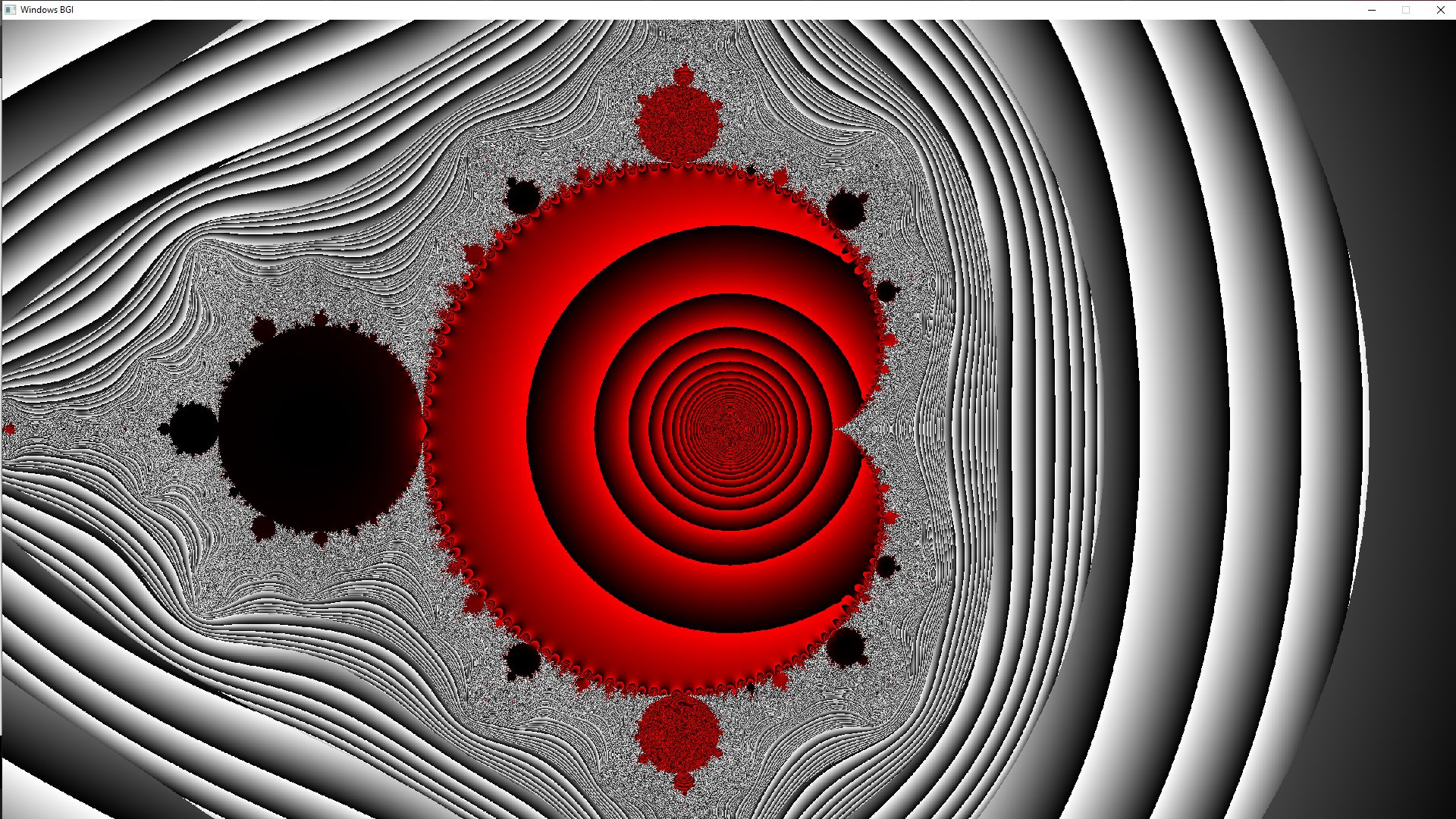
Want to learn from the best curated videos and practice problems, check out the C++ Foundation Course for Basic to Advanced C++ and C++ STL Course for the language and STL. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course.