Программа MapReduce - Анализ погодных данных для анализа жарких и холодных дней
Здесь мы напишем программу Map-Reduce для анализа наборов данных о погоде, чтобы понять ее программную модель обработки данных. Датчики погоды собирают информацию о погоде по всему миру в большом объеме данных журнала. Эти данные о погоде частично структурированы и ориентированы на записи.
Эти данные хранятся в строчно-ориентированном формате ASCII, где каждая строка представляет собой отдельную запись. В каждой строке есть много полей, таких как долгота, широта, максимальная и минимальная дневная температура, среднесуточная температура и т. Д. Для простоты мы сосредоточимся на основном элементе, то есть температуре. Мы будем использовать данные Национальных центров экологической информации (NCEI). Он содержит огромное количество исторических данных о погоде, которые мы можем использовать для анализа данных.
Постановка задачи:
Анализ погодных данных Фэрбенкса, Аляска, чтобы найти холодные и жаркие дни с помощью MapReduce Hadoop.
Шаг 1:
Мы можем скачать набор данных по этой ссылке для разных городов в разные годы. выберите год по вашему выбору и выберите любой из текстовых файлов данных для анализа. В моем случае я выбрал набор данных CRND0103-2020-AK_Fairbanks_11_NE.txt для анализа жарких и холодных дней в Фэрбенксе, Аляска.
Мы можем получить информацию о данных из файла README.txt, доступного на сайте NCEI.
Шаг 2:
Ниже приведен пример нашего набора данных, где столбец 6 и столбец 7 показывают максимальную и минимальную температуру соответственно.
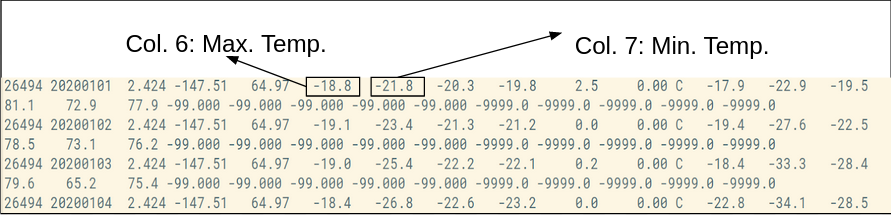
Шаг 3:
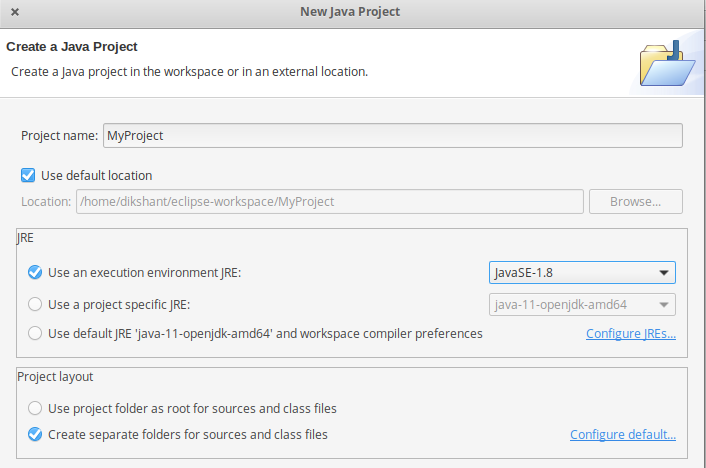
Make a project in Eclipse with below steps:
- First Open Eclipse -> then select File -> New -> Java Project ->Name it MyProject -> then select use an execution environment -> choose JavaSE-1.8 then next -> Finish.
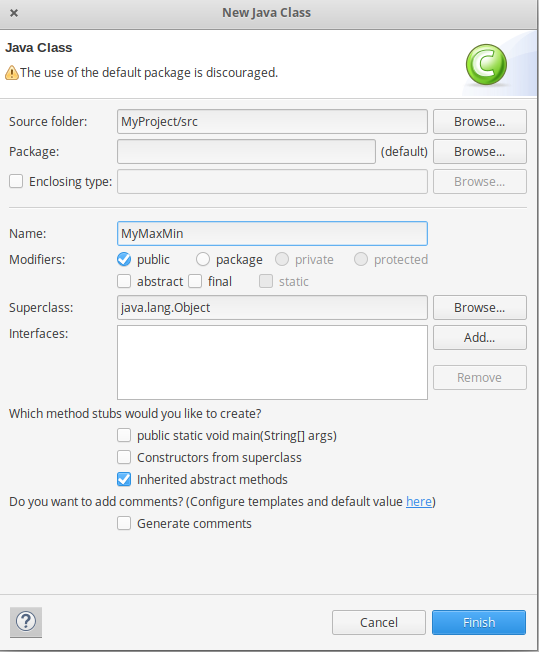
- In this Project Create Java class with name MyMaxMin -> then click Finish
- Copy the below source code to this MyMaxMin java class
// importing Librariesimportjava.io.IOException;importjava.util.Iterator;importorg.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;importorg.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;importorg.apache.hadoop.io.Text;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;importorg.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;importorg.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;publicclassMyMaxMin {// Mapper/*MaxTemperatureMapper class is static* and extends Mapper abstract class* having four Hadoop generics type* LongWritable, Text, Text, Text.*/publicstaticclassMaxTemperatureMapperextendsMapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> {/*** @method map* This method takes the input as a text data type.* Now leaving the first five tokens, it takes* 6th token is taken as temp_max and* 7th token is taken as temp_min. Now* temp_max > 30 and temp_min < 15 are* passed to the reducer.*/// the data in our data set with// this value is inconsistent datapublicstaticfinalintMISSING =9999;@Overridepublicvoidmap(LongWritable arg0, Text Value, Context context)throwsIOException, InterruptedException {// Convert the single row(Record) to// String and store it in String// variable name lineString line = Value.toString();// Check for the empty lineif(!(line.length() ==0)) {// from character 6 to 14 we have// the date in our datasetString date = line.substring(6,14);// similarly we have taken the maximum// temperature from 39 to 45 charactersfloattemp_Max = Float.parseFloat(line.substring(39,45).trim());// similarly we have taken the minimum// temperature from 47 to 53 charactersfloattemp_Min = Float.parseFloat(line.substring(47,53).trim());// if maximum temperature is// greater than 30, it is a hot dayif(temp_Max >30.0) {// Hot daycontext.write(newText("The Day is Hot Day :"+ date),newText(String.valueOf(temp_Max)));}// if the minimum temperature is// less than 15, it is a cold dayif(temp_Min <15) {// Cold daycontext.write(newText("The Day is Cold Day :"+ date),newText(String.valueOf(temp_Min)));}}}}// Reducer/*MaxTemperatureReducer class is staticand extends Reducer abstract classhaving four Hadoop generics typeText, Text, Text, Text.*/publicstaticclassMaxTemperatureReducerextendsReducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {/*** @method reduce* This method takes the input as key and* list of values pair from the mapper,* it does aggregation based on keys and* produces the final context.*/publicvoidreduce(Text Key, Iterator<Text> Values, Context context)throwsIOException, InterruptedException {// putting all the values in// temperature variable of type StringString temperature = Values.next().toString();context.write(Key,newText(temperature));}}/*** @method main* This method is used for setting* all the configuration properties.* It acts as a driver for map-reduce* code.*/publicstaticvoidmain(String[] args)throwsException {// reads the default configuration of the// cluster from the configuration XML filesConfiguration conf =newConfiguration();// Initializing the job with the// default configuration of the clusterJob job =newJob(conf,"weather example");// Assigning the driver class namejob.setJarByClass(MyMaxMin.class);// Key type coming out of mapperjob.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);// value type coming out of mapperjob.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);// Defining the mapper class namejob.setMapperClass(MaxTemperatureMapper.class);// Defining the reducer class namejob.setReducerClass(MaxTemperatureReducer.class);// Defining input Format class which is// responsible to parse the dataset// into a key value pairjob.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);// Defining output Format class which is// responsible to parse the dataset// into a key value pairjob.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);// setting the second argument// as a path in a path variablePath OutputPath =newPath(args[1]);// Configuring the input path// from the filesystem into the jobFileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,newPath(args[0]));// Configuring the output path from// the filesystem into the jobFileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,newPath(args[1]));// deleting the context path automatically// from hdfs so that we don"t have// to delete it explicitlyOutputPath.getFileSystem(conf).delete(OutputPath);// exiting the job only if the// flag value becomes falseSystem.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ?0:1);}} - Now we need to add external jar for the packages that we have import. Download the jar package Hadoop Common and Hadoop MapReduce Core according to your Hadoop version.
You can check Hadoop Version:
hadoop version
- Now we add these external jars to our MyProject. Right Click on MyProject -> then select Build Path-> Click on Configue Build Path and select Add External jars…. and add jars from it’s download location then click -> Apply and Close.
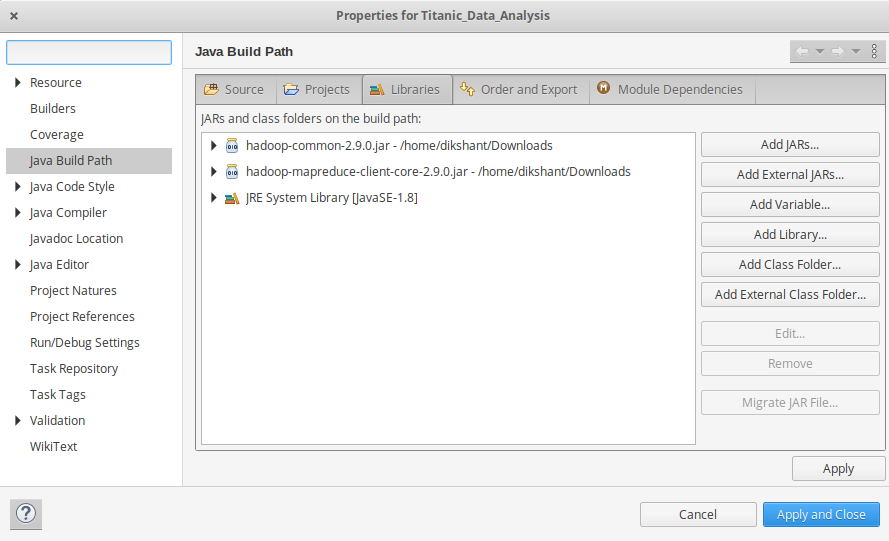
- Now export the project as jar file. Right-click on MyProject choose Export.. and go to Java -> JAR file click -> Next and choose your export destination then click -> Next.
choose Main Class as MyMaxMin by clicking -> Browse and then click -> Finish -> Ok.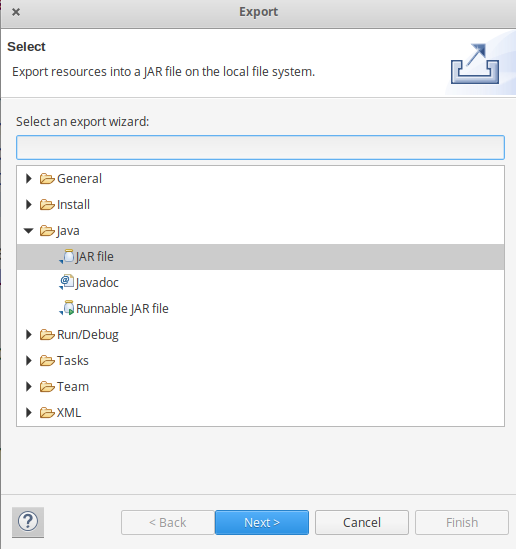
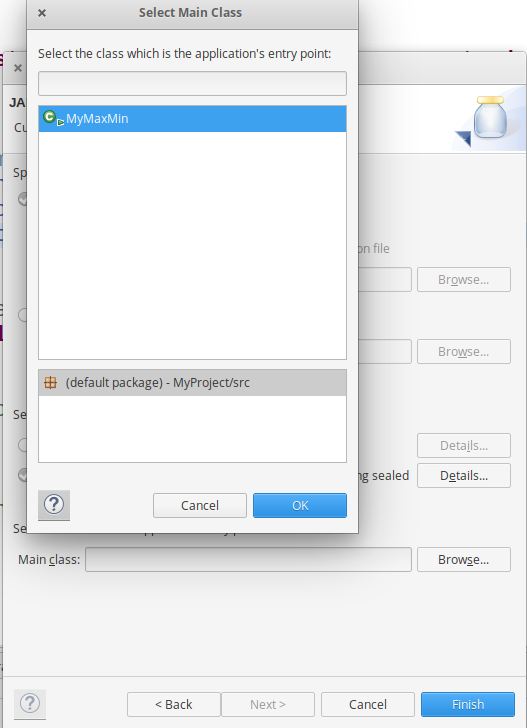
Step 4:
Start our Hadoop Daemons
start-dfs.sh
start-yarn.sh
Step 5:
Move your dataset to the Hadoop HDFS.
Syntax:
hdfs dfs -put /file_path /destination
In below command / shows the root directory of our HDFS.
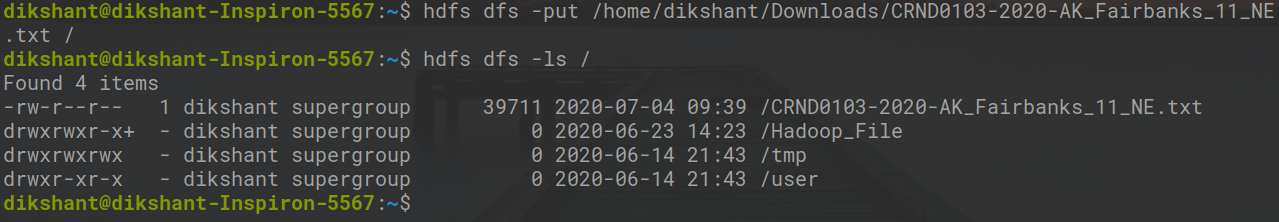
hdfs dfs -put /home/dikshant/Downloads/CRND0103-2020-AK_Fairbanks_11_NE.txt /
Check the file sent to our HDFS.
hdfs dfs -ls /
Step 6:
Now Run your Jar File with below command and produce the output in MyOutput File.
Syntax:
hadoop jar /jar_file_location /dataset_location_in_HDFS /output-file_name
Command:
hadoop jar /home/dikshant/Documents/Project.jar /CRND0103-2020-AK_Fairbanks_11_NE.txt /MyOutput
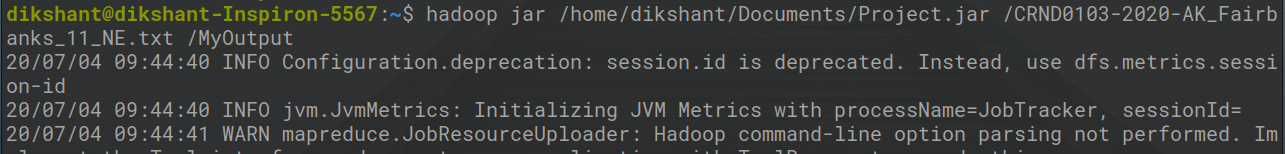
Step 7:
Now Move to localhost:50070/, under utilities select Browse the file system and download part-r-00000 in /MyOutput directory to see result.
Step 8:
See the result in the Downloaded File.
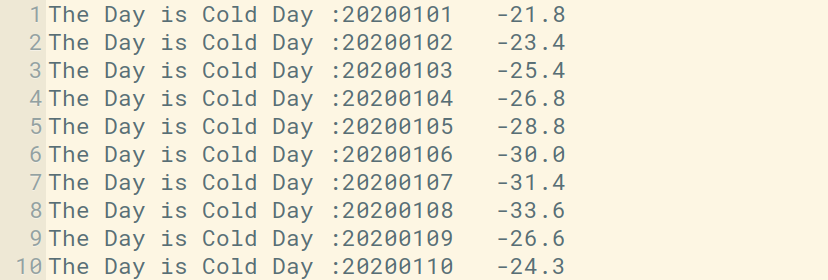
In the above image, you can see the top 10 results showing the cold days. The second column is a day in yyyy/mm/dd format. For Example, 20200101 means
year = 2020 month = 01 Date = 01