Бинарный поиск
Для отсортированного массива arr [] из n элементов напишите функцию для поиска данного элемента x в arr [].
Простой подход - выполнить линейный поиск . Временная сложность описанного выше алгоритма O (n). Другой подход к выполнению той же задачи - использование двоичного поиска.
Двоичный поиск: поиск в отсортированном массиве путем многократного деления интервала поиска пополам. Начните с интервала, охватывающего весь массив. Если значение ключа поиска меньше, чем значение в середине интервала, сузьте интервал до нижней половины. В противном случае сузьте его до верхней половины. Неоднократно проверяйте, пока значение не будет найдено или интервал не станет пустым.
Пример :
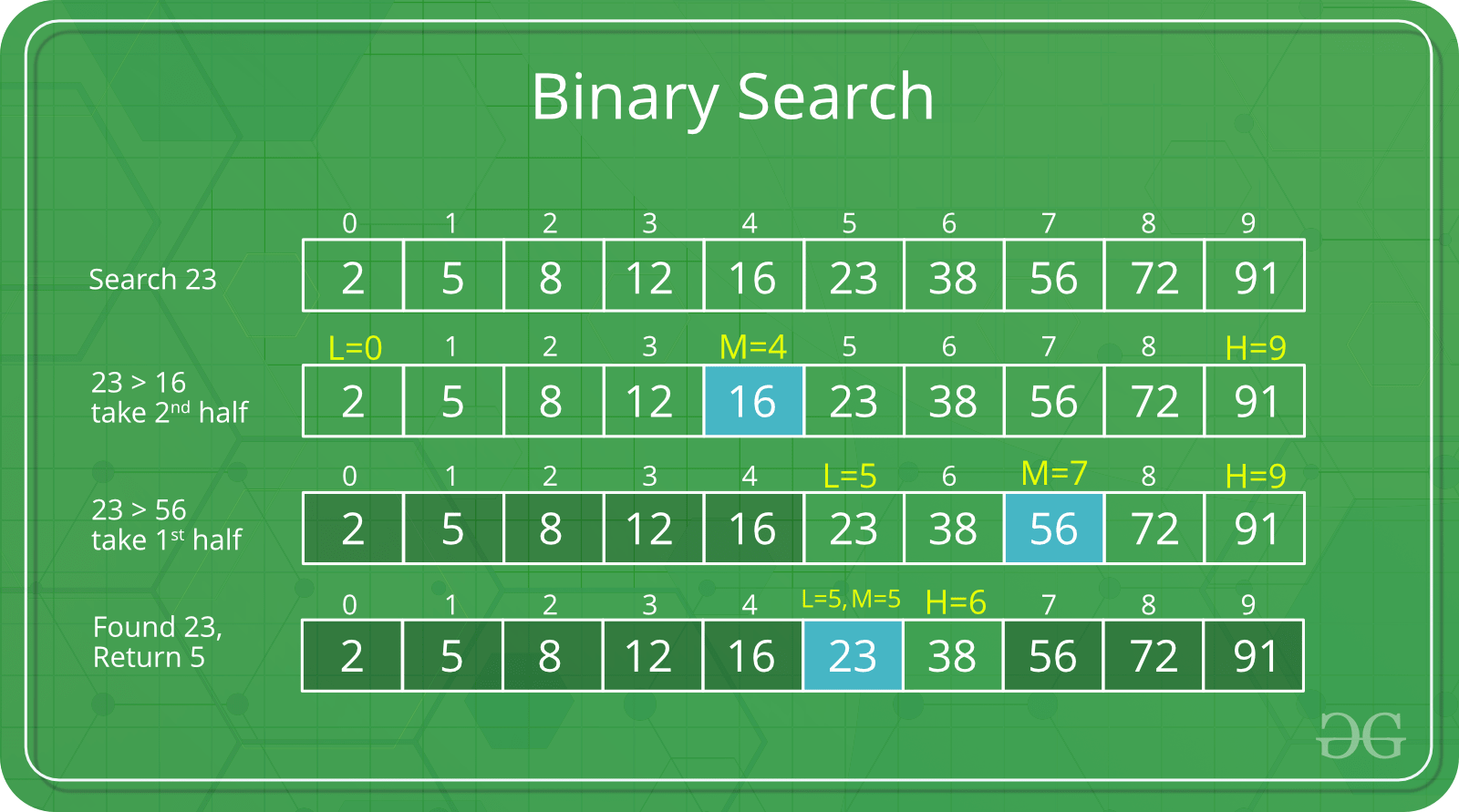
Идея двоичного поиска состоит в том, чтобы использовать информацию о том, что массив отсортирован, и уменьшить временную сложность до O (Log n).
Мы практически игнорируем половину элементов сразу после одного сравнения.
- Сравните x со средним элементом.
- Если x соответствует среднему элементу, мы возвращаем средний индекс.
- Иначе Если x больше среднего элемента, то x может находиться только в правой половине подмассива после среднего элемента. Итак, мы возвращаемся к правой половине.
- Иначе (x меньше) повторяется для левой половины.
Recursive implementation of Binary Search
C++
// C++ program to implement recursive Binary Search#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// A recursive binary search function. It returns// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,// otherwise -1int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x){ if (r >= l) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2; // If the element is present at the middle // itself if (arr[mid] == x) return mid; // If element is smaller than mid, then // it can only be present in left subarray if (arr[mid] > x) return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x); // Else the element can only be present // in right subarray return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x); } // We reach here when element is not // present in array return -1;}int main(void){ int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 }; int x = 10; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x); (result == -1) ? cout << "Element is not present in array" : cout << "Element is present at index " << result; return 0;} |
C
// C program to implement recursive Binary Search#include <stdio.h>// A recursive binary search function. It returns// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,// otherwise -1int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x){ if (r >= l) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2; // If the element is present at the middle // itself if (arr[mid] == x) return mid; // If element is smaller than mid, then // it can only be present in left subarray if (arr[mid] > x) return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x); // Else the element can only be present // in right subarray return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x); } // We reach here when element is not // present in array return -1;}int main(void){ int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 }; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); int x = 10; int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x); (result == -1) ? printf("Element is not present in array") : printf("Element is present at index %d", result); return 0;} |
Java
// Java implementation of recursive Binary Searchclass BinarySearch { // Returns index of x if it is present in arr[l.. // r], else return -1 int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x) { if (r >= l) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2; // If the element is present at the // middle itself if (arr[mid] == x) return mid; // If element is smaller than mid, then // it can only be present in left subarray if (arr[mid] > x) return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x); // Else the element can only be present // in right subarray return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x); } // We reach here when element is not present // in array return -1; } // Driver method to test above public static void main(String args[]) { BinarySearch ob = new BinarySearch(); int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 }; int n = arr.length; int x = 10; int result = ob.binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x); if (result == -1) System.out.println("Element not present"); else System.out.println("Element found at index " + result); }}/* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra */ |
Python3
# Python3 Program for recursive binary search.# Returns index of x in arr if present, else -1def binarySearch (arr, l, r, x): # Check base case if r >= l: mid = l + (r - l) // 2 # If element is present at the middle itself if arr[mid] == x: return mid # If element is smaller than mid, then it # can only be present in left subarray elif arr[mid] > x: return binarySearch(arr, l, mid-1, x) # Else the element can only be present # in right subarray else: return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x) else: # Element is not present in the array return -1# Driver Codearr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ]x = 10# Function callresult = binarySearch(arr, 0, len(arr)-1, x)if result != -1: print ("Element is present at index % d" % result)else: print ("Element is not present in array") |
C#
// C# implementation of recursive Binary Searchusing System;class GFG { // Returns index of x if it is present in // arr[l..r], else return -1 static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int l, int r, int x) { if (r >= l) { int mid = l + (r - l) / 2; // If the element is present at the // middle itself if (arr[mid] == x) return mid; // If element is smaller than mid, then // it can only be present in left subarray if (arr[mid] > x) return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x); // Else the element can only be present // in right subarray return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x); } // We reach here when element is not present // in array return -1; } // Driver method to test above public static void Main() { int[] arr = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 }; int n = arr.Length; int x = 10; int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x); if (result == -1) Console.WriteLine("Element not present"); else Console.WriteLine("Element found at index " + result); }}// This code is contributed by Sam007. |
PHP
<?php// PHP program to implement// recursive Binary Search// A recursive binary search// function. It returns location// of x in given array arr[l..r]// is present, otherwise -1function binarySearch($arr, $l, $r, $x){if ($r >= $l){ $mid = ceil($l + ($r - $l) / 2); // If the element is present // at the middle itself if ($arr[$mid] == $x) return floor($mid); // If element is smaller than // mid, then it can only be // present in left subarray if ($arr[$mid] > $x) return binarySearch($arr, $l, $mid - 1, $x); // Else the element can only // be present in right subarray return binarySearch($arr, $mid + 1, $r, $x);}// We reach here when element// is not present in arrayreturn -1;}// Driver Code$arr = array(2, 3, 4, 10, 40);$n = count($arr);$x = 10;$result = binarySearch($arr, 0, $n - 1, $x);if(($result == -1))echo "Element is not present in array";elseecho "Element is present at index ", $result; // This code is contributed by anuj_67.?> |
Javascript
<script>// JavaScript program to implement recursive Binary Search// A recursive binary search function. It returns// location of x in given array arr[l..r] is present,// otherwise -1function binarySearch(arr, l, r, x){ if (r >= l) { let mid = l + Math.floor((r - l) / 2); // If the element is present at the middle // itself if (arr[mid] == x) return mid; // If element is smaller than mid, then // it can only be present in left subarray if (arr[mid] > x) return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x); // Else the element can only be present // in right subarray return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x); } // We reach here when element is not // present in array return -1;}let arr = [ 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 ];let x = 10;let n = arr.lengthlet result = binarySearch(arr, 0, n - 1, x);(result == -1) ? document.write( "Element is not present in array") : document.write("Element is present at index " +result);</script> |
Выход :
Элемент присутствует в индексе 3
Здесь вы можете создать функцию проверки для упрощения реализации.
Here is recursive implementation with check function which I feel is a much easier implementation:
C++
C++#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;//define array globallyconst int N = 1e6 +4;int a[N];int n;//array size//elememt to be searched in array int k;bool check(int dig){ //element at dig position in array int ele=a[dig]; //if k is less than //element at dig position //then we need to bring our higher ending to dig //and then continue further if(k<=ele) { return 1; } else { return 0; }}void binsrch(int lo,int hi){ while(lo<hi) { int mid=(lo+hi)/2; if(check(mid)) { hi=mid; } else { lo=mid+1; } } //if a[lo] is k if(a[lo]==k) cout<<"Element found at index "<<lo;// 0 based indexing else cout<<"Element doesnt exist in array";//element was not in our array}int main(){ cin>>n; for(int i=0; i<n; i++)РЕКОМЕНДУЕМЫЕ СТАТЬИ |