Дерево Прото Ван Эмде Боас | Комплект 3 | Вставка и запрос isMember
Пожалуйста, прочтите предыдущие статьи о Дереве Прото Ван Эмде Боаса, чтобы понять это правильно.
Procedure for Insert:
- Base Case: If the size of Proto-VEB is 2 then assign true to the bit array( Here we in code we assign Proto-VEB(1) due to recursive structure and so now it is not nullptr and it act as true ) at the position of key.
- Until we reach at the base case, we will recursively call insert on cluster containing key and also now we use the key as the position of the key in that cluster instead of the query key.
- We will do the same procedure for the summary which will assign true according to the inserted key.
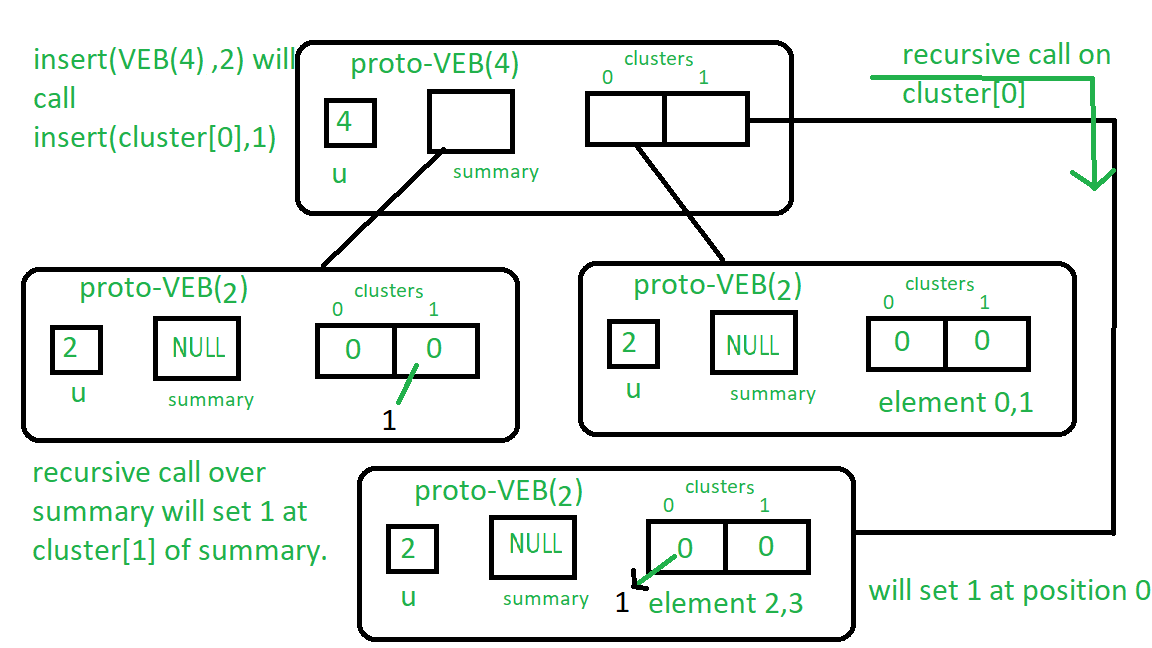
Example: Let’s insert 2 into Proto-VEB (u=4): From the procedure of insert we will start recursion as size of Proto-VEB is greater than 2 so we recursively call insert() on cluster number 2/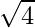 which is 1 and it’s position 2%
which is 1 and it’s position 2%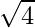 which is 0 so recursive call will be insert(cluster[1], 0).
which is 0 so recursive call will be insert(cluster[1], 0).
And cluster[1] is size 2 Proto-VEB, we reached at the base case so it will assign true at( in code Proto-VEB(1) as true ) cluster[1] 0th place.
Likewise, we will do the same procedure over summary.
See the image below for more clarity:
Follow the instructions written near the boxes from top to bottom.
isMember procedure: This procedure returns boolean value according to whether the key is present in Proto-VEB or not. It is quite trivial to understand see the image above to get the idea about it.
- Base Case: If the Proto-VEB size is 2 then check if bit array value at the key position is true or not and return value accordingly. (In code we check whether pointer at the key position is nullptr or not.)
- Recursion: we do recursive call over cluster containing key until we reach the base case.
Implementation of above algorithm:
// C++ implementation of the approach#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std; class Proto_Van_Emde_Boas {public: // Total number of keys int universe_size; // Summary Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* summary; // Clusters array of Proto-VEB pointers vector<Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*> clusters; int root(int u) { return int(sqrt(u)); } // Function to return cluster numbers // in which key is present int high(int x) { return x / root(universe_size); } // Function to return position of x in cluster int low(int x) { return x % root(universe_size); } // Function to return the index from // cluster number and position int generate_index(int cluster, int position) { return cluster * root(universe_size) + position; } // Constructor Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(int size) { universe_size = size; // Base case if (size <= 2) { // Set summary to nullptr as there is no // more summary for size 2 summary = nullptr; // Vector of two pointers // nullptr in starting clusters = vector<Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*>(size, nullptr); } else { // Assiging Proto-VEB(sqrt(u)) to summary summary = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(root(size)); // Creating array of Proto-VEB Tree pointers of size sqrt(u) // first all nullptrs are going to assign clusters = vector<Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*>(root(size), nullptr); // Assigning Proto-VEB(sqrt(u)) to all its clusters for (int i = 0; i < root(size); i++) { clusters[i] = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(root(size)); } } }}; // Function that returns true if the// key is present in the treebool isMember(Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key){ // If key is greater then universe_size then // returns false if (key >= helper->universe_size) return false; // If we reach at base case // the just return whether // pointer is nullptr then false // else return true if (helper->universe_size == 2) { return helper->clusters[key]; } else { // Recursively go deep into the // level of Proto-VEB tree using its // cluster index and its position return isMember(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key)); }} // Function to insert a key in the treevoid insert(Proto_Van_Emde_Boas*& helper, int key){ // If we reach at base case // then assign Proto-VEB(1) in place // of nullptr if (helper->universe_size == 2) { helper->clusters[key] = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(1); } else { // Recursively using index of cluster and its // position in cluster insert(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key)); // Also do the same recusion in summary VEB insert(helper->summary, helper->high(key)); }} // Driver codeint main(){ Proto_Van_Emde_Boas* hello = new Proto_Van_Emde_Boas(4); cout << isMember(hello, 3); insert(hello, 3); cout << isMember(hello, 3);} |
Insert Algorithm Complexity Recurrence:
T(u) = 2T() + O(1)
This algorithm runs in O(log2(u)) worst-case time.
isMember Algorithm Complexity Recurrence:
T(u) = T() + O(1)
This algorithm runs in O(log2(log2(u))) worst-case time.
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important DSA concepts with the DSA Self Paced Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course.
In case you wish to attend live classes with industry experts, please refer Geeks Classes Live and Geeks Classes Live USA