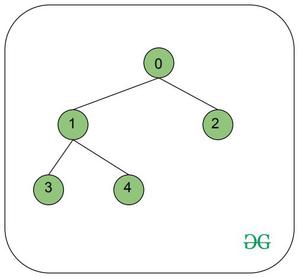
Сумма узлов и соответствующих соседей на пути от корня до вершины V
Для корневого дерева с N вершинами, массива values [] , который представляет значение, присвоенное каждому узлу, и вершины V , задача состоит в том, чтобы вычислить сумму значений узлов и ближайших соседей, лежащих на пути от корня ( всегда 0 ) до V.
Примеры:
Input: N = 8, values = {1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 4, 3, 6}, V = 7
Output: 16
Explanation:
Path from root (0) to V (7) = 0 -> 1 -> 4 -> 7
Neighbors of 0 = (2, 3), Sum = 1(node 0) + 3(node 2) + 0(node 3) = 4
Neighbors of 1 = (5), Sum = 2(node 1) + 4(node 5) = 6
No neighbor of 4, Sum = 0(node 4) = 0
No neighbor of 7, Sum = 6(node 7) = 6
Total sum = 4 + 6 + 0 + 6 = 16Input: N = 5, values = {5, 6, 2, 9, 0}, V = 2
Output: 13
Подход:
Идея состоит в том, чтобы сохранить родительский элемент каждого узла в массиве и добавить значение каждого родителя с его дочерним элементом и сохранить его в родительском узле . Теперь каждый узел будет содержать сумму своего значения и значения соответствующих соседей. Используйте этот массив, чтобы найти необходимую сумму пути от корня до вершины V.
Выполните следующие действия, чтобы решить проблему:
- Инициализируйте массив для хранения значений каждого узла и его соответствующих соседей с помощью DFS Traversal.
- Итерируйте от вершины V к корню, используя массив, и продолжайте добавлять значения всех узлов, найденных на пути.
- Наконец, выведите полученную сумму .
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ Program to implement// the above appraoch#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// Creating Adjacency listvector<vector<int>> constructTree(int n, vector<vector<int>> edges){ vector<vector<int>> adjl(n); for (auto e : edges) { int u = e[0]; int v = e[1]; adjl[u].push_back(v); adjl[v].push_back(u); } return adjl;}// Function to perform DFS traversalvoid DFS(vector<vector<int>> adjl, vector<int> &parent, int u, int p){ // Initializing parent of each node to p parent[u] = p; // Iterate over the children for (int v : adjl[u]) { if (v != p) { DFS(adjl, parent, v, u); } }}// Function to add values of children to// respective parent nodesvector<int> valuesFromChildren(vector<int> parent, vector<int> values){ vector<int> valuesChildren(parent.size()); for (int i = 0; i < parent.size(); i++) { // Root node if (parent[i] == -1) continue; else { int p = parent[i]; valuesChildren[p] += values[i]; } } return valuesChildren;}// Function to return sum of values of// each node in path from V to the rootint findSumOfValues(int v, vector<int> parent, vector<int> valuesChildren){ int cur_node = v; int sum = 0; // Path from node V to root node while (cur_node != -1) { sum += valuesChildren[cur_node]; cur_node = parent[cur_node]; } return sum;}// Driver Codeint main(){ int n = 8; // Insert edges into the graph vector<vector<int>> edges = {{0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 4}, {1, 5}, {4, 7}, {3, 6}}; int v = 7; // Values assigned to each vertex vector<int> values = {1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 4, 3, 6}; // Constructing the tree // using adjacency list vector<vector<int>> adjl = constructTree(n, edges); // Parent array vector<int> parent(n); // store values in the parent array DFS(adjl, parent, 0, -1); // Add values of children to the parent vector<int> valuesChildren = valuesFromChildren(parent, values); // Find sum of nodes lying in the path int sum = findSumOfValues(v, parent, valuesChildren); // Add root node since // its value is not included yet sum += values[0]; cout << sum << endl;}// This code is contributed by// sanjeev2552 |
Java
// Java Program to implement// the above appraochimport java.io.*;import java.util.*;class GFG { // Creating Adjacency list private static List<List<Integer> > constructTree(int n, int[][] edges) { List<List<Integer> > adjl = new ArrayList<List<Integer> >(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { adjl.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); } for (int[] e : edges) { int u = e[0]; int v = e[1]; adjl.get(u).add(v); adjl.get(v).add(u); } return adjl; } // Function to perform DFS traversal private static void DFS( List<List<Integer> > adjl, int[] parent, int u, int p) { // Initializing parent of each node to p parent[u] = p; // Iterate over the children for (int v : adjl.get(u)) { if (v != p) { DFS(adjl, parent, v, u); } } } // Function to add values of children to // respective parent nodes private static int[] valuesFromChildren( int[] parent, int[] values) { int[] valuesChildren = new int[parent.length]; for (int i = 0; i < parent.length; i++) { // Root node if (parent[i] == -1) continue; else { int p = parent[i]; valuesChildren[p] += values[i]; } } return valuesChildren; } // Function to return sum of values of // each node in path from V to the root private static int findSumOfValues( int v, int[] parent, int[] valuesChildren) { int cur_node = v; int sum = 0; // Path from node V to root node while (cur_node != -1) { sum += valuesChildren[cur_node]; cur_node = parent[cur_node]; } return sum; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 8; // Insert edges into the graph int[][] edges = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 0, 3 }, { 1, 4 }, { 1, 5 }, { 4, 7 }, { 3, 6 } }; int v = 7; // Values assigned to each vertex int[] values = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 4, 3, 6 }; // Constructing the tree // using adjacency list List<List<Integer> > adjl = constructTree(n, edges); // Parent array int[] parent = new int[n]; // store values in the parent array DFS(adjl, parent, 0, -1); // Add values of children to the parent int[] valuesChildren = valuesFromChildren(parent, values); // Find sum of nodes lying in the path int sum = findSumOfValues( v, parent, valuesChildren); // Add root node since // its value is not included yet sum += values[0]; System.out.println(sum); }} |
C#
// C# program to implement// the above appraochusing System;using System.Collections.Generic;class GFG{// Creating Adjacency listprivate static List<List<int>> constructTree(int n, int[,] edges){ List<List<int> > adjl = new List<List<int> >(); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { adjl.Add(new List<int>()); } for(int i = 0; i < edges.GetLength(0); i++) { int u = edges[i, 0]; int v = edges[i, 1]; adjl[u].Add(v); adjl[v].Add(u); } return adjl;}// Function to perform DFS traversalprivate static void DFS(List<List<int> > adjl, int[] parent, int u, int p){ // Initializing parent of each node to p parent[u] = p; // Iterate over the children foreach(int v in adjl[u]) { if (v != p) { DFS(adjl, parent, v, u); } }}// Function to add values of children to// respective parent nodesprivate static int[] valuesFromChildren(int[] parent, int[] values){ int[] valuesChildren = new int[parent.Length]; for(int i = 0; i < parent.Length; i++) { // Root node if (parent[i] == -1) continue; else { int p = parent[i]; valuesChildren[p] += values[i]; } } return valuesChildren;}// Function to return sum of values of// each node in path from V to the rootprivate static int findSumOfValues(int v, int[] parent, int[] valuesChildren){ int cur_node = v; int sum = 0; // Path from node V to root node while (cur_node != -1) { sum += valuesChildren[cur_node]; cur_node = parent[cur_node]; } return sum;}// Driver Codepublic static void Main(string[] args){ int n = 8; // Insert edges into the graph int[, ] edges = { { 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 0, 3 }, { 1, 4 }, { 1, 5 }, { 4, 7 }, { 3, 6 } }; int v = 7; // Values assigned to each vertex int[] values = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 4, 3, 6 }; // Constructing the tree // using adjacency list List<List<int>> adjl = constructTree(n, edges); // Parent array int[] parent = new int[n]; // store values in the parent array DFS(adjl, parent, 0, -1); // Add values of children to the parent int[] valuesChildren = valuesFromChildren(parent, values); // Find sum of nodes lying in the path int sum = findSumOfValues(v, parent, valuesChildren); // Add root node since // its value is not included yet sum += values[0]; Console.WriteLine(sum);РЕКОМЕНДУЕМЫЕ СТАТЬИ |