Регрессия и ее типы в программировании на R
Регрессионный анализ - это статистический инструмент для оценки взаимосвязи между двумя или более переменными. Всегда есть одна переменная ответа и одна или несколько переменных-предикторов. Регрессионный анализ широко используется для соответствующей подгонки данных и последующего прогнозирования данных для прогнозирования. Это помогает предприятиям и организациям узнать о поведении своего продукта на рынке, используя переменную зависимую / ответную и независимую / предикторную переменную. В этой статье давайте узнаем о различных типах регрессии в программировании на R с помощью примеров.
Типы регрессии
В программировании R широко используются три основных типа регрессии. Они есть:
- Линейная регрессия
- Множественная регрессия
- Логистическая регрессия
Линейная регрессия
Модель линейной регрессии - одна из наиболее широко используемых среди трех типов регрессии. В линейной регрессии взаимосвязь оценивается между двумя переменными, т. Е. Одной переменной ответа и одной переменной-предиктором. Линейная регрессия дает прямую линию на графике. Математически,
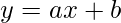
where,
x indicates predictor or independent variable
y indicates response or dependent variable
a and b are coefficients
Реализация в R
In R programming, lm() function is used to create linear regression model.
Syntax:
lm(formula)Parameter:
formula: represents the formula on which data has to be fitted
To know about more optional parameters, use below command in console: help(“lm”)
Example:
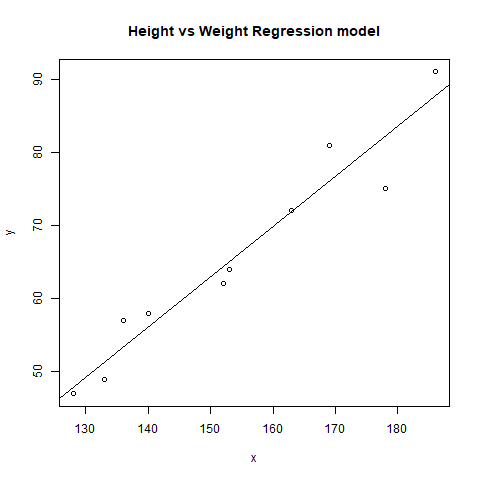
In this example, let us plot the linear regression line on the graph and predict the weight based using height.
# R program to illustrate# Linear Regression # Height vectorx <- c(153, 169, 140, 186, 128, 136, 178, 163, 152, 133) # Weight vectory <- c(64, 81, 58, 91, 47, 57, 75, 72, 62, 49) # Create a linear regression modelmodel <- lm(y~x) # Print regression modelprint(model) # Find the weight of a person # With height 182df <- data.frame(x = 182)res <- predict(model, df)cat("
Predicted value of a person with height = 182")print(res) # Output to be present as PNG filepng(file = "linearRegGFG.png") # Plotplot(x, y, main = "Height vs Weight Regression model")abline(lm(y~x)) # Save the file.dev.off() |
Выход:
Вызов:
lm (формула = y ~ x)
Коэффициенты:
(Перехват) x
-39,7137 0,6847
Прогнозируемое значение человека с ростом = 182
1
84,9098
Множественная регрессия
Множественная регрессия - это еще один метод регрессионного анализа, который является расширением модели линейной регрессии, поскольку для ее создания используется несколько переменных-предикторов. Математически,
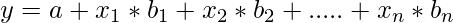
Реализация в R
Multiple regression in R programming uses the same lm() function to create the model.
Syntax:
lm(formula, data)Parameters:
formula: represents the formula on which data has to be fitted
data: represents dataframe on which formula has to be applied
Example:
Let us create multiple regression model of airquality dataset present in R base package and plot the model on the graph.
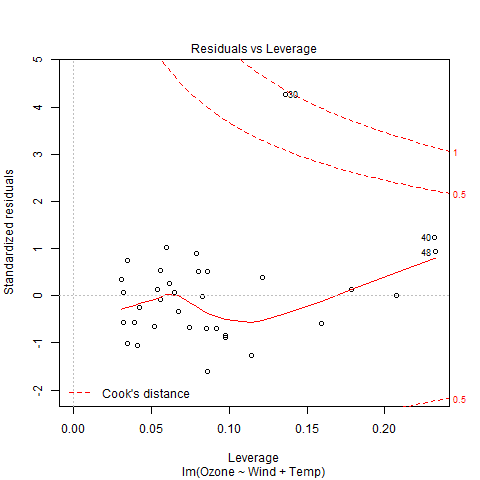
# R program to illustrate# Multiple Linear Regression # Using airquality datasetinput <- airquality[1:50, c("Ozone", "Wind", "Temp")] # Create regression modelmodel <- lm(Ozone~Wind + Temp, data = input) # Print the regression modelcat("Regression model:
")print(model) # Output to be present as PNG filepng(file = "multipleRegGFG.png") # Plotplot(model) # Save the file.dev.off() |
Выход:
Модель регрессии:
Вызов:
лм (формула = Озон ~ Ветер + Температура, данные = ввод)
Коэффициенты:
(Перехват) Температура ветра
-58,239 -0,739 1,329
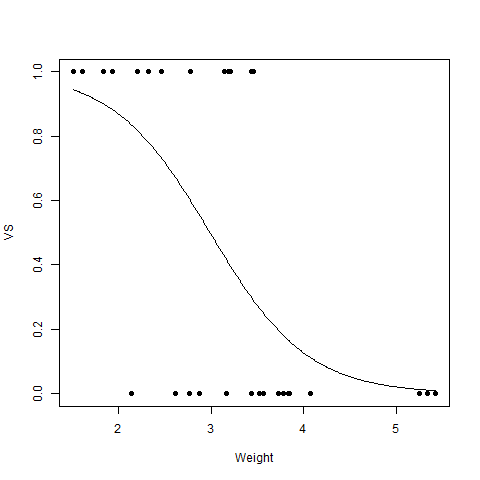
Логистическая регрессия
Логистическая регрессия - еще один широко используемый метод регрессионного анализа, который предсказывает значение с диапазоном. Кроме того, он используется для прогнозирования значений категориальных данных. Например, электронная почта является либо спамом, либо не спамом, победителем или проигравшим, мужчиной или женщиной и т. Д. Математически,
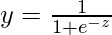
where,
y represents response variable
z represents equation of independent variables or features
Реализация в R
In R programming, glm() function is used to create logistic regression model.
Syntax:
glm(formula, data, family)Parameters:
formula: represents a formula on the basis of which model has to be fitted
data: represents dataframe on which formula has to be applied
family: represents the type of function to be used. “binomial” for logistic regression
Example:
# R program to illustrate# Logistic Regression # Using mtcars dataset # To create the logistic modelmodel <- glm(formula = vs ~ wt, family = binomial, data = mtcars) # Creating a range of wt valuesx <- seq(min(mtcars$wt), max(mtcars$wt), 0.01) # Predict using weighty <- predict(model, list(wt = x), type = "response") # Print modelprint(model) # Output to be present as PNG filepng(file = "LogRegGFG.png") # Plotplot(mtcars$wt, mtcars$vs, pch = 16, xlab = "Weight", ylab = "VS")lines(x, y) # Saving the filedev.off() |
Выход:
Вызов: glm (формула = vs ~ wt, family = binomial, data = mtcars)
Коэффициенты:
(Перехват) вес
5,715 -1,911
Степень свободы: 31 Всего (т. Е. Нулевая); 30 Остаточный
Нулевое отклонение: 43,86
Остаточное отклонение: 31,37 AIC: 35,37