Проверить, находится ли данный узел на пути между узлами U и V
Опубликовано: 12 Января, 2022
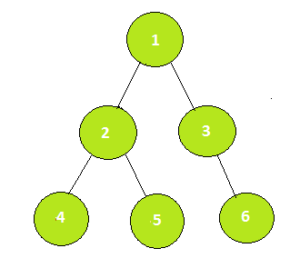
Для трех вершин U , V и R двоичного дерева задача состоит в том, чтобы проверить, лежит ли R на пути между U и V. Если его нет в пути, выведите « Нет», в противном случае выведите « Да» .
Примеры:
Input: U = 4, V = 6, R = 2
Output: Yes
Path 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 6 contains 2
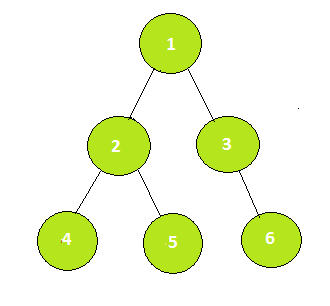
Input: U = 4, V = 6, R = 5
Output: No
Path 4 -> 2 -> 1 -> 3 -> 6 does not contain 5
Рекомендуется: сначала попробуйте свой подход в {IDE}, прежде чем переходить к решению.
Подход: идея состоит в том, чтобы использовать наименьшего общего предка двух узлов. R существует на пути между U и V в следующих случаях:
- R - самый низкий общий предок U и V.
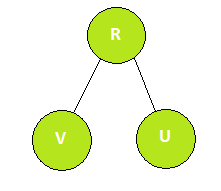
- R находится в левом поддереве самого низкого общего предка U и V и находится выше V.
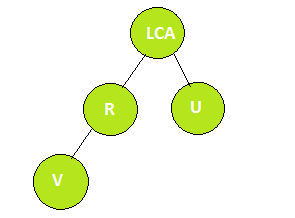
- R находится в правом поддереве самого низкого общего предка U и V и находится выше U.
To know more about the lowest commom ancestor, read the post here.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// CPP Program to implement the above appraoch#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;class GfG{ public: // Table for storing 2^ith parent vector<vector<int>> table; // Variable to store the height of the tree int height; // Graph vector<vector<int>> Graph; // Arrays to mark start and end time for a node vector<int> timeIn, timeOut; // Timer int time; // constructor for initializing // the global variables GfG(int n) { // log(n) with base 2 height = (int)ceil(log2(n)); // Filling with -1 as initial table.resize(n + 1, vector<int>(height + 1, -1)); // Fill the graph with empty lists Graph.resize(n + 1); timeIn.resize(n + 1); timeOut.resize(n + 1); time = 0; } // Dfs for pre-processing sparse table and // calculating start and end time void dfs(int s, int p) { // Parent at 1 node distance is always // it"s direct parent table[s][0] = p; // Start time noted timeIn[s] = ++time; // Filling sparse table recursively for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++) table[s][i] = table[table[s][i - 1]][i - 1]; // Traversing children of source for (int child : Graph[s]) { if (child == p) continue; dfs(child, s); } // End time noted timeOut[s] = ++time; } // Helper function to check lowest common Ancestor bool check(int u, int v) { return timeIn[u] <= timeIn[v] && timeOut[u] >= timeOut[v]; } // Function to return Lowest Common Ancestor of U and V int lowestCommonAncestor(int U, int V) { if (check(U, V)) return U; if (check(V, U)) return V; for (int i = height; i >= 0; i--) { if (!check(table[U][i], V)) U = table[U][i]; } return table[U][0]; } // Function that return true if R // exists on the path between U // and V in the given tree bool isPresent(int U, int V, int R) { // Dfs dfs(1, 1); // Calculating LCA between U and V int LCA = lowestCommonAncestor(U, V); // Calculating LCA between U and R int LCA_1 = lowestCommonAncestor(U, R); // Calculating LCA between U and V int LCA_2 = lowestCommonAncestor(V, R); if (LCA == R || (LCA_1 == LCA && LCA_2 == R) || (LCA_2 == LCA && LCA_1 == R)) { return true; } return false; }};// Driver codeint main(int argc, char const *argv[]){ // Number of vertices int n = 6; GfG *obj = new GfG(n); // Create the graph obj->Graph[1].push_back(2); obj->Graph[2].push_back(1); obj->Graph[1].push_back(3); obj->Graph[3].push_back(1); obj->Graph[2].push_back(4); obj->Graph[4].push_back(2); obj->Graph[2].push_back(5); obj->Graph[5].push_back(2); obj->Graph[3].push_back(6); obj->Graph[6].push_back(3); int U = 4, V = 6, R = 2; if (obj->isPresent(U, V, R)) cout << "Yes" << endl; else cout << "No" << endl;}// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 |
Java
// Java implementation of the approachimport java.util.*;class GfG { // Table for storing 2^ith parent private static int table[][]; // Variable to store the height of the tree private static int height; // Graph private static ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> > Graph; // Arrays to mark start and end time for a node private static int timeIn[]; private static int timeOut[]; // Timer private static int time; // Private constructor for initializing // the global variables private GfG(int n) { // log(n) with base 2 height = (int)Math.ceil(Math.log10(n) / Math.log10(2)); table = new int[n + 1][height + 1]; // Fill the graph with empty lists Graph = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer> >(); for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) Graph.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); timeIn = new int[n + 1]; timeOut = new int[n + 1]; time = 0; } // Filling with -1 as initial private static void preprocessing(int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { Arrays.fill(table[i], -1); } } // Dfs for pre-processing sparse table and // calculating start and end time private static void dfs(int s, int p) { // Parent at 1 node distance is always // it"s direct parent table[s][0] = p; // Start time noted timeIn[s] = ++time; // Filling sparse table recursively for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++) table[s][i] = table[table[s][i - 1]][i - 1]; // Traversing children of source for (int child : Graph.get(s)) { if (child == p) continue; dfs(child, s); } // End time noted timeOut[s] = ++time; } // Helper function to check lowest common Ancestor private static boolean check(int u, int v) { return timeIn[u] <= timeIn[v] && timeOut[u] >= timeOut[v]; } // Function to return Lowest Common Ancestor of U and V private static int lowestCommonAncestor(int U, int V) { if (check(U, V)) return U; if (check(V, U)) return V; for (int i = height; i >= 0; i--) { if (!check(table[U][i], V)) U = table[U][i]; } return table[U][0]; } // Function that return true if R // exists on the path between U // and V in the given tree private static boolean isPresent(int U, int V, int R) { // Dfs dfs(1, 1); // Calculating LCA between U and V int LCA = lowestCommonAncestor(U, V); // Calculating LCA between U and R int LCA_1 = lowestCommonAncestor(U, R); // Calculating LCA between U and V int LCA_2 = lowestCommonAncestor(V, R); if (LCA == R || (LCA_1 == LCA && LCA_2 == R) || (LCA_2 == LCA && LCA_1 == R)) { return true; } return false; } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { // Number of vertices int n = 6; GfG obj = new GfG(n); // Create the graph preprocessing(n); Graph.get(1).add(2); Graph.get(2).add(1); Graph.get(1).add(3); Graph.get(3).add(1); Graph.get(2).add(4); Graph.get(4).add(2); Graph.get(2).add(5); Graph.get(5).add(2); Graph.get(3).add(6); Graph.get(6).add(3); int U = 4, V = 6, R = 2; if (isPresent(U, V, R)) System.out.print("Yes"); else System.out.print("No"); }} |
C#
// C# implementation of the approachusing System;using System.Collections.Generic;class GfG{ // Table for storing 2^ith parent private static int [,]table; // Variable to store the height of the tree private static int height; // Graph private static List<List<int> > Graph; // Arrays to mark start and end time for a node private static int []timeIn; private static int []timeOut; // Timer private static int time; // Private constructor for initializing // the global variables private GfG(int n) { // log(n) with base 2 height = (int)Math.Ceiling(Math.Log10(n) / Math.Log10(2)); table = new int[n + 1, height + 1]; // Fill the graph with empty lists Graph = new List<List<int> >(); for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) Graph.Add(new List<int>()); timeIn = new int[n + 1]; timeOut = new int[n + 1]; time = 0; } // Filling with -1 as initial private static void preprocessing(int n) { for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { for(int j = 0; j < height + 1; j++) table[i, j] = -1; } } // Dfs for pre-processing sparse table and // calculating start and end time private static void dfs(int s, int p) { // Parent at 1 node distance is always // it"s direct parent table[s, 0] = p; // Start time noted timeIn[s] = ++time; // Filling sparse table recursively for (int i = 1; i <= height; i++) table[s, i] = table[table[s, i - 1], i - 1]; // Traversing children of source foreach (int child in Graph[s]) { if (child == p) continue; dfs(child, s); } // End time noted timeOut[s] = ++time; } // Helper function to check lowest common Ancestor private static bool check(int u, int v) { return timeIn[u] <= timeIn[v] && timeOut[u] >= timeOut[v]; }
РЕКОМЕНДУЕМЫЕ СТАТЬИ |