Проектирование полосового эллиптического фильтра IIR с использованием Scipy-Python
IIR расшифровывается как Infinite Impulse Response, это одна из ярких характеристик многих систем, инвариантных по линейному времени, которые характеризуются наличием импульсной характеристики h (t) / h (n), которая не достигает 0 ни на одном этапе, а вместо этого сохраняется неопределенно долго. .
Что такое полосовой эллиптический фильтр IIR?
Эллиптический фильтр - это особый тип фильтра, который используется в цифровой обработке сигналов, когда требуется быстрый переход от полосы пропускания к полосе заграждения.
Технические характеристики следующие:
- Частота полосы пропускания: 1400-2100 Гц
- Частота стоп-полосы: 1050-24500 Гц
- Пульсация полосы пропускания: 0,4 дБ
- Затухание в полосе задерживания: 50 дБ
- Частота дискретизации: 7 кГц
- Мы построим график амплитуды и фазовой характеристики фильтра.
Пошаговый подход:
Шаг 1: Импорт всех необходимых библиотек.
Python3
# import required libraryimport numpy as npimport scipy.signal as signalimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt |
Шаг 2: Определение пользовательских функций mfreqz () и impz () . Mfreqz - это функция для графика амплитуды и фазы, а impz - это функция для импульсной и ступенчатой характеристики].
Python3
# Function to depict magnitude # and phase plotdef mfreqz(b, a, Fs): # Compute frequency response of the # filter using signal.freqz function wz, hz = signal.freqz(b, a) # Calculate Magnitude from hz in dB Mag = 20*np.log10(abs(hz)) # Calculate phase angle in degree from hz Phase = np.unwrap(np.arctan2(np.imag(hz), np.real(hz)))*(180/np.pi) # Calculate frequency in Hz from wz Freq = wz*Fs/(2*np.pi) # Plot filter magnitude and phase responses using subplot. fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) # Plot Magnitude response sub1 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 1) sub1.plot(Freq, Mag, "r", linewidth=2) sub1.axis([1, Fs/2, -100, 5]) sub1.set_title("Magnitute Response", fontsize=20) sub1.set_xlabel("Frequency [Hz]", fontsize=20) sub1.set_ylabel("Magnitude [dB]", fontsize=20) sub1.grid() # Plot phase angle sub2 = plt.subplot(2, 1, 2) sub2.plot(Freq, Phase, "g", linewidth=2) sub2.set_ylabel("Phase (degree)", fontsize=20) sub2.set_xlabel(r"Frequency (Hz)", fontsize=20) sub2.set_title(r"Phase response", fontsize=20) sub2.grid() plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5) fig.tight_layout() plt.show() # Define impz(b,a) to calculate impulse# response and step response of a system# input: b= an array containing numerator# coefficients,a= an array containing# denominator coefficientsdef impz(b, a): # Define the impulse sequence of length 60 impulse = np.repeat(0., 60) impulse[0] = 1. x = np.arange(0, 60) # Compute the impulse response response = signal.lfilter(b, a, impulse) # Plot filter impulse and step response: fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.subplot(211) plt.stem(x, response, "m", use_line_collection=True) plt.ylabel("Amplitude", fontsize=15) plt.xlabel(r"n (samples)", fontsize=15) plt.title(r"Impulse response", fontsize=15) plt.subplot(212) step = np.cumsum(response) # Compute step response of the system plt.stem(x, step, "g", use_line_collection=True) plt.ylabel("Amplitude", fontsize=15) plt.xlabel(r"n (samples)", fontsize=15) plt.title(r"Step response", fontsize=15) plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5) fig.tight_layout() plt.show() |
Шаг 3: Определите переменные с заданными характеристиками фильтра.
Python3
# Given specification # Sampling frequency in HzFs = 7000 # Pass band frequency in Hzfp = np.array([ 1400 , 2100 ]) # Stop band frequency in Hzfs = np.array([ 1050 , 2450 ]) # Pass band ripple in dBAp = 0.4 # Stop band attenuation in dBAs = 50 |
Шаг 4. Вычислите частоту среза
Python3
# Compute pass band and stop band edge frequencies # Normalized passband edge# frequencies wrt Nyquist ratewp = fp / (Fs / 2 ) # Normalized stopband# edge frequenciesws = fs / (Fs / 2 ) |
Шаг 5: Вычислить порядок цифрового фильтра Elliptic Bandpass.
Python3
# Compute order of the elliptic filter# using signal.ellipordN, wc = signal.ellipord(wp, ws, Ap, As) # Print the order of the filter and# cutoff frequenciesprint ( 'Order of the filter=' , N)print ( 'Cut-off frequency=' , wc) |

Шаг 6: Разработайте цифровой эллиптический полосовой фильтр.
Python3
# Design digital elliptic bandpass filter# using signal.ellip functionz, p = signal.ellip(N, Ap, As, wc, 'bandpass' ) # Print numerator and denomerator# coefficients of the filterprint ( 'Numerator Coefficients:' , z)print ( 'Denominator Coefficients:' , p) |

Шаг 7: Постройте график амплитуды и фазовой характеристики.
Python3
# Depicting visulalizations # Call mfreqz to plot the magnitude and phase responsemfreqz(z, p, Fs) |
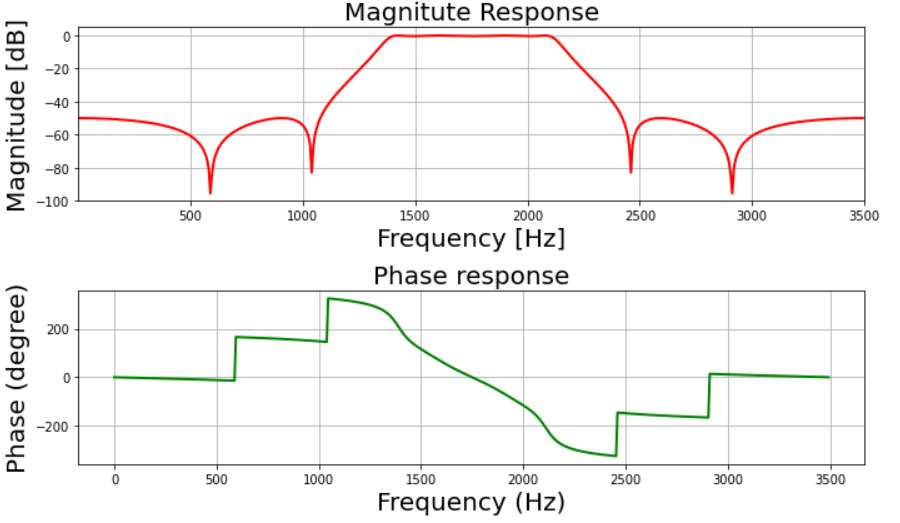
Шаг 8: Постройте импульсную и ступенчатую характеристики фильтра.
Python3
# Call impz function to plot impulse# and step response of the filterimpz(z, p) |
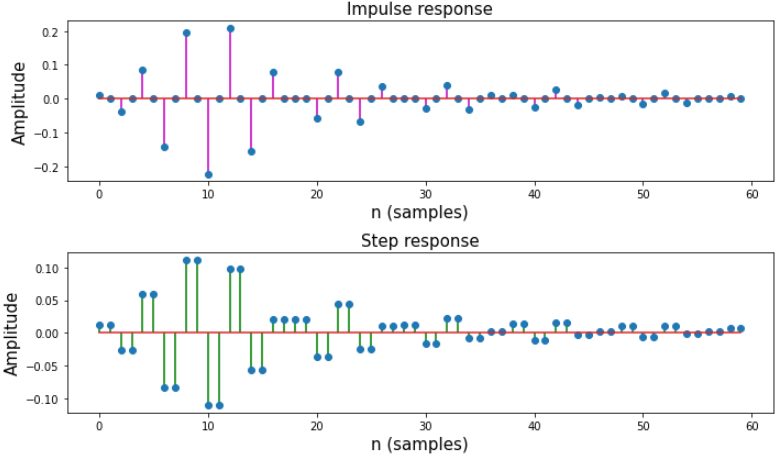
Ниже приведена полная реализация описанного выше пошагового подхода:
Python3
# Import required libraryimport numpy as npimport scipy.signal as signalimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Function to depict magnitude# and phase plotdef mfreqz(b, a, Fs): # Compute frequency response of the # filter using signal.freqz function wz, hz = signal.freqz(b, a) # Calculate Magnitude from hz in dB Mag = 20 * np.log10( abs (hz)) # Calculate phase angle in degree from hz Phase = np.unwrap(np.arctan2(np.imag(hz), np.real(hz))) * ( 180 / np.pi) # Calculate frequency in Hz from wz Freq = wz * Fs / ( 2 * np.pi) # Plot filter magnitude and phase responses using subplot. fig = plt.figure(figsize = ( 10 , 6 )) # Plot Magnitude response sub1 = plt.subplot( 2 , 1 , 1 ) sub1.plot(Freq, Mag, 'r' , linewidth = 2 ) sub1.axis([ 1 , Fs / 2 , - 100 , 5 ]) sub1.set_title( 'Magnitute Response' , fontsize = 20 ) sub1.set_xlabel( 'Frequency [Hz]' , fontsize = 20 ) sub1.set_ylabel( 'Magnitude [dB]' , fontsize = 20 ) sub1.grid() # Plot phase angle sub2 = plt.subplot( 2 , 1 , 2 ) sub2.plot(Freq, Phase, 'g' , linewidth = 2 ) sub2.set_ylabel( 'Phase (degree)' , fontsize = 20 ) sub2.set_xlabel(r 'Frequency (Hz)' , fontsize = 20 ) sub2.set_title(r 'Phase response' , fontsize = 20 ) sub2.grid() plt.subplots_adjust(hspace = 0.5 ) fig.tight_layout() plt.show() # Define impz(b,a) to calculate impulse# response and step response of a system# input: b= an array containing numerator# coefficients,a= an array containing# denominator coefficientsdef impz(b, a): # Define the impulse sequence of length 60 impulse = np.repeat( 0. , 60 ) impulse[ 0 ] = 1. x = np.arange( 0 , 60 ) # Compute the impulse response response = signal.lfilter(b, a, impulse) # Plot filter impulse and step response: fig = plt.figure(figsize = ( 10 , 6 )) plt.subplot( 211 ) plt.stem(x, response, 'm' , use_line_collection = True ) plt.ylabel( 'Amplitude' , fontsize = 15 ) plt.xlabel(r 'n (samples)' , fontsize = 15 ) plt.title(r 'Impulse response' , fontsize = 15 ) plt.subplot( 212 ) step = np.cumsum(response) # Compute step response of the system plt.stem(x, step, 'g' , use_line_collection = True ) plt.ylabel( 'Amplitude' , fontsize = 15 ) plt.xlabel(r 'n (samples)' , fontsize = 15 ) plt.title(r 'Step response' , fontsize = 15 ) plt.subplots_adjust(hspace = 0.5 ) fig.tight_layout() plt.show() # Given specification # Sampling frequency in HzFs = 7000 # Pass band frequency in Hzfp = np.array([ 1400 , 2100 ]) # Stop band frequency in Hzfs = np.array([ 1050 , 2450 ]) # Pass band ripple in dBAp = 0.4 # Stop band attenuation in dBAs = 50 # Compute pass band and# stop band edge frequencies# Normalized passband edge frequencies# wrt Nyquist ratewp = fp / (Fs / 2 ) # Normalized stopband edge frequenciesws = fs / (Fs / 2 ) # Compute order of the elliptic filter# using signal.ellipordN, wc = signal.ellipord(wp, ws, Ap, As) # Print the order of the filter and cutoff frequenciesprint ( 'Order of the filter=' , N)print ( 'Cut-off frequency=' , wc) # Design digital elliptic bandpass filter# using signal.ellip() functionz, p = signal.ellip(N, Ap, As, wc, 'bandpass' ) # Print numerator and denomerator coefficients of the filterprint ( 'Numerator Coefficients:' , z)print ( 'Denominator Coefficients:' , p) # Depicting visulalizations # Call mfreqz to plot the magnitude and# phase responsemfreqz(z, p, Fs)# Call impz function to plot impulse and# step response of the filterimpz(z, p) |
Выход:




Внимание компьютерщик! Укрепите свои основы с помощью базового курса программирования Python и изучите основы.
Для начала подготовьтесь к собеседованию. Расширьте свои концепции структур данных с помощью курса Python DS. А чтобы начать свое путешествие по машинному обучению, присоединяйтесь к курсу Машинное обучение - базовый уровень.