Последовательность Аронсона
Учитывая целое число 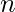 , сгенерируйте первый
, сгенерируйте первый 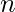 условия последовательности Аронсона.
условия последовательности Аронсона.
Последовательность Аронсона - это бесконечная последовательность целых чисел, полученная из индекса T (или t) в предложении:
“T is the first, fourth, eleventh, sixteenth, … letter in this sentence.”
- Первое вхождение T в предложении находится в индексе 1 (индексация на основе 1), а номер, упомянутый первым, является первым, то есть 1
- Точно так же второе вхождение t в предложении находится под индексом 4, а указанное второе число является четвертым, то есть 4
- Точно так же третье вхождение t в предложении находится в индексе 11, а третье упомянутое число - одиннадцатое, то есть 11.
- Точно так же серия продолжается как 1, 4, 11, 16,…
Примеры:
Input: n = 3
Output: 1, 4, 11Input: n = 6
Output: 1, 4, 11, 16, 24, 29
Рекомендуется: сначала попробуйте свой подход в {IDE}, прежде чем переходить к решению.
Подход: простая идея - сохранить строку «T is the», чтобы получить первые два члена последовательности. Для каждого из этих терминов преобразуйте его в слова в порядковой форме, добавьте в строку и вычислите значение следующих более высоких терминов. Повторите этот процесс для каждого из последующих более высоких членов, сгенерированных n-2 раза, чтобы сгенерировать первые n членов последовательности Аронсона.
Чтобы преобразовать числа в слова, см. Здесь.
Ниже представлена реализация описанного выше подхода:
C ++
// C++ program to generate the// first n terms of Aronson's sequence #include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std; // Returns the given number in wordsstring convert_to_words(string num){ // Get number of digits in given number int len = num.length(); // Base cases if (len == 0 || len > 4) { return "" ; } /* The following arrays contain one digit(both cardinal and ordinal forms), two digit(<20, ordinal forms) numbers, and multiples(ordinal forms) and powers of 10. */ string single_digits_temp[] = { "" , "one" , "two" , "three" , "four" , "five" , "six" , "seven" , "eight" , "nine" }; string single_digits[] = { "" , "first" , "second" , "third" , "fourth" , "fifth" , "sixth" , "seventh" , "eighth" , "ninth" }; string two_digits[] = { "" , "tenth" , "eleventh" , "twelfth" , "thirteenth" , "fourteenth" , "fifteenth" , "sixteenth" , "seventeenth" , "eighteenth" , "nineteenth" }; string tens_multiple[] = { "" , "tenth" , "twentieth" , "thirtieth" , "fortieth" , "fiftieth" , "sixtieth" , "seventieth" , "eightieth" , "ninetieth" }; string tens_power[] = { "hundred" , "thousand" }; string word = "" ; // If single digit number if (len == 1) { word += single_digits[num[0] - '0' ]; return word; } int i = 0, ctr = 0; string s = " " ; while (i < len) { if (len >= 3) { if (num[i] != '0' ) { word += single_digits_temp[num[i] - '0' ] + " " ; // here len can be 3 or 4 word += tens_power[len - 3] + " " ; ctr++; } len--; num.erase(0, 1); } // last two digits else { if (ctr != 0) { s = " and " ; word.erase(word.length() - 1); } // Handle all powers of 10 if (num[i + 1] == '0' ) if (num[i] == '0' ) word = word + "th" ; else word += s + tens_multiple[num[i] - '0' ]; // Handle two digit numbers < 20 else if (num[i] == '1' ) word += s + two_digits[num[i + 1] - '0' + 1]; else { if (num[i] != '0' ) word += s + tens_multiple[num[i] - '0' ] .substr(0, tens_multiple[num[i] - '0' ] .length() - 4) + "y " ; else word += s; word += single_digits[num[i + 1] - '0' ]; } i += 2; } if (i == len) { if (word[0] == ' ' ) word.erase(0, 1); } } return word;} // Function to print the first n terms// of Aronson's sequencevoid Aronsons_sequence( int n){ string str = "T is the " ; int ind = 0; for ( int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { // check if character // is alphabet or not if ( isalpha (str[i])) { ind += 1; } if (str[i] == 't' or str[i] == 'T' ) { n -= 1; // convert number to words // in ordinal format and append str += convert_to_words(to_string(ind)) + ", " ; cout << ind << ", " ; } if (n == 0) break ; }} // Driver codeint main( void ){ int n = 6; Aronsons_sequence(n); return 0;} |
Джава
// Java program to generate the// first n terms of Aronson's sequenceimport java.util.*; class GFG{ // Returns the given number in wordsstatic String convert_to_words( char [] num){ // Get number of digits in given number int len = num.length; // Base cases if (len == 0 || len > 4 ) { return "" ; } /* The following arrays contain one digit(both cardinal and ordinal forms), two digit(<20, ordinal forms) numbers, and multiples(ordinal forms) and powers of 10. */ String single_digits_temp[] = { "" , "one" , "two" , "three" , "four" , "five" , "six" , "seven" , "eight" , "nine" }; String single_digits[] = { "" , "first" , "second" , "third" , "fourth" , "fifth" , "sixth" , "seventh" , "eighth" , "ninth" }; String two_digits[] = { "" , "tenth" , "eleventh" , "twelfth" , "thirteenth" , "fourteenth" , "fifteenth" , "sixteenth" , "seventeenth" , "eighteenth" , "nineteenth" }; String tens_multiple[] = { "" , "tenth" , "twentieth" , "thirtieth" , "fortieth" , "fiftieth" , "sixtieth" , "seventieth" , "eightieth" , "ninetieth" }; String tens_power[] = { "hundred" , "thousand" }; String word = "" ; // If single digit number if (len == 1 ) { word += single_digits[num[ 0 ] - '0' ]; return word; } int i = 0 , ctr = 0 ; String s = " " ; while (i < len) { if (len >= 3 ) { if (num[i] != '0' ) { word += single_digits_temp[num[i] - '0' ] + " " ; // here len can be 3 or 4 word += tens_power[len - 3 ] + " " ; ctr++; } len--; num=Arrays.copyOfRange(num, 1 , num.length); } // last two digits else { if (ctr != 0 ) { s = " and " ; word = word.substring( 0 ,word.length() - 1 ); } // Handle all powers of 10 if (num[i + 1 ] == '0' ) if (num[i] == '0' ) word = word + "th" ; else word += s + tens_multiple[num[i] - '0' ]; // Handle two digit numbers < 20 else if (num[i] == '1' ) word += s + two_digits[num[i + 1 ] - '0' + 1 ]; else { if (num[i] != '0' ) word += s + tens_multiple[num[i] - '0' ] .substring( 0 , tens_multiple[num[i] - '0' ] .length() - 4 ) + "y " ; else word += s; word += single_digits[num[i + 1 ] - '0' ]; } i += 2 ; } if (i == len) { if (word.charAt( 0 ) == ' ' ) word = word.substring( 1 ,word.length()); } } return word;} // Function to print the first n terms// of Aronson's sequencestatic void Aronsons_sequence( int n){ String str = "T is the " ; int ind = 0 ; for ( int i = 0 ; i < str.length(); i++) { // check if character // is alphabet or not if (Character.isAlphabetic(str.charAt(i))) { ind += 1 ; } if (str.charAt(i) == 't' || str.charAt(i) == 'T' ) { n -= 1 ; // convert number to words // in ordinal format and append str += convert_to_words(String.valueOf(ind).toCharArray()) + ", " ; System.out.print(ind+ ", " ); } if (n == 0 ) break ; }} // Driver codepublic static void main(String[] args){ int n = 6 ; Aronsons_sequence(n);}} // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar |
C #
// C# program to generate the// first n terms of Aronson's sequenceusing System; class GFG{ // Returns the given number in wordsstatic String convert_to_words( char [] num){ // Get number of digits in given number int len = num.Length; // Base cases if (len == 0 || len > 4) { return "" ; } /* The following arrays contain one digit(both cardinal and ordinal forms), two digit(<20, ordinal forms) numbers, and multiples(ordinal forms) and powers of 10. */ String []single_digits_temp = { "" , "one" , "two" , "three" , "four" , "five" , "six" , "seven" , "eight" , "nine" }; String []single_digits = { "" , "first" , "second" , "third" , "fourth" , "fifth" , "sixth" , "seventh" , "eighth" , "ninth" }; String []two_digits = { "" , "tenth" , "eleventh" , "twelfth" , "thirteenth" , "fourteenth" , "fifteenth" , "sixteenth" , "seventeenth" , "eighteenth" , "nineteenth" }; String []tens_multiple = { "" , "tenth" , "twentieth" , "thirtieth" , "fortieth" , "fiftieth" , "sixtieth" , "seventieth" , "eightieth" , "ninetieth" }; String []tens_power = { "hundred" , "thousand" }; String word = "" ; // If single digit number if (len == 1) { word += single_digits[num[0] - '0' ]; return word; } int i = 0, ctr = 0; String s = " " ; while (i < len) { if (len >= 3) { if (num[i] != '0' ) { word += single_digits_temp[num[i] - '0' ] + " " ; // here len can be 3 or 4 word += tens_power[len - 3] + " " ; ctr++; } len--; Array.Copy(num, 1, num, 0, num.Length - 1);
|