Поиск с равномерной стоимостью (Дейкстра для больших графов)
Поиск с равномерной стоимостью - это вариант алгоритма Диджикстры. Здесь вместо того, чтобы вставлять все вершины в приоритетную очередь, мы вставляем только исходный код, а затем вставляем одну за другой, когда это необходимо. На каждом шаге мы проверяем, находится ли элемент уже в очереди приоритетов (используя массив посещений). Если да, то выполняем клавишу уменьшения, иначе вставляем.
Этот вариант Dijsktra полезен для бесконечных графов и тех графов, которые слишком велики для представления в памяти. Поиск по единообразной стоимости в основном используется в искусственном интеллекте.
Примеры:
Вход :
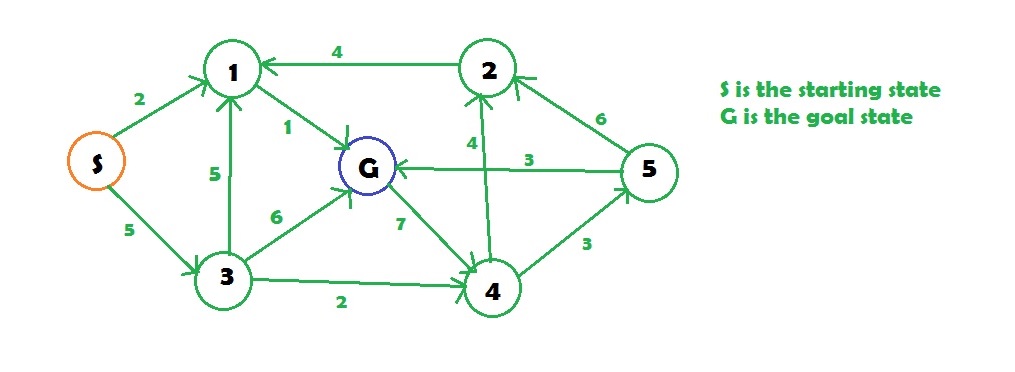
Выход : Минимальная стоимость от S до G = 3
Uniform-Cost Search is similar to Dijikstra’s algorithm . In this algorithm from the starting state we will visit the adjacent states and will choose the least costly state then we will choose the next least costly state from the all un-visited and adjacent states of the visited states, in this way we will try to reach the goal state (note we wont continue the path through a goal state ), even if we reach the goal state we will continue searching for other possible paths( if there are multiple goals) . We will keep a priority queue which will give the least costliest next state from all the adjacent states of visited states .
CPP
// C++ implemenatation of above approach#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// graphvector<vector<int> > graph;// map to store cost of edgesmap<pair<int, int>, int> cost;// returns the minimum cost in a vector( if// there are multiple goal states)vector<int> uniform_cost_search(vector<int> goal, int start){ // minimum cost upto // goal state from starting // state vector<int> answer; // create a priority queue priority_queue<pair<int, int> > queue; // set the answer vector to max value for (int i = 0; i < goal.size(); i++) answer.push_back(INT_MAX); // insert the starting index queue.push(make_pair(0, start)); // map to store visited node map<int, int> visited; // count int count = 0; // while the queue is not empty while (queue.size() > 0) { // get the top element of the // priority queue pair<int, int> p = queue.top(); // pop the element queue.pop(); // get the original value p.first *= -1; // check if the element is part of // the goal list if (find(goal.begin(), goal.end(), p.second) != goal.end()) { // get the position int index = find(goal.begin(), goal.end(), p.second) - goal.begin(); // if a new goal is reached if (answer[index] == INT_MAX) count++; // if the cost is less if (answer[index] > p.first) answer[index] = p.first; // pop the element queue.pop(); // if all goals are reached if (count == goal.size()) return answer; } // check for the non visited nodes // which are adjacent to present node if (visited[p.second] == 0) for (int i = 0; i < graph[p.second].size(); i++) { // value is multiplied by -1 so that // least priority is at the top queue.push(make_pair((p.first + cost[make_pair(p.second, graph[p.second][i])]) * -1, graph[p.second][i])); } // mark as visited visited[p.second] = 1; } return answer;}// main functionint main(){ // create the graph graph.resize(7); // add edge graph[0].push_back(1); graph[0].push_back(3); graph[3].push_back(1); graph[3].push_back(6); graph[3].push_back(4); graph[1].push_back(6); graph[4].push_back(2); graph[4].push_back(5); graph[2].push_back(1); graph[5].push_back(2); graph[5].push_back(6); graph[6].push_back(4); // add the cost cost[make_pair(0, 1)] = 2; cost[make_pair(0, 3)] = 5; cost[make_pair(1, 6)] = 1; cost[make_pair(3, 1)] = 5; cost[make_pair(3, 6)] = 6; cost[make_pair(3, 4)] = 2; cost[make_pair(2, 1)] = 4; cost[make_pair(4, 2)] = 4; cost[make_pair(4, 5)] = 3; cost[make_pair(5, 2)] = 6; cost[make_pair(5, 6)] = 3; cost[make_pair(6, 4)] = 7; // goal state vector<int> goal; // set the goal // there can be multiple goal states goal.push_back(6); // get the answer vector<int> answer = uniform_cost_search(goal, 0); // print the answer cout << "Minimum cost from 0 to 6 is = " << answer[0] << endl; return 0;} |
Python3
# Python3 implemenatation of above approach# returns the minimum cost in a vector( if# there are multiple goal states)def uniform_cost_search(goal, start): # minimum cost upto # goal state from starting global graph,cost answer = [] # create a priority queue queue = [] # set the answer vector to max value for i in range(len(goal)): answer.append(10**8) # insert the starting index queue.append([0, start]) # map to store visited node visited = {} # count count = 0 # while the queue is not empty while (len(queue) > 0): # get the top element of the queue = sorted(queue) p = queue[-1] # pop the element del queue[-1] # get the original value p[0] *= -1 # check if the element is part of # the goal list if (p[1] in goal): # get the position index = goal.index(p[1]) # if a new goal is reached if (answer[index] == 10**8): count += 1 # if the cost is less if (answer[index] > p[0]): answer[index] = p[0] # pop the element del queue[-1] queue = sorted(queue) if (count == len(goal)): return answer # check for the non visited nodes # which are adjacent to present node if (p[1] not in visited): for i in range(len(graph[p[1]])): # value is multiplied by -1 so that # least priority is at the top queue.append( [(p[0] + cost[(p[1], graph[p[1]][i])])* -1, graph[p[1]][i]]) # mark as visited visited[p[1]] = 1 return answer# main functionif __name__ == "__main__": # create the graph graph,cost = [[] for i in range(8)],{} # add edge graph[0].append(1) graph[0].append(3) graph[3].append(1) graph[3].append(6) graph[3].append(4) graph[1].append(6) graph[4].append(2) graph[4].append(5) graph[2].append(1) graph[5].append(2) graph[5].append(6) graph[6].append(4) # add the cost cost[(0, 1)] = 2 cost[(0, 3)] = 5 cost[(1, 6)] = 1 cost[(3, 1)] = 5 cost[(3, 6)] = 6 cost[(3, 4)] = 2 cost[(2, 1)] = 4 cost[(4, 2)] = 4 cost[(4, 5)] = 3 cost[(5, 2)] = 6 cost[(5, 6)] = 3 cost[(6, 4)] = 7 # goal state goal = [] # set the goal # there can be multiple goal states goal.append(6) # get the answer answer = uniform_cost_search(goal, 0) # print the answer print("Minimum cost from 0 to 6 is = ",answer[0])# This code is contributed by mohit kumar 29 |
C#
// C# implemenatation of above approachusing System;using System.Collections;using System.Collections.Generic;class GFG{// graphstatic List<List<int>> graph=new List<List<int>>();// map to store cost of edgesstatic Dictionary<Tuple<int,int>,int> cost= new Dictionary<Tuple<int,int>,int>();// returns the minimum cost in a vector( if// there are multiple goal states)static List<int> uniform_cost_search(List<int> goal, int start){ // minimum cost upto // goal state from starting // state List<int> answer=new List<int>(); // create a priority queue List<Tuple<int, int> > queue = new List<Tuple<int, int> >(); // set the answer vector to max value for (int i = 0; i < goal.Count; i++) answer.Add(int.MaxValue); // insert the starting index queue.Add(new Tuple<int,int>(0, start)); // map to store visited node Dictionary<int, int> visited=new Dictionary<int,int>(); // count int count = 0; // while the queue is not empty while (queue.Count > 0) { // get the top element of the // priority queue Tuple<int, int> q = queue[0]; Tuple<int, int> p = new Tuple<int,int>(-q.Item1,q.Item2); // pop the element queue.RemoveAt(0); // check if the element is part of // the goal list if (goal.Contains(p.Item2)) { // get the position int index = goal.IndexOf(p.Item2); // if a new goal is reached if (answer[index] == int.MaxValue) count++; // if the cost is less if (answer[index] > p.Item1) answer[index] = p.Item1; // pop the element queue.RemoveAt(0); // if all goals are reached if (count == goal.Count) return answer; } // check for the non visited nodes // which are adjacent to present node if (!visited.ContainsKey(p.Item2)) for (int i = 0; i < graph[p.Item2].Count; i++) { // value is multiplied by -1 so that // least priority is at the top queue.Add(new Tuple<int,int>((p.Item1 + (cost.ContainsKey(new Tuple<int,int>(p.Item2, graph[p.Item2][i])) ? cost[new Tuple<int,int>(p.Item2, graph[p.Item2][i])] : 0))*-1, graph[p.Item2][i])); } // mark as visited visited[p.Item2] = 1; } return answer;}// main functionpublic static void Main(params string []args){ // create the graph graph=new List<List<int>>();
РЕКОМЕНДУЕМЫЕ СТАТЬИ |