Найти, есть ли путь между двумя вершинами в неориентированном графе
Для неориентированного графа с N вершинами и E ребрами и двумя вершинами (U, V) из графа задача состоит в том, чтобы определить, существует ли путь между этими двумя вершинами. Выведите «Да», если путь существует, и «Нет» в противном случае.
Примеры:
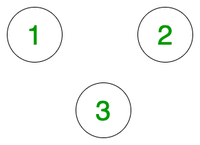
U = 1, V = 2
Output: No
Explanation:
There is no edge between the two points and hence its not possible to reach 2 from 1.Input:
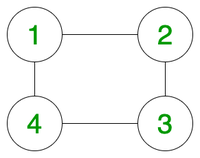
U = 1, V = 3
Output: Yes
Explanation: Vertex 3 from vertex 1 via vertices 2 or 4.
Наивный подход:
Идея состоит в том, чтобы использовать алгоритм Флойда Уоршалла. Чтобы решить проблему, нам нужно попробовать все промежуточные вершины в диапазоне [1, N] и проверить:
- Если между двумя узлами уже существует прямое ребро.
- Или у нас есть путь от узла i к промежуточному узлу k и от узла k к узлу j .
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to detect if a path// exists between any two vertices// for the given undirected graph#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;// Class representing a undirected// graph using matrix// representationclass Graph { int V; int** g;public: Graph(int V); // Function to add an edge to graph void addEdge(int v, int w); // Function to check if // there exists a path or not bool isReachable(int s, int d); // function to compute paths // in the matrix using // Floyd Warshall Algorithm void computePaths();};Graph::Graph(int V){ this->V = V; g = new int*[V + 1]; for (int i = 1; i < V + 1; i++) { // Rows may not be contiguous g[i] = new int[V + 1]; // Initialize all entries // as false to indicate // that there are // no edges initially memset(g[i], 0, (V + 1) * sizeof(int)); } // Initializing node to itself // as it is always reachable for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) g[i][i] = 1;}// Function to add edge between nodesvoid Graph::addEdge(int v, int w){ g[v][w] = 1; g[w][v] = 1;}// Function to compute the pathvoid Graph::computePaths(){ // Use Floyd Warshall algorithm // to detect if a path exists for (int k = 1; k <= V; k++) { // Try every vertex as an // intermediate vertex // to check if a path exists for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= V; j++) g[i][j] = g[i][j] | (g[i][k] && g[k][j]); } }}// Function to check if nodes are reachablebool Graph::isReachable(int s, int d){ if (g[s][d] == 1) return true; else return false;}// Driver codeint main(){ Graph _g(4); _g.addEdge(1, 2); _g.addEdge(2, 3); _g.addEdge(1, 4); _g.computePaths(); int u = 4, v = 3; if (_g.isReachable(u, v)) cout << "Yes
"; else cout << "No
"; return 0;} |
Java
// Java program to detect if a path// exists between any two vertices// for the given undirected graphimport java.util.Arrays;class GFG{// Class representing a undirected// graph using matrix representationstatic class Graph{ int V; int[][] g; public Graph(int V) { this.V = V; // Rows may not be contiguous g = new int[V + 1][V + 1]; for(int i = 0; i < V + 1; i++) { // Initialize all entries // as false to indicate // that there are // no edges initially Arrays.fill(g[i], 0); } // Initializing node to itself // as it is always reachable for(int i = 1; i <= V; i++) g[i][i] = 1; } // Function to add edge between nodes void addEdge(int v, int w) { g[v][w] = 1; g[w][v] = 1; } // Function to check if nodes are reachable boolean isReachable(int s, int d) { if (g[s][d] == 1) return true; else return false; } // Function to compute the path void computePaths() { // Use Floyd Warshall algorithm // to detect if a path exists for(int k = 1; k <= V; k++) { // Try every vertex as an // intermediate vertex // to check if a path exists for(int i = 1; i <= V; i++) { for(int j = 1; j <= V; j++) g[i][j] = g[i][j] | ((g[i][k] != 0 && g[k][j] != 0) ? 1 : 0); } } }};// Driver codepublic static void main(String[] args){ Graph _g = new Graph(4); _g.addEdge(1, 2); _g.addEdge(2, 3); _g.addEdge(1, 4); _g.computePaths(); int u = 4, v = 3; if (_g.isReachable(u, v)) System.out.println("Yes"); else System.out.println("No");}}// This code is contributed by sanjeev2552 |
Python3
# Python3 program to detect if a path# exists between any two vertices# for the given undirected graph# Class representing a undirected# graph using matrix# representationclass Graph: def __init__(self, V): self.V = V # Initialize all entries # as false to indicate # that there are # no edges initially self.g = [[0 for j in range(self.V + 1)] for i in range(self.V + 1)] # Initializing node to itself # as it is always reachable for i in range(self.V + 1): self.g[i][i] = 1 # Function to add edge between nodes def addEdge(self, v, w): self.g[v][w] = 1 self.g[w][v] = 1 # Function to compute the path def computePaths(self): # Use Floyd Warshall algorithm # to detect if a path exists for k in range(1, self.V + 1): # Try every vertex as an # intermediate vertex # to check if a path exists for i in range(1, self.V + 1): for j in range(1, self.V + 1): self.g[i][j] = (self.g[i][j] | (self.g[i][k] and self.g[k][j])) # Function to check if nodes # are reachable def isReachable(self, s, d): if (self.g[s][d] == 1): return True else: return False # Driver codeif __name__=="__main__": _g = Graph(4) _g.addEdge(1, 2) _g.addEdge(2, 3) _g.addEdge(1, 4) _g.computePaths() u = 4 v = 3 if (_g.isReachable(u, v)): print("Yes") else: print("No") # This code is contributed by rutvik_56 |
Yes
Сложность времени: O (V 3 )
Вспомогательное пространство: O (V 2 )
Efficient Solution
We can either use BFS or DFS to find if there is a path from u to v. Below is a BFS based solution
C++
// C++ program to check if there is exist a path between// two vertices of an undirected graph.#include <iostream>#include <list>using namespace std;// This class represents an undirected graph// using adjacency list representationclass Graph { int V; // No. of vertices // Pointer to an array containing adjacency lists list<int>* adj;public: Graph(int V); // Constructor // function to add an edge to graph void addEdge(int v, int w); bool isReachable(int s, int d);};Graph::Graph(int V){ this->V = V; adj = new list<int>[V];}void Graph::addEdge(int v, int w){ adj[v].push_back(w); adj[w].push_back(v);}// A BFS based function to check whether d is reachable from s.bool Graph::isReachable(int s, int d){ // Base case if (s == d) return true; // Mark all the vertices as not visited bool* visited = new bool[V]; for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) visited[i] = false; // Create a queue for BFS list<int> queue; // Mark the current node as visited and enqueue it visited[s] = true; queue.push_back(s); // it will be used to get all adjacent vertices of a vertex list<int>::iterator i; while (!queue.empty()) { // Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it s = queue.front(); queue.pop_front(); // Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex s // If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark it // visited and enqueue it for (i = adj[s].begin(); i != adj[s].end(); ++i) { // If this adjacent node is the destination node, // then return true if (*i == d) return true; // Else, continue to do BFS if (!visited[*i]) { visited[*i] = true; queue.push_back(*i); } } } // If BFS is complete without visiting d return false;}// Driver program to test methods of graph classint main(){ // Create a graph given in the above diagram Graph g(4); g.addEdge(0, 1); g.addEdge(0, 2); g.addEdge(1, 2); g.addEdge(2, 0); g.addEdge(2, 3); g.addEdge(3, 3); int u = 1, v = 3; if (g.isReachable(u, v)) cout << "
There is a path from " << u << " to " << v; elseРЕКОМЕНДУЕМЫЕ СТАТЬИ |