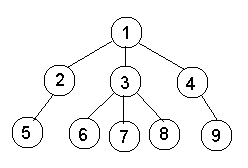
LCA в дереве с использованием техники бинарного подъема
Учитывая двоичное дерево, задача состоит в том, чтобы найти наименьшего общего предка данных двух узлов в дереве.
Пусть G - дерево, тогда LCA двух узлов u и v определяется как узел w в дереве, который является предком как u, так и v и наиболее удален от корневого узла. Если один узел является предком другого, чем этот конкретный узел - это LCA этих двух узлов.
Пример:
Input:
Output:
The LCA of 6 and 9 is 1.
The LCA of 5 and 9 is 1.
The LCA of 6 and 8 is 3.
The LCA of 6 and 1 is 1.
Подход: в статье описывается подход, известный как двоичный подъем, чтобы найти наименьшего общего предка двух узлов в дереве. Для решения проблемы LCA может быть много подходов. Мы обсуждаем технику бинарного лифтинга, остальные можно прочитать здесь и здесь.
Двоичный подъем - это подход динамического программирования, при котором мы предварительно вычисляем массив memo [1, n] [1, log (n)], где memo [i] [j] содержит 2 ^ j-го предка узла i. Для вычисления значений memo [] [] может использоваться следующая рекурсия
memo[i][j] = parent[i] if j = 0 and
memo[i][j] = memo[memo[i][j – 1]][j – 1] if j > 0.
Сначала мы проверяем, является ли узел предком другого или нет, и если один узел является предком другого, то это LCA этих двух узлов, в противном случае мы находим узел, который не является общим предком как u, так и v и является самым высоким ( то есть такой узел x, что x не является общим предком u и v, но memo [x] [0] является) в дереве. Найдя такой узел (пусть это будет x), мы печатаем первого предка x, то есть memo [x] [0], который будет требуемым LCA.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ implementation of the approach #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; // Pre-processing to calculate values of memo[][] void dfs(int u, int p, int **memo, int *lev, int log, vector<int> *g) { // Using recursion formula to calculate // the values of memo[][] memo[u][0] = p; for (int i = 1; i <= log; i++) memo[u][i] = memo[memo[u][i - 1]][i - 1]; for (int v : g[u]) { if (v != p) { lev[v] = lev[u] + 1; dfs(v, u, memo, lev, log, g); } } } // Function to return the LCA of nodes u and v int lca(int u, int v, int log, int *lev, int **memo) { // The node which is present farthest // from the root node is taken as u // If v is farther from root node // then swap the two if (lev[u] < lev[v]) swap(u, v); // Finding the ancestor of u // which is at same level as v for (int i = log; i >= 0; i--) if ((lev[u] - pow(2, i)) >= lev[v]) u = memo[u][i]; // If v is the ancestor of u // then v is the LCA of u and v if (u == v) return u; // Finding the node closest to the root which is // not the common ancestor of u and v i.e. a node // x such that x is not the common ancestor of u // and v but memo[x][0] is for (int i = log; i >= 0; i--) { if (memo[u][i] != memo[v][i]) { u = memo[u][i]; v = memo[v][i]; } } // Returning the first ancestor // of above found node return memo[u][0]; } // Driver Code int main() { // Number of nodes int n = 9; // vector to store tree vector<int> g[n + 1]; int log = (int)ceil(log2(n)); int **memo = new int *[n + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) memo[i] = new int[log + 1]; // Stores the level of each node int *lev = new int[n + 1]; // Initialising memo values with -1 for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) memset(memo[i], -1, sizeof memo[i]); // Add edges g[1].push_back(2); g[2].push_back(1); g[1].push_back(3); g[3].push_back(1); g[1].push_back(4); g[4].push_back(1); g[2].push_back(5); g[5].push_back(2); g[3].push_back(6); g[6].push_back(3); g[3].push_back(7); g[7].push_back(3); g[3].push_back(8); g[8].push_back(3); g[4].push_back(9); g[9].push_back(4); dfs(1, 1, memo, lev, log, g); cout << "The LCA of 6 and 9 is " << lca(6, 9, log, lev, memo) << endl; cout << "The LCA of 5 and 9 is " << lca(5, 9, log, lev, memo) << endl; cout << "The LCA of 6 and 8 is " << lca(6, 8, log, lev, memo) << endl; cout << "The LCA of 6 and 1 is " << lca(6, 1, log, lev, memo) << endl; return 0; } // This code is contributed by // sanjeev2552 |
Java
// Java implementation of the approach import java.util.*; public class GFG { // ArrayList to store tree static ArrayList<Integer> g[]; static int memo[][], lev[], log; // Pre-processing to calculate values of memo[][] static void dfs(int u, int p) { // Using recursion formula to calculate // the values of memo[][] memo[u][0] = p; for (int i = 1; i <= log; i++) memo[u][i] = memo[memo[u][i - 1]][i - 1]; for (int v : g[u]) { if (v != p) { // Calculating the level of each node lev[v] = lev[u] + 1; dfs(v, u); } } } // Function to return the LCA of nodes u and v static int lca(int u, int v) { // The node which is present farthest // from the root node is taken as u // If v is farther from root node // then swap the two if (lev[u] < lev[v]) { int temp = u; u = v; v = temp; } // Finding the ancestor of u // which is at same level as v for (int i = log; i >= 0; i--) { if ((lev[u] - (int)Math.pow(2, i)) >= lev[v]) u = memo[u][i]; } // If v is the ancestor of u // then v is the LCA of u and v if (u == v) return u; // Finding the node closest to the root which is // not the common ancestor of u and v i.e. a node // x such that x is not the common ancestor of u // and v but memo[x][0] is for (int i = log; i >= 0; i--) { if (memo[u][i] != memo[v][i]) { u = memo[u][i]; v = memo[v][i]; } } // Returning the first ancestor // of above found node return memo[u][0]; } // Driver code public static void main(String args[]) { // Number of nodes int n = 9; g = new ArrayList[n + 1]; // log(n) with base 2 log = (int)Math.ceil(Math.log(n) / Math.log(2)); memo = new int[n + 1][log + 1]; // Stores the level of each node lev = new int[n + 1]; // Initialising memo values with -1 for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) Arrays.fill(memo[i], -1); for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) g[i] = new ArrayList<>(); // Add edges g[1].add(2); g[2].add(1); g[1].add(3); g[3].add(1); g[1].add(4); g[4].add(1); g[2].add(5); g[5].add(2); g[3].add(6); g[6].add(3); g[3].add(7); g[7].add(3); g[3].add(8); g[8].add(3); g[4].add(9); g[9].add(4); dfs(1, 1); System.out.println("The LCA of 6 and 9 is " + lca(6, 9)); System.out.println("The LCA of 5 and 9 is " + lca(5, 9)); System.out.println("The LCA of 6 and 8 is " + lca(6, 8)); System.out.println("The LCA of 6 and 1 is " + lca(6, 1)); } } |
Python3
# Python3 implementation of the above approach import math # Pre-processing to calculate values of memo[][]def dfs(u, p, memo, lev, log, g): # Using recursion formula to calculate # the values of memo[][] memo[u][0] = p for i in range(1, log + 1): memo[u][i] = memo[memo[u][i - 1]][i - 1] for v in g[u]: if v != p: lev[v] = lev[u] + 1 dfs(v, u, memo, lev, log, g) # Function to return the LCA of nodes u and v def lca(u, v, log, lev, memo): # The node which is present farthest # from the root node is taken as u # If v is farther from root node # then swap the two if lev[u] < lev[v]: swap(u, v) # Finding the ancestor of u # which is at same level as v for i in range(log, -1, -1): if (lev[u] - pow(2, i)) >= lev[v]: u = memo[u][i] # If v is the ancestor of u # then v is the LCA of u and v if u == v: return v # Finding the node closest to the # root which is not the common ancestor # of u and v i.e. a node x such that x # is not the common ancestor of u # and v but memo[x][0] is for i in range(log, -1, -1): if memo[u][i] != memo[v][i]: u = memo[u][i] v = memo[v][i] # Returning the first ancestor # of above found node return memo[u][0] # Driver code # Number of nodes n = 9 log = math.ceil(math.log(n, 2))g = [[] for i in range(n + 1)] memo = [[-1 for i in range(log + 1)] for j in range(n + 1)] # Stores the level of each node lev = [0 for i in range(n + 1)] # Add edges g[1].append(2)g[2].append(1)g[1].append(3)g[3].append(1)g[1].append(4)g[4].append(1)g[2].append(5)g[5].append(2)g[3].append(6)g[6].append(3)g[3].append(7)g[7].append(3)g[3].append(8)g[8].append(3)g[4].append(9)g[9].append(4) dfs(1, 1, memo, lev, log, g) print("The LCA of 6 and 9 is", lca(6, 9, log, lev, memo))print("The LCA of 5 and 9 is", lca(5, 9, log, lev, memo))print("The LCA of 6 and 8 is", lca(
|