jQuery UI | Вкладки
Вкладки используются для создания нескольких разделов на веб-странице, которые можно менять местами, как гармошку. Это помогает группировать контент и просматривать контент из определенной группы за раз.
Вкладки создаются с помощью специальной разметки, которая выглядит следующим образом:
- Вкладки должны быть заключены в упорядоченный список или неупорядоченный список.
- Каждый заголовок вкладки должен быть заключен отдельно в элемент списка и привязанный тег, заключенный с атрибутом href, определяющим содержимое для каждой панели вкладок.
- Каждая панель вкладок может быть пустой, но у нее должен быть собственный идентификатор, соответствующий хешированному имени, введенному в элемент привязки соответствующей вкладки.
Содержимое внутри панели вкладок может быть определено на той же странице или может быть загружено через Ajax, оба они обрабатываются атрибутом href, связанным с тегом привязки этой панели.
Ниже мы напишем код для простой 4-панельной вкладки с использованием jquery UI.
Вкладки указываются в теге div с идентификатором. Идентификатор которого указан внутри кода jquery. Здесь мы выбрали вторую вкладку в качестве вкладки по умолчанию, которая будет выбрана при открытии веб-страницы. Вы можете изменить его, указав другое значение в активном параметре.
Примечание: вкладки индексируются, начиная с «0».
Ниже приведены примеры вкладок jQuery:
Пример 1. Этот пример кода представляет собой простую вкладку jquery, все вкладки доступны для оценки.
- Программа:
<html><head><linkhref=rel='stylesheet'></head><style>b{float: right;margin: 7px;color: lime;}#geeks a:hover{color: lime;background: gray;}</style><body><br><br><divid="geeks"><ul><li><ahref="#Algorithms">Algorithms</a></li><li><ahref="#Data_Structure">Data Structure</a></li><li><ahref="#Practice">Practice</a></li><li><ahref="#interview">interview</a></li><b>GeeksforGeeks</b></ul><divid='Algorithms'><p>The answer to this is simple, we can have all theabove things only if we have performance. Soperformance is like currency through which we canbuy all the above things. Another reasonfor studying performance is – speed is fun!</p></div><divid='Data_Structure'><p>For example, let us say, we want to store marks ofall students in a class, we can use an array to storethem. This helps in reducing the use of number ofvariables as we don't need to create a separatevariable for marks of every subject. All marks canbe accessed by simply traversing the array.</p></div><divid='Practice'><p>Asymptotic Analysis is the big idea that handlesabove issues in analyzing algorithms. In AsymptoticAnalysis, we evaluate the performance of an algorithmin terms of input size (we don't measure the actualrunning time). We calculate, how does the time(or space) taken by an algorithm increases withthe input size.</p></div><divid='interview'><p>Also, in Asymptotic analysis, we always talk aboutinput sizes larger than a constant value. It mightbe possible that those large inputs are never givento your software and an algorithm which isasymptotically slower, always performs better foryour particular situation. So, you may end up choosingan algorithm that is Asymptotically slower but fasterfor your software.</p></div></div><scriptsrc=</script><scriptsrc=</script><script>$(document).ready(function() {$("#geeks").tabs({active: 0})})</script></body></html> - Выход:
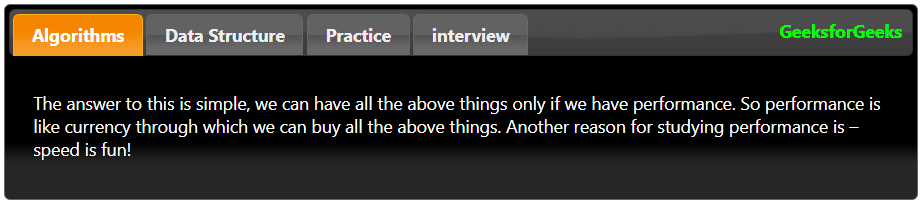
Пример 2: По умолчанию все вкладки закрыты, но вы также можете оставить все вкладки закрытыми по умолчанию. Для этого мы используем опцию Collapsible и устанавливаем ее значение на «True», а значение активной опции устанавливаем на false.
- Программа:
<html><head><linkhref=rel='stylesheet'></head><style>b{float: right;margin: 7px;color: lime;}#geeks a:hover{color: lime;background: gray;}</style><body><br><br><divid="geeks"><ul><li><ahref="#Algorithms">Algorithms</a></li><li><ahref="#Data_Structure">Data Structure</a></li><li><ahref="#Practice">Practice</a></li><li><ahref="#interview">interview</a></li><b>GeeksforGeeks</b></ul><divid='Algorithms'><p>The answer to this is simple, we can have all theabove things only if we have performance. Soperformance is like currency through which we canbuy all the above things. Another reasonfor studying performance is – speed is fun!</p></div><divid='Data_Structure'><p>For example, let us say, we want to store marks ofall students in a class, we can use an array to storethem. This helps in reducing the use of number ofvariables as we don't need to create a separatevariable for marks of every subject. All marks canbe accessed by simply traversing the array.</p></div><divid='Practice'><p>Asymptotic Analysis is the big idea that handlesabove issues in analyzing algorithms. In AsymptoticAnalysis, we evaluate the performance of an algorithmin terms of input size (we don't measure the actualrunning time). We calculate, how does the time(or space) taken by an algorithm increases withthe input size.</p></div><divid='interview'><p>Also, in Asymptotic analysis, we always talk aboutinput sizes larger than a constant value. It mightbe possible that those large inputs are never givento your software and an algorithm which isasymptotically slower, always performs better foryour particular situation. So, you may end up choosingan algorithm that is Asymptotically slower but fasterfor your software.</p></div></div><scriptsrc=</script><scriptsrc=</script><script>$(document).ready(function() {$("#geeks").tabs({active: false,collapsible: true})})</script></body></html> - Выход:

Пример 3: В этом примере мы отключим вкладки. Мы можем отключить определенные вкладки или все вкладки с помощью параметра отключения . Сначала мы отключаем все вкладки, для которых мы установили значение «Истина» для параметра отключения.
- Программа:
<html><head><linkhref=rel='stylesheet'></head><style>b{float: right;margin: 7px;color: lime;}#geeks a:hover{color: lime;background: gray;}</style><body><br><br><divid="geeks"><ul><li><ahref="#Algorithms">Algorithms</a></li><li><ahref="#Data_Structure">Data Structure</a></li><li><ahref="#Practice">Practice</a></li><li><ahref="#interview">interview</a></li><b>GeeksforGeeks</b></ul><divid='Algorithms'><p>The answer to this is simple, we can have all theabove things only if we have performance. Soperformance is like currency through which we canbuy all the above things. Another reasonfor studying performance is – speed is fun!</p></div><divid='Data_Structure'><p>For example, let us say, we want to store marks ofall students in a class, we can use an array to storethem. This helps in reducing the use of number ofvariables as we don't need to create a separatevariable for marks of every subject. All marks canbe accessed by simply traversing the array.</p></div><divid='Practice'><p>Asymptotic Analysis is the big idea that handlesabove issues in analyzing algorithms. In AsymptoticAnalysis, we evaluate the performance of an algorithmin terms of input size (we don't measure the actualrunning time). We calculate, how does the time(or space) taken by an algorithm increases withthe input size.</p></div><divid='interview'><p>Also, in Asymptotic analysis, we always talk aboutinput sizes larger than a constant value. It mightbe possible that those large inputs are never givento your software and an algorithm which isasymptotically slower, always performs better foryour particular situation. So, you may end up choosingan algorithm that is Asymptotically slower but fasterfor your software.</p></div></div><scriptsrc=</script><scriptsrc=</script><script>$(document).ready(function() {$( "#geeks" ).tabs({disabled:true})})</script></body></html> - Выход:
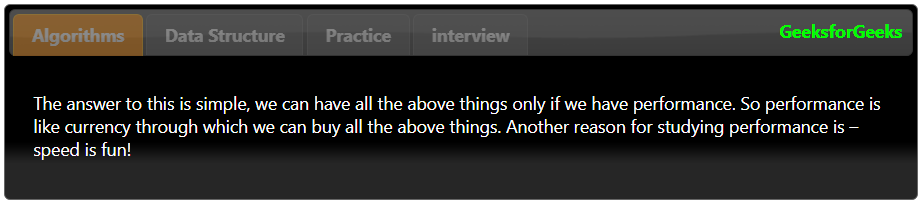
Пример 4: В этом примере мы отключим некоторые определенные вкладки. В приведенном ниже коде мы отключаем 1-ю и 3-ю вкладку (0-я 2-я с точки зрения индексации):
- Программа:
<html><head><linkhref=rel='stylesheet'></head><style>b{float: right;margin: 7px;color: lime;}#geeks a:hover{color: lime;background: gray;}</style><body><br><br><divid="geeks"><ul><li><ahref="#Algorithms">Algorithms</a></li><li><ahref="#Data_Structure">Data Structure</a></li><li><ahref="#Practice">Practice</a></li><li><ahref="#interview">interview</a></li><b>GeeksforGeeks</b></ul><РЕКОМЕНДУЕМЫЕ СТАТЬИ