Дерево Ван Эмде Боаса - Набор 3 | Преемник и предшественник
Настоятельно рекомендуется сначала прочитать предыдущие статьи о Дереве Ван Эмде Боаса.
Порядок получения правопреемника:
- Базовый случай: если размер дерева равен 2, тогда, если ключ запроса равен 0, а ключ - 1 присутствует в дереве, тогда верните 1, так как оно будет преемником. В противном случае верните null.
- Если ключ меньше минимального, то мы можем легко сказать, что минимум будет преемником ключа запроса.
- Рекурсивный случай:
- Сначала ищем преемника в кластере, в котором присутствует ключ.
- Если мы найдем преемника в кластере, сгенерируйте его индекс и верните его.
- В противном случае найдите следующий кластер, по крайней мере, с одним присутствующим ключом, и верните минимальный индекс этого кластера.
См. Запрос для преемника 0 на изображении ниже: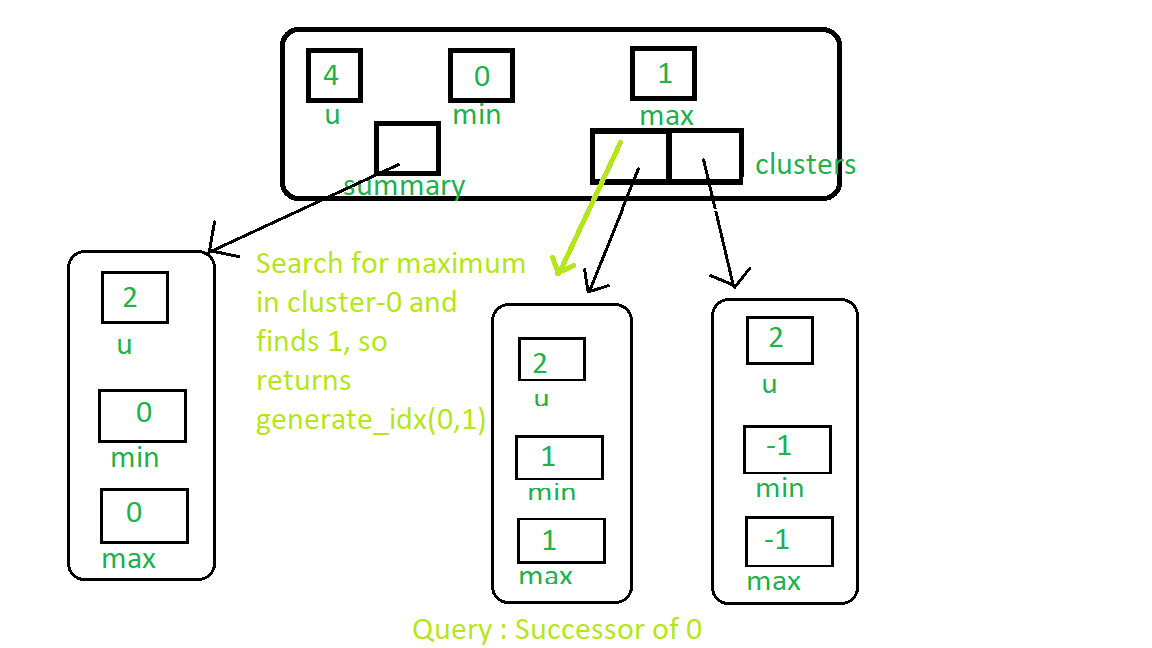
На изображении ниже представлен преемник 1 запроса к дереву VEB, содержащему ключи 1 и 2: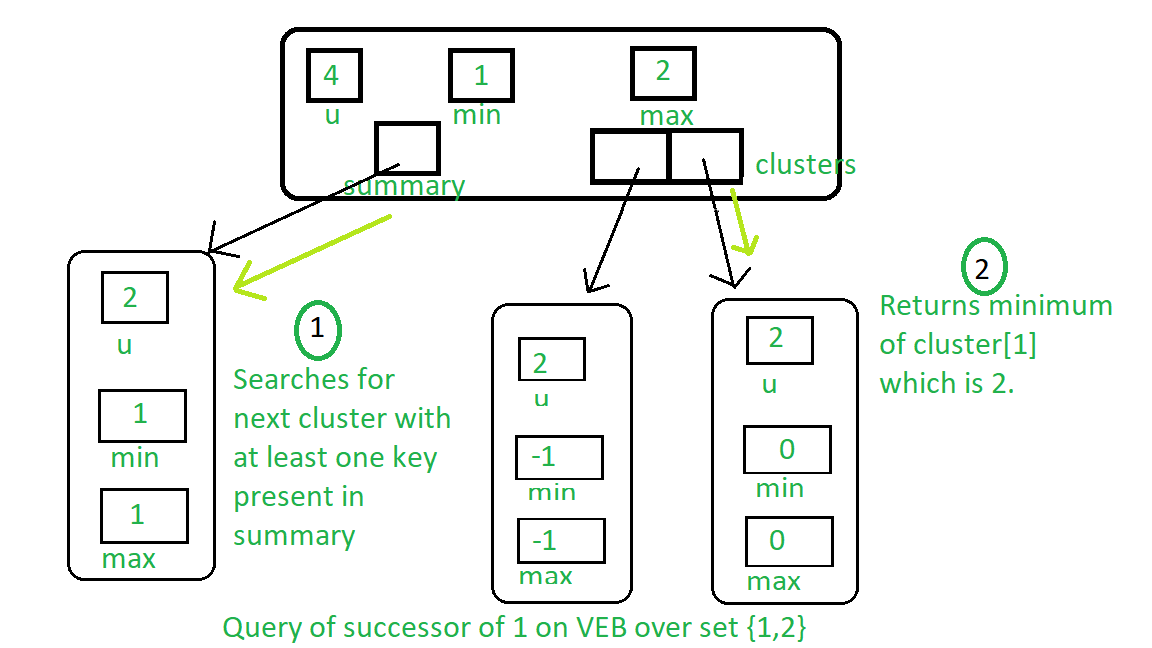
Порядок действий для предшественника:
- Базовый случай: если размер дерева равен 2, тогда, если ключ запроса равен 1, а ключ-0 присутствует в дереве, тогда верните 0, так как он будет предшественником. В противном случае верните null.
- Если ключ больше, чем максимум, то мы можем легко сказать, что максимум будет предшественником ключа запроса.
- Рекурсивный случай:
- Сначала мы ищем предшественника в кластере, в котором присутствует ключ.
- Если мы найдем предшественника в кластере, сгенерируйте его индекс и верните его.
- В противном случае ищите предыдущий кластер, в котором присутствует хотя бы один ключ. Если какой-либо кластер присутствует, верните индекс максимума этого кластера.
- Если кластера с этим свойством нет, посмотрите, не является ли из-за ленивого распространения минимум дерева (в котором присутствует кластер) меньше ключа, если да, то верните минимум, в противном случае верните ноль.
Below image represents query predecessor of key-2: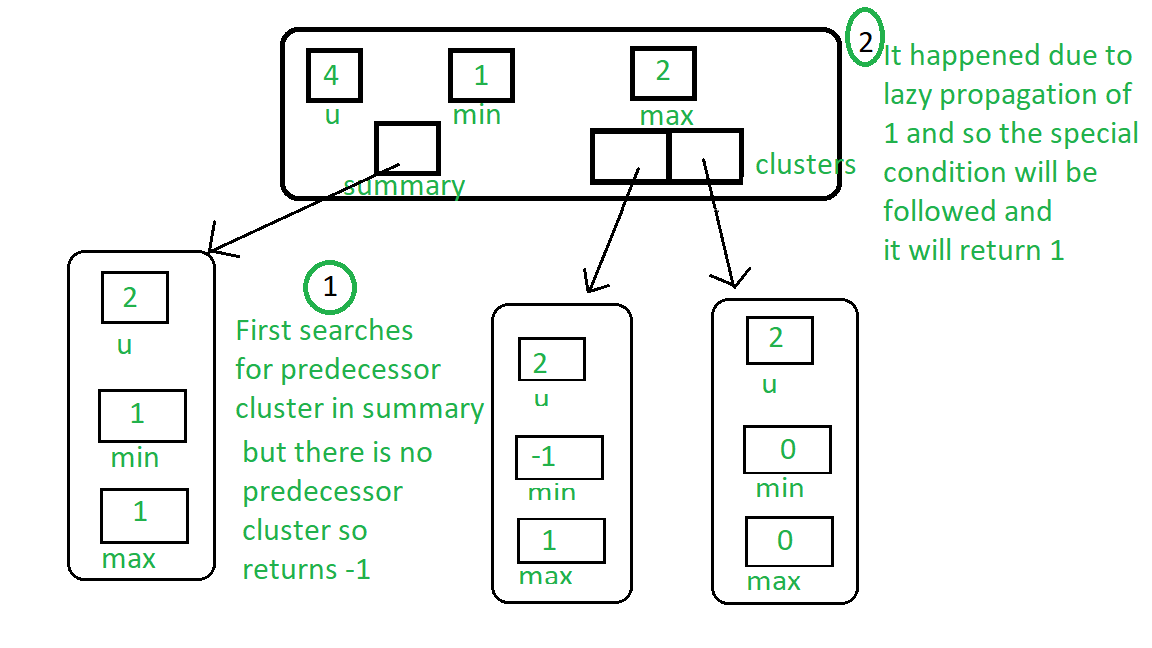
#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std; class Van_Emde_Boas { public: int universe_size; int minimum; int maximum; Van_Emde_Boas* summary; vector<Van_Emde_Boas*> clusters; // Function to return cluster numbers // in which key is present int high(int x) { int div = ceil(sqrt(universe_size)); return x / div; } // Function to return position of x in cluster int low(int x) { int mod = ceil(sqrt(universe_size)); return x % mod; } // Function to return the index from // cluster number and position int generate_index(int x, int y) { int ru = ceil(sqrt(universe_size)); return x * ru + y; } // Constructor Van_Emde_Boas(int size) { universe_size = size; minimum = -1; maximum = -1; // Base case if (size <= 2) { summary = nullptr; clusters = vector<Van_Emde_Boas*>(0, nullptr); } else { int no_clusters = ceil(sqrt(size)); // Assigning VEB(sqrt(u)) to summary summary = new Van_Emde_Boas(no_clusters); // Creating array of VEB Tree pointers of size sqrt(u) clusters = vector<Van_Emde_Boas*>(no_clusters, nullptr); // Assigning VEB(sqrt(u)) to all its clusters for (int i = 0; i < no_clusters; i++) { clusters[i] = new Van_Emde_Boas(ceil(sqrt(size))); } } }}; // Function to return the minimum value// from the tree if it existsint VEB_minimum(Van_Emde_Boas* helper){ return (helper->minimum == -1 ? -1 : helper->minimum);} // Function to return the maximum value// from the tree if it existsint VEB_maximum(Van_Emde_Boas* helper){ return (helper->maximum == -1 ? -1 : helper->maximum);} // Function to insert a key in the treevoid insert(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key){ // If no key is present in the tree // then set both minimum and maximum // to the key (Read the previous article // for more understanding about it) if (helper->minimum == -1) { helper->minimum = key; helper->maximum = key; } else { if (key < helper->minimum) { // If the key is less than the current minimum // then swap it with the current minimum // because this minimum is actually // minimum of one of the internal cluster // so as we go deeper into the Van Emde Boas // we need to take that minimum to its real position // This concept is similar to "Lazy Propagation" swap(helper->minimum, key); } // Not base case then... if (helper->universe_size > 2) { // If no key is present in the cluster then insert key into // both cluster and summary if (VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]) == -1) { insert(helper->summary, helper->high(key)); // Sets the minimum and maximum of cluster to the key // as no other keys are present we will stop at this level // we are not going deeper into the structure like // Lazy Propagation helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]->minimum = helper->low(key); helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]->maximum = helper->low(key); } else { // If there are other elements in the tree then recursively // go deeper into the structure to set attributes accordingly insert(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key)); } } // Sets the key as maximum it is greater than current maximum if (key > helper->maximum) { helper->maximum = key; } }} // Function that returns true if the// key is present in the treebool isMember(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key){ // If universe_size is less than the key // then we can not search the key so returns // false if (helper->universe_size < key) { return false; } // If at any point of our traversal // of the tree if the key is the minimum // or the maximum of the subtree, then // the key is present so returns true if (helper->minimum == key || helper->maximum == key) { return true; } else { // If after attending above condition, // if the size of the tree is 2 then // the present key must be // maximum or minimum of the tree if it // is not then it returns false becuase key // can not be present in the sub tree if (helper->universe_size == 2) { return false; } else { // Recursive call over the cluster // in which the key can be present // and also pass the new position of the key // i.e., low(key) return isMember(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key)); } }} // Function to find the successor of the given keyint VEB_successor(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key){ // Base case: If key is 0 and its successor // is present then return 1 else return null if (helper->universe_size == 2) { if (key == 0 && helper->maximum == 1) { return 1; } else { return -1; } } // If key is less then minimum then return minimum // because it will be successor of the key else if (helper->minimum != -1 && key < helper->minimum) { return helper->minimum; } else { // Find successor inside the cluster of the key // First find the maximum in the cluster int max_incluster = VEB_maximum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]); int offset{ 0 }, succ_cluster{ 0 }; // If there is any key( maximum!=-1 ) present in the cluster then find // the successor inside of the cluster if (max_incluster != -1 && helper->low(key) < max_incluster) { offset = VEB_successor(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key)); return helper->generate_index(helper->high(key), offset); } // Otherwise look for the next cluster with at least one key present else { succ_cluster = VEB_successor(helper->summary, helper->high(key)); // If there is no cluster with any key present // in summary then return null if (succ_cluster == -1) { return -1; } // Find minimum in successor cluster which will // be the successor of the key else { offset = VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[succ_cluster]); return helper->generate_index(succ_cluster, offset); } } }} // Function to find the predecessor of the given keyint VEB_predecessor(Van_Emde_Boas* helper, int key){ // Base case: If the key is 1 and it"s predecessor // is present then return 0 else return null if (helper->universe_size == 2) { if (key == 1 && helper->minimum == 0) { return 0; } else return -1; } // If the key is greater than maximum of the tree then // return key as it will be the predecessor of the key else if (helper->maximum != -1 && key > helper->maximum) { return helper->maximum; } else { // Find predecessor in the cluster of the key // First find minimum in the key to check whether any key // is present in the cluster int min_incluster = VEB_minimum(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)]); int offset{ 0 }, pred_cluster{ 0 }; // If any key is present in the cluster then find predecessor in // the cluster if (min_incluster != -1 && helper->low(key) > min_incluster) { offset = VEB_predecessor(helper->clusters[helper->high(key)], helper->low(key)); return helper->generate_index(helper->high(key), offset); } // Otherwise look for predecessor in the summary which // returns the index of predecessor cluster with any key present else { pred_cluster = VEB_predecessor(helper->summary, helper->high(key)); // If no predecessor cluster then... if (pred_cluster == -1) { // Special case which is due to lazy propagation if (helper->minimum != -1 && key > helper->minimum) { return helper->minimum; } else return -1; } // Otherwise find maximum in the predecessor cluster else { offset = VEB_maximum(helper->clusters[pred_cluster]); return helper->generate_index(pred_cluster, offset); } } }} // Driver codeint main(){ Van_Emde_Boas* veb = new Van_Emde_Boas(8); // Inserting Keys insert(veb, 2); insert(veb, 3); insert(veb, 4); insert(veb, 6); // Queries cout << VEB_successor(veb, 2) << endl; cout << VEB_predecessor(veb, 6) << endl; cout << VEB_successor(veb, 4) << endl; return 0;} |
3 4 6
Вниманию читателя! Не прекращайте учиться сейчас. Освойте все важные концепции DSA с помощью самостоятельного курса DSA по приемлемой для студентов цене и будьте готовы к работе в отрасли. Чтобы завершить подготовку от изучения языка к DS Algo и многому другому, см. Полный курс подготовки к собеседованию .
Если вы хотите посещать живые занятия с отраслевыми экспертами, пожалуйста, обращайтесь к Geeks Classes Live и Geeks Classes Live USA.