Дерево тернарного поиска (удаление)
В сообщении SET 1 о TST мы описали, как вставлять и искать узел в TST. В этой статье мы обсудим алгоритм удаления узла из TST.
Во время операции удаления мы удаляем ключ снизу вверх, используя рекурсию. Возможны следующие случаи при удалении ключа из дерева.
- Ключ может отсутствовать в TST.
Решение: операция удаления не должна изменять TST. - Ключ представлен как уникальный ключ (ни одна часть ключа не содержит другого ключа (префикса), и сам ключ не является префиксом другого ключа в TST).
Решение: удалите все узлы. - Ключ - это префиксный ключ другого длинного ключа в TST.
Решение: снимите отметку с листового узла. - Ключ присутствует в TST, имея по крайней мере один другой ключ в качестве префиксного ключа.
Решение: удалите узлы от конца ключа до первого листового узла самого длинного префиксного ключа.
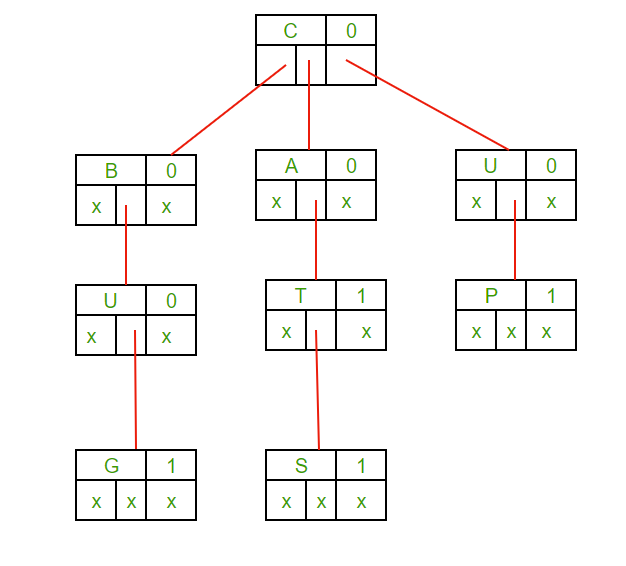
Explanation for delete_node function
- Let suppose we want to delete string “BIG”,since it is not present in TST so after matching with first character ‘B’, delete_node function will return zero. Hence nothing is deleted.
- Now we want to delete string “BUG”, it is Uniquely present in TST i.e neither it has part which is the prefix of other string nor it is prefix to any other string, so it will be deleted completely.
- Now we want to delete string “CAT”, since it is prefix of string “CATS”, we cannot delete anthing from the string “CAT” and we can only unmark the leaf node which will ensure that “CAT” is no longer a member string of TST.
- Now we want to delete string “CATS”, since it has a prefix string “CAT” which also is a member string of TST so we can only delete last character of string “CATS” which will ensure that string “CAT” still remains the part of TST.
C
// C program to demonstrate deletion in// Ternary Search Tree (TST). For insert// and other functions, refer#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h> // structure of a node in TSTstruct Node{ char key; int isleaf; struct Node *left; struct Node *eq; struct Node *right;}; // function to create a Node in TSTstruct Node *createNode(char key){ struct Node *temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); temp->key = key; temp->isleaf = 0; temp->left = NULL; temp->eq = NULL; temp->right = NULL; return temp;}; // function to insert a Node in TSTvoid insert_node(struct Node **root ,char *s){ if (!(*root)) (*root) = createNode(*s); if ((*s)<(*root)->key) insert_node( &(*root)->left ,s); else if ((*s)>(*root)->key) insert_node( &(*root)->right ,s); else if ((*s) == (*root)->key) { if (*(s+1) == "�") { (*root)->isleaf = 1; return; } insert_node( &(*root)->eq ,s+1); }} // function to display the TSTvoid display(struct Node *root, char str[], int level){ if (!root) return; display(root->left ,str ,level); str[level] = root->key; if (root->isleaf == 1) { str[level+1] = "�"; printf("%s
",str); } display(root->eq ,str ,level+1); display(root->right ,str ,level);} // to check if current Node is leaf node or notint isLeaf(struct Node *root){ return root->isleaf == 1;} // to check if current node has any child node or notint isFreeNode(struct Node *root){ if (root->left ||root->eq ||root->right) return 0; return 1;} // function to delete a string in TSTint delete_node(struct Node *root, char str[], int level ,int n){ if (root == NULL) return 0; // CASE 4 Key present in TST, having // atleast one other key as prefix key. if (str[level+1] == "�") { // Unmark leaf node if present if (isLeaf(root)) { root->isleaf=0; return isFreeNode(root); } // else string is not present in TST and // return 0 else return 0; } else { // CASE 3 Key is prefix key of another // long key in TST. if (str[level] < root->key) delete_node(root->left ,str ,level ,n); else if (str[level] > root->key) delete_node(root->right ,str ,level ,n); // CASE 1 Key may not be there in TST. else if (str[level] == root->key) { // CASE 2 Key present as unique key if( delete_node(root->eq ,str ,level+1 ,n) ) { // delete the last node, neither it // has any child // nor it is part of any other string free(root->eq); return !isLeaf(root) && isFreeNode(root); } } } return 0;} // Driver functionint main(){ struct Node *temp = NULL; insert_node(&temp ,"CAT"); insert_node(&temp ,"BUGS"); insert_node(&temp ,"CATS"); insert_node(&temp ,"UP"); int level = 0; char str[20]; int p = 0; printf( "1.Content of the TST before " "deletion:
" ); display(temp ,str ,level); level = 0; delete_node(temp ,"CAT" ,level ,5); level = 0; printf("
2.Content of the TST after " "deletion:
"); display(temp, str, level); return 0;} |
C++
// C++ program to demonstrate deletion in// Ternary Search Tree (TST)// For insert and other functions, refer #include<iostream>using namespace std; // structure of a node in TSTstruct Node{ char key; int isleaf; struct Node *left; struct Node *eq; struct Node *right;}; // function to create a node in TSTstruct Node *createNode(char key){ struct Node *temp = new Node; temp->key = key; temp->isleaf = 0; temp->left = NULL; temp->eq = NULL; temp->right = NULL; return temp;}; // function to insert a Node in TSTvoid insert_node(struct Node **root, char *s){ if (!(*root)) { (*root) = createNode(*s); } if ((*s)<(*root)->key) insert_node( &(*root)->left, s); else if ((*s)>(*root)->key) insert_node( &(*root)->right, s); else if ((*s) == (*root)->key) { if (*(s+1) == "�") { (*root)->isleaf = 1; return; } insert_node( &(*root)->eq, s+1); }} // function to display the TSTvoid display(struct Node *root, char str[], int level){ if (!root) return; display(root->left, str, level); str[level] = root->key; if (root->isleaf == 1) { str[level+1] = "�"; cout<< str <<endl; } display(root->eq, str, level+1); display(root->right, str, level);} //to check if current node is leaf node or notint isLeaf(struct Node *root){ return root->isleaf == 1;} // to check if current node has any child// node or notint isFreeNode(struct Node *root){ if (root->left ||root->eq ||root->right) return 0; return 1;} // function to delete a string in TSTint delete_node(struct Node *root, char str[], int level, int n){ if (root == NULL) return 0; // CASE 4 Key present in TST, having atleast // one other key as prefix key. if (str[level+1] == "�") { // Unmark leaf node if present if (isLeaf(root)) { root->isleaf = 0; return isFreeNode(root); } // else string is not present in TST and // return 0 else return 0; } // CASE 3 Key is prefix key of another long // key in TST. if (str[level] < root->key) return delete_node(root->left, str, level, n); if (str[level] > root->key) return delete_node(root->right, str, level, n); // CASE 1 Key may not be there in TST. if (str[level] == root->key) { // CASE 2 Key present as unique key if (delete_node(root->eq, str, level+1, n)) { // delete the last node, neither it has // any child nor it is part of any other // string delete(root->eq); return !isLeaf(root) && isFreeNode(root); } } return 0;} // Driver functionint main(){ struct Node *temp = NULL; insert_node(&temp, "CAT"); insert_node(&temp, "BUGS"); insert_node(&temp, "CATS"); insert_node(&temp, "UP"); int level = 0; char str[20]; int p = 0; cout << "1.Content of the TST before deletion:
"; display(temp, str, level); level = 0; delete_node(temp,"CAT", level, 5); level = 0; cout << "
2.Content of the TST after deletion:
"; display(temp, str, level); return 0;} |
Выход:
1.Content of the TST before deletion: BUGS CAT CATS UP 2.Content of the TST after deletion: BUGS CATS UP
Эта статья предоставлена Яшем Сингла . Если вам нравится GeeksforGeeks, и вы хотели бы внести свой вклад, вы также можете написать статью на сайте deposit.geeksforgeeks.org или отправить свою статью по электронной почте: grant@geeksforgeeks.org. Посмотрите, как ваша статья появляется на главной странице GeeksforGeeks, и помогите другим гикам.
Пожалуйста, напишите комментарии, если вы обнаружите что-то неправильное, или вы хотите поделиться дополнительной информацией по теме, обсужденной выше.
Вниманию читателя! Не переставай учиться сейчас. Освойте все важные концепции DSA с помощью самостоятельного курса DSA по приемлемой для студентов цене и будьте готовы к работе в отрасли. Чтобы завершить подготовку от изучения языка к DS Algo и многому другому, см. Полный курс подготовки к собеседованию .
Если вы хотите посещать живые занятия с отраслевыми экспертами, пожалуйста, обращайтесь к Geeks Classes Live и Geeks Classes Live USA.