CSS | unicode-bidi Свойство
Опубликовано: 2 Февраля, 2022
Свойство unicode-bidi в HTML DOM применяется вместе со свойством direction, чтобы определить, как двунаправленный текст обрабатывается в документе.
Синтаксис:
юникод-биди: нормальный | внедрить | переопределить биди | начальный | наследовать;
Property Values:
- normal: It is the default value. The additional level of embedding does not open from the element.
Syntax:
unicode-bidi: normal;
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>CSS unicode-bidi Property</title><!-- style for unicode-bidi property --><style>.GFG {direction: rtl;unicode-bidi: normal;}</style></head><body><h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1><h2>CSS unicode-bidi Property</h2><divclass="GFG">A computer science portal for geeks</div></body></html>Output:

- embed: This value is used to open an additional level of embedding.
Syntax:
unicode-bidi:embed;
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>CSS unicode-bidi Property</title><!-- style for unicode-bidi property --><style>.GFG {direction: rtl;unicode-bidi: embed;}</style></head><body><h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1><h2>CSS unicode-bidi Property</h2><divclass="GFG">A computer science portal for geeks</div></body></html>Output:

- bidi-override: This value creates an override for inline element and in case of block element, it creates an override for inline-level descendants not within another block element.
Syntax:
unicode-bidi:bidi-override;
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>CSS unicode-bidi Property</title><!-- style for unicode-bidi property --><style>.GFG {direction: rtl;unicode-bidi: bidi-override;}</style></head><body><h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1><h2>CSS unicode-bidi Property</h2><divclass="GFG">A computer science portal for geeks</div></body></html>Output:
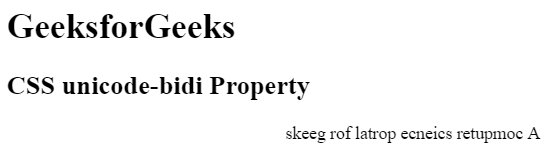
- initial: It sets the unicode-bidi property to its default value.
Syntax:
unicode-bidi: initial;
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>CSS unicode-bidi Property</title><!-- style for unicode-bidi property --><style>.GFG {direction: rtl;unicode-bidi: initial;}</style></head><body><h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1><h2>CSS unicode-bidi Property</h2><divclass="GFG">A computer science portal for geeks</div></body></html>Output:

- inherit: The unicode-bidi property is inherited from its parent element.
Syntax:
unicode-bidi: inherit;
Example:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>CSS unicode-bidi Property</title><!-- style for unicode-bidi property --><style>.Geeks {direction: rtl;unicode-bidi: bidi-override;}.GFG {unicode-bidi: inherit;}</style></head><body><h1>GeeksforGeeks</h1><h2>CSS unicode-bidi Property</h2><divclass="Geeks"><divclass="GFG">A computer science portal for geeks</div></div></body></html>Output:
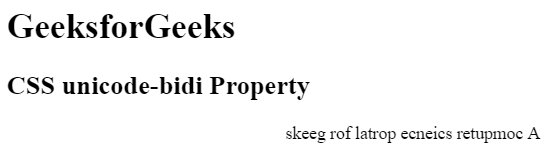
- isolate-override: It applies the isolation behavior of the isolate keyword to the surrounding content and the override behavior of the bidi-override to the inner content.
Syntax:
unicode-bidi: isolate-override;
- plaintext: It makes the element directionality calculated without considering its parent bidirectional state or the value of the direction property.
Syntax:
unicode-bidi: plaintext;
Supported Browsers: The browser supported by unicode-bidi property are listed below:
- Google Chrome 2.0
- Internet Explorer 5.5
- Firefox 1.0
- Safari 1.3
- Opera 9.2