Векторизованные операции в NumPy
Массивы Numpy однородны по своей природе, что означает, что это массив, содержащий данные только одного типа. Списки и кортежи Python, которые не ограничены типом содержащихся в них данных. Концепция векторизованных операций в NumPy позволяет использовать более оптимальные и предварительно скомпилированные функции и математические операции с объектами массивов NumPy и последовательностями данных. Вывод и операции будут ускоряться по сравнению с простыми не векторизованными операциями.
Example 1 : Using vectorized sum method on NumPy array. We will compare the vectorized sum method along with simple non-vectorized operation i.e the iterative method to calculate the sum of numbers from 0 – 14,999.
# importing the modulesimport numpy as npimport timeit # vectorized sumprint(np.sum(np.arange(15000))) print("Time taken by vectorized sum : ", end = "")%timeit np.sum(np.arange(15000)) # itersative sumtotal = 0for item in range(0, 15000): total += itema = totalprint("
" + str(a)) print("Time taken by iterative sum : ", end = "")%timeit a |
Output :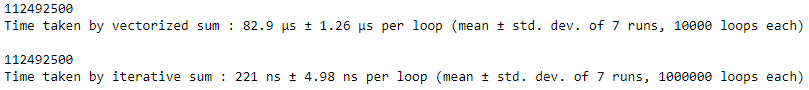
The above example shows the more optimal nature of vectorized operations of NumPy when compared with non-vectorized operations. This means when computational efficiency is the key factor in a program and we should avoid using these simple operations, rather we should use NumPy vectorized functions.
Example 2 : Here we will compare numpy exponential function with python built-in math library exponential function to calculate the exponential value of each entry in a particular object.
# importing the modulesimport numpy as npimport timeitimport math # vectorized operationprint("Time taken by vectorized operation : ", end = "")%timeit np.exp(np.arange(150)) # non-vectorized operationprint("Time taken by non-vectorized operation : ", end = "")%timeit [math.exp(item) for item in range(150)] |
Output :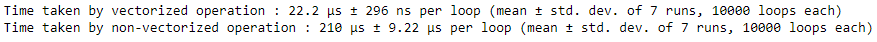
Here as we can see NumPy vectorized operations are more optimized in calculating value and along with one more limitation of Python math library i.e math library range limit, as it not suitable for very large value, unlike NumPy vectorized operation which can be used to calculate the exponential value of very large range limit as well.
The above two examples justify the optimal nature of NumPy vectorized functions and operations when compared and used in place of simple or non-vectorized function or operations in a python program or script.
Attention geek! Strengthen your foundations with the Python Programming Foundation Course and learn the basics.
To begin with, your interview preparations Enhance your Data Structures concepts with the Python DS Course. And to begin with your Machine Learning Journey, join the Machine Learning – Basic Level Course