Создание представления - представления на основе функций Django
Создание представления относится к представлению (логике) для создания экземпляра таблицы в базе данных. Это похоже на получение ввода от пользователя и его сохранение в указанной таблице. Django предоставляет необычную поддержку для создания представлений, но давайте проверим, как это делается вручную с помощью представления на основе функций. Эта статья посвящена созданию представления, в котором используются такие концепции, как Django Forms, Django Models.
Для создания представления нам нужен проект с некоторыми моделями и формами, которые будут использоваться для создания экземпляров этой модели.
Django Create View - представления на основе функций
Illustration of How to create and use create view using an Example. Consider a project named geeksforgeeks having an app named geeks.
Refer to the following articles to check how to create a project and an app in Django.
- How to Create a Basic Project using MVT in Django?
- How to Create an App in Django ?
After you have a project and an app, let’s create a model of which we will be creating instances through our view. In geeks/models.py,
# import the standard Django Model# from built-in libraryfrom django.db import models # declare a new model with a name "GeeksModel"class GeeksModel(models.Model): # fields of the model title = models.CharField(max_length = 200) description = models.TextField() # renames the instances of the model # with their title name def __str__(self): return self.title |
After creating this model, we need to run two commands in order to create Database for the same.
Python manage.py makemigrations Python manage.py migrate
Now we will create a Django ModelForm for this model. Refer this article for more on modelform – Django ModelForm – Create form from Models. create a file forms.py in geeks folder,
from django import formsfrom .models import GeeksModel # creating a formclass GeeksForm(forms.ModelForm): # create meta class class Meta: # specify model to be used model = GeeksModel # specify fields to be used fields = [ "title", "description", ] |
Now we have everything ready for back end. Let’s create a view and template for the same. In geeks/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import render # relative import of formsfrom .models import GeeksModelfrom .forms import GeeksForm def create_view(request): # dictionary for initial data with # field names as keys context ={} # add the dictionary during initialization form = GeeksForm(request.POST or None) if form.is_valid(): form.save() context["form"]= form return render(request, "create_view.html", context) |
Create a template in templates/create_view.html,
<form method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <!-- Security token --> {% csrf_token %} <!-- Using the formset --> {{ form.as_p }} <input type="submit" value="Submit"></form> |
Let’s check what is there on http://localhost:8000/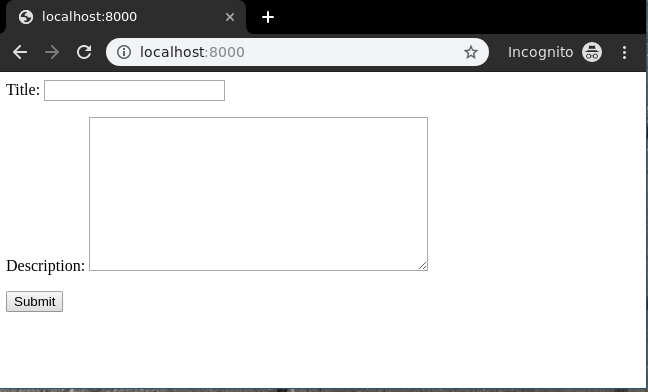
Now let’s try to enter data in this form,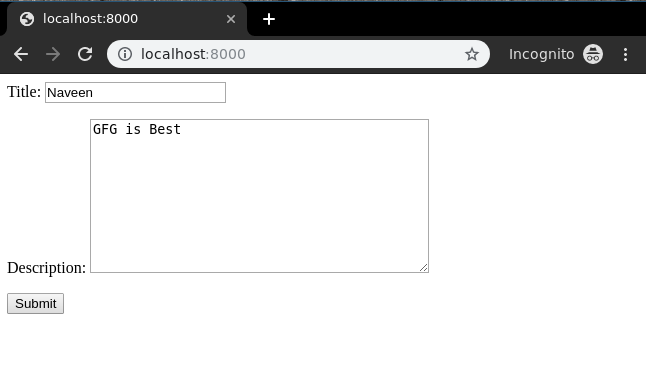
Bingo.! Create view is working and we can verify it using the instance created through the admin panel.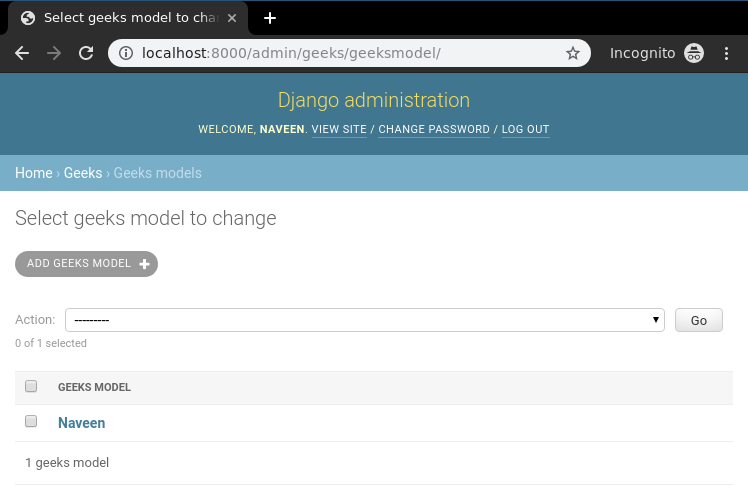
This way one can create create view for a model in Django.
Attention geek! Strengthen your foundations with the Python Programming Foundation Course and learn the basics.
To begin with, your interview preparations Enhance your Data Structures concepts with the Python DS Course. And to begin with your Machine Learning Journey, join the Machine Learning – Basic Level Course