Шифр ROT13
Шифр ROT13 (читается как «повернуть на 13 позиций») - это частный случай шифра Ceaser, в котором сдвиг всегда равен 13.
Таким образом, каждая буква сдвигается на 13 позиций, чтобы зашифровать или расшифровать сообщение.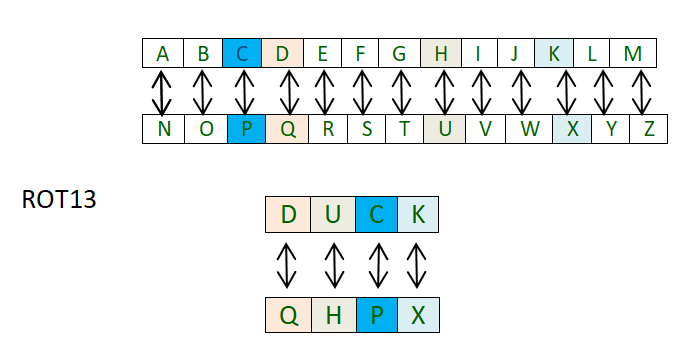
я
Вы, должно быть, думаете, что это просто еще один шифр Цезаря, так что же на этот раз изменилось? Ну разница в его реализации. Подход заключается в использовании двух отдельных словарей Python.
- Первый, который ищет различные буквы в соответствии с их местом в английском алфавите, чтобы получить сдвинутый номер
- Второй, чтобы получить буквы, соответствующие сдвинутым числам.
Рекомендуется: сначала попробуйте свой подход в {IDE}, прежде чем переходить к решению.
Code :
Python
# Python program to implement # ROT13 Caesar cipher """This script uses dictionaries instead of "chr()" & "ord()" function""" # Dictionary to lookup the index of alphabetsdict1 = {"A" : 1, "B" : 2, "C" : 3, "D" : 4, "E" : 5, "F" : 6, "G" : 7, "H" : 8, "I" : 9, "J" : 10, "K" : 11, "L" : 12, "M" : 13, "N" : 14, "O" : 15, "P" : 16, "Q" : 17, "R" : 18, "S" : 19, "T" : 20, "U" : 21, "V" : 22, "W" : 23, "X" : 24, "Y" : 25, "Z" : 26} # Dictionary to lookup alphabets # corresponding to the index after shiftdict2 = {0 : "Z", 1 : "A", 2 : "B", 3 : "C", 4 : "D", 5 : "E", 6 : "F", 7 : "G", 8 : "H", 9 : "I", 10 : "J", 11 : "K", 12 : "L", 13 : "M", 14 : "N", 15 : "O", 16 : "P", 17 : "Q", 18 : "R", 19 : "S", 20 : "T", 21 : "U", 22 : "V", 23 : "W", 24 : "X", 25 : "Y"} # Function to encrypt the string # according to the shift provideddef encrypt(message, shift): cipher = "" for letter in message: # checking for space if(letter != " "): # looks up the dictionary and # adds the shift to the index num = ( dict1[letter] + shift ) % 26 # looks up the second dictionary for # the shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num] else: # adds space cipher += " " return cipher # Function to decrypt the string # according to the shift provideddef decrypt(message, shift): decipher = "" for letter in message: # checks for space if(letter != " "): # looks up the dictionary and # subtracts the shift to the index num = ( dict1[letter] - shift + 26) % 26 # looks up the second dictionary for the # shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num] else: # adds space decipher += " " return decipher # driver function to run the programdef main(): # use "upper()" function to convert any lowercase characters to uppercase message = "GEEKS FOR GEEKS" shift = 13 result = encrypt(message.upper(), shift) print (result) message = "TRRXF SBE TRRXF" shift = 13 result = decrypt(message.upper(), shift) print (result) # Executes the main functionif __name__ == "__main__": main() |
C++
// CPP program to implement// ROT13 Caesar Cipher #include<bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std; // Map to lookup the index of alphabetsmap <char,int> dict1; // Map to lookup alphabets corresponding// to the index after shiftmap <int,char> dict2; // Function to create map to lookupvoid create_dict(){ for(int i = 1; i < 27; i++) dict1[char(64 + i)] = i; dict2[0] = "Z"; for(int i = 1; i < 26; i++) dict2[i] = char(64 + i); return;} // Function to encrypt the string// according to the shift providedstring encrypt(string message, int shift){ string cipher = ""; for(int i = 0; i < message.size(); i++) { // Checking for namespace if(message[i] != " ") { // loooks up the map and // adds the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] + shift) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them cipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space cipher += " "; } } return cipher;} // Function to decrypt the string// according to the shift providedstring decrypt(string message, int shift){ string decipher = ""; for(int i = 0; i < message.size(); i++) { // checks for space if(message[i] != " ") { // looks up the map and // subtracts the shift to the index int num = (dict1[message[i]] - shift + 26) % 26; // looks up the second map for the // shifted alphabets and adds them decipher += dict2[num]; } else { // adds space decipher += " "; } } return decipher;} // Driver codeint main(){ create_dict(); string message = "GEEKS FOR GEEKS"; int shift = 13; cout << encrypt(message, shift) << "
"; message = "TRRXF SBE TRRXF"; shift = 13; cout << decrypt(message, shift) << "
"; return 0;}// This code is contributed by Sachin Bisht |
Output : TRRXF SBE TRRXF GEEKS FOR GEEKS
Анализ: Шифр ROT13 не очень безопасен, так как это всего лишь частный случай шифра Caeser. Шифр Caeser можно взломать либо с помощью частотного анализа, либо просто перепробовав все 25 ключей, тогда как шифр ROT13 можно взломать, просто сдвинув буквы на 13 позиций. Поэтому практического применения он не имеет.
Применение: ROT13 использовался в группе новостей net.jokes к началу 1980-х годов.
Эта статья предоставлена Палашем Нигамом. Если вам нравится GeeksforGeeks, и вы хотели бы внести свой вклад, вы также можете написать статью на сайте deposit.geeksforgeeks.org или отправить свою статью по электронной почте: grant@geeksforgeeks.org. Посмотрите, как ваша статья появляется на главной странице GeeksforGeeks, и помогите другим гикам.
Пожалуйста, напишите комментарии, если вы обнаружите что-то неправильное, или вы хотите поделиться дополнительной информацией по теме, обсужденной выше.