Самый длинный возможный маршрут в матрице с препятствиями
Учитывая матрицу M x N, с несколькими произвольно размещенными препятствиями, вычислите длину максимально возможного маршрута от источника до пункта назначения в матрице. Нам разрешено перемещаться только в соседние клетки, которые не являются препятствиями. Маршрут не может содержать никаких диагональных перемещений, и место, которое однажды было посещено на определенном пути, не может быть посещено снова.
Например, самый длинный путь без препятствий от источника к месту назначения выделен для матрицы ниже. Длина пути 24.
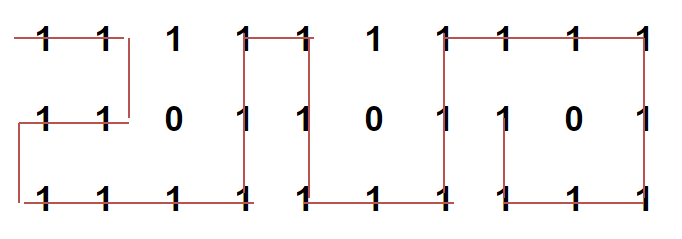
Рекомендуется: сначала попробуйте свой подход в {IDE}, прежде чем переходить к решению.
Идея состоит в том, чтобы использовать Backtracking. Мы начинаем с исходной ячейки матрицы, продвигаемся вперед во всех четырех разрешенных направлениях и рекурсивно проверяем, приводят ли они к решению или нет. Если пункт назначения найден, мы обновляем значение самого длинного пути, иначе, если ни одно из вышеперечисленных решений не работает, мы возвращаем false из нашей функции.
Below is C++ implementation of above idea –
// C++ program to find Longest Possible Route in a// matrix with hurdles#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;#define R 3#define C 10 // A Pair to store status of a cell. found is set to// true of destination is reachable and value stores// distance of longest pathstruct Pair{ // true if destination is found bool found; // stores cost of longest path from current cell to // destination cell int value;}; // Function to find Longest Possible Route in the// matrix with hurdles. If the destination is not reachable// the function returns false with cost INT_MAX.// (i, j) is source cell and (x, y) is destination cell.Pair findLongestPathUtil(int mat[R][C], int i, int j, int x, int y, bool visited[R][C]){ // if (i, j) itself is destination, return true if (i == x && j == y) { Pair p = { true, 0 }; return p; } // if not a valid cell, return false if (i < 0 || i >= R || j < 0 || j >= C || mat[i][j] == 0 || visited[i][j]) { Pair p = { false, INT_MAX }; return p; } // include (i, j) in current path i.e. // set visited(i, j) to true visited[i][j] = true; // res stores longest path from current cell (i, j) to // destination cell (x, y) int res = INT_MIN; // go left from current cell Pair sol = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i, j - 1, x, y, visited); // if destination can be reached on going left from current // cell, update res if (sol.found) res = max(res, sol.value); // go right from current cell sol = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i, j + 1, x, y, visited); // if destination can be reached on going right from current // cell, update res if (sol.found) res = max(res, sol.value); // go up from current cell sol = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i - 1, j, x, y, visited); // if destination can be reached on going up from current // cell, update res if (sol.found) res = max(res, sol.value); // go down from current cell sol = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i + 1, j, x, y, visited); // if destination can be reached on going down from current // cell, update res if (sol.found) res = max(res, sol.value); // Backtrack visited[i][j] = false; // if destination can be reached from current cell, // return true if (res != INT_MIN) { Pair p = { true, 1 + res }; return p; } // if destination can"t be reached from current cell, // return false else { Pair p = { false, INT_MAX }; return p; }} // A wrapper function over findLongestPathUtil()void findLongestPath(int mat[R][C], int i, int j, int x, int y){ // create a boolean matrix to store info about // cells already visited in current route bool visited[R][C]; // initailize visited to false memset(visited, false, sizeof visited); // find longest route from (i, j) to (x, y) and // print its maximum cost Pair p = findLongestPathUtil(mat, i, j, x, y, visited); if (p.found) cout << "Length of longest possible route is " << p.value; // If the destination is not reachable else cout << "Destination not reachable from given source";} // Driver codeint main(){ // input matrix with hurdles shown with number 0 int mat[R][C] = { { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 }, { 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1 }, { 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 } }; // find longest path with source (0, 0) and // destination (1, 7) findLongestPath(mat, 0, 0, 1, 7); return 0;} |
Выход:
Длина максимально длинного маршрута 24
Эта статья предоставлена Адитьей Гоэлем . Если вам нравится GeeksforGeeks, и вы хотели бы внести свой вклад, вы также можете написать статью на сайте deposit.geeksforgeeks.org или отправить свою статью по электронной почте: grant@geeksforgeeks.org. Посмотрите, как ваша статья появляется на главной странице GeeksforGeeks, и помогите другим гикам.
Пожалуйста, напишите комментарии, если вы обнаружите что-то неправильное, или вы хотите поделиться дополнительной информацией по теме, обсужденной выше.