Python | Панды DataFrame.to_string
Pandas DataFrame - это двумерная потенциально неоднородная табличная структура данных с изменяемым размером и помеченными осями (строки и столбцы). Арифметические операции выравниваются по меткам строк и столбцов. Его можно рассматривать как dict-подобный контейнер для объектов Series. Это основная структура данных Pandas.
Pandas DataFrame.to_string() function render a DataFrame to a console-friendly tabular output.
Syntax: DataFrame.to_string(buf=None, columns=None, col_space=None, header=True, index=True, na_rep=’NaN’, formatters=None, float_format=None, sparsify=None, index_names=True, justify=None, max_rows=None, max_cols=None, show_dimensions=False, decimal=’.’, line_width=None)
Parameter :
buf : Buffer to write to.
columns : The subset of columns to write. Writes all columns by default.
col_space : The minimum width of each column.
header : Write out the column names. If a list of strings is given, it is assumed to be aliases for the column names.
index : Whether to print index (row) labels.
na_rep : String representation of NAN to use.
formatters : Formatter functions to apply to columns’ elements by position or name.
float_format : Formatter function to apply to columns’ elements if they are floats. The result of this function must be a unicode string.
sparsify : Set to False for a DataFrame with a hierarchical index to print every multiindex key at each row.
index_names : Prints the names of the indexes.
max_rows : Maximum number of rows to display in the console.
max_cols : Maximum number of columns to display in the console.
show_dimensions : Display DataFrame dimensions (number of rows by number of columns).
decimal : Character recognized as decimal separator, e.g. ‘, ’ in Europe.
line_width : Width to wrap a line in characters.Returns : str (or unicode, depending on data and options)
Example #1: Use DataFrame.to_string() function to render the given DataFrame to a console-friendly tabular output. Do not include the index labels in the output.
# importing pandas as pdimport pandas as pd # Creating the DataFramedf = pd.DataFrame({"Weight":[45, 88, 56, 15, 71], "Name":["Sam", "Andrea", "Alex", "Robin", "Kia"], "Age":[14, 25, 55, 8, 21]}) # Create the indexindex_ = pd.date_range("2010-10-09 08:45", periods = 5, freq ="H") # Set the indexdf.index = index_ # Print the DataFrameprint(df) |
Выход :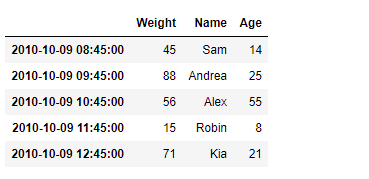
Now we will use DataFrame.to_string() function to render the given DataFrame to a console-friendly tabular output.
# print in tabular formatresult = df.to_string(index = False) # Print the resultprint(result) |
Output :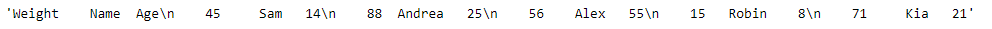
As we can see in the output, the DataFrame.to_string() function has successfully rendered the given dataframe to the console friendly tabular output.
Example #2: Use DataFrame.to_string() function to render the given DataFrame to a console-friendly tabular output. Represent the missing value in the given Dataframe by the string ‘Missing’.
# importing pandas as pdimport pandas as pd # Creating the DataFramedf = pd.DataFrame({"A":[12, 4, 5, None, 1], "B":[7, 2, 54, 3, None], "C":[20, 16, 11, 3, 8], "D":[14, 3, None, 2, 6]}) # Create the indexindex_ = ["Row_1", "Row_2", "Row_3", "Row_4", "Row_5"] # Set the indexdf.index = index_ # Print the DataFrameprint(df) |
Выход :
Now we will use DataFrame.to_string() function to render the given DataFrame to a console-friendly tabular output.
# print in tabular formatresult = df.to_string(na_rep = "Missing") # Print the resultprint(result) |
Output :
As we can see in the output, the DataFrame.to_string() function has successfully rendered the given dataframe to the console-friendly tabular output.
Внимание компьютерщик! Укрепите свои основы с помощью базового курса программирования Python и изучите основы.
Для начала подготовьтесь к собеседованию. Расширьте свои концепции структур данных с помощью курса Python DS. А чтобы начать свое путешествие по машинному обучению, присоединяйтесь к курсу Машинное обучение - базовый уровень.