Python - Pandas dataframe.append ()
Python - отличный язык для анализа данных, в первую очередь из-за фантастической экосистемы пакетов Python, ориентированных на данные. Pandas - один из таких пакетов, который значительно упрощает импорт и анализ данных.
Pandas dataframe.append() function is used to append rows of other dataframe to the end of the given dataframe, returning a new dataframe object. Columns not in the original dataframes are added as new columns and the new cells are populated with NaN value.
Syntax: DataFrame.append(other, ignore_index=False, verify_integrity=False, sort=None)
Parameters :
other : DataFrame or Series/dict-like object, or list of these
ignore_index : If True, do not use the index labels.
verify_integrity : If True, raise ValueError on creating index with duplicates.
sort : Sort columns if the columns of self and other are not aligned. The default sorting is deprecated and will change to not-sorting in a future version of pandas. Explicitly pass sort=True to silence the warning and sort. Explicitly pass sort=False to silence the warning and not sort.Returns: appended : DataFrame
Example #1: Create two data frames and append the second to the first one.
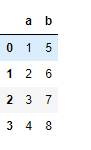
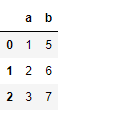
# Importing pandas as pdimport pandas as pd # Creating the first Dataframe using dictionarydf1 = df = pd.DataFrame({"a":[1, 2, 3, 4], "b":[5, 6, 7, 8]}) # Creating the Second Dataframe using dictionarydf2 = pd.DataFrame({"a":[1, 2, 3], "b":[5, 6, 7]}) # Print df1print(df1, "
") # Print df2df2 |
Now append df2 at the end of df1.
# to append df2 at the end of df1 dataframedf1.append(df2) |
Output :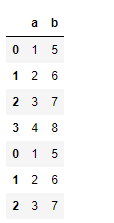
Notice the index value of second data frame is maintained in the appended data frame. If we do not want it to happen then we can set ignore_index=True.
# A continuous index value will be maintained# across the rows in the new appended data frame.df1.append(df2, ignore_index = True) |
Выход :
Пример №2: Добавить фрейм данных другой формы.
For unequal no. of columns in the data frame, non-existent value in one of the dataframe will be filled with NaN values.
# Importing pandas as pdimport pandas as pd # Creating the first Dataframe using dictionarydf1 = pd.DataFrame({"a":[1, 2, 3, 4], "b":[5, 6, 7, 8]}) # Creating the Second Dataframe using dictionarydf2 = pd.DataFrame({"a":[1, 2, 3], "b":[5, 6, 7], "c":[1, 5, 4]}) # for appending df2 at the end of df1df1.append(df2, ignore_index = True) |
Выход :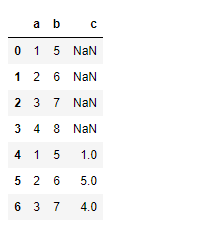
Notice, the new cells are populated with NaN values.
Внимание компьютерщик! Укрепите свои основы с помощью базового курса программирования Python и изучите основы.
Для начала подготовьтесь к собеседованию. Расширьте свои концепции структур данных с помощью курса Python DS. А чтобы начать свое путешествие по машинному обучению, присоединяйтесь к курсу Машинное обучение - базовый уровень.