Произведение длин всех циклов в неориентированном графе
Опубликовано: 24 Января, 2022
Дан неориентированный и невзвешенный граф. Задача - найти произведение длин всех образующихся в нем циклов.
Пример 1: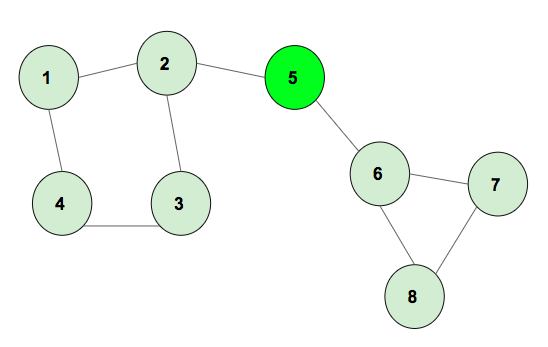
The above graph has two cycles of length 4 and 3, the product of cycle lengths is 12.
Пример 2: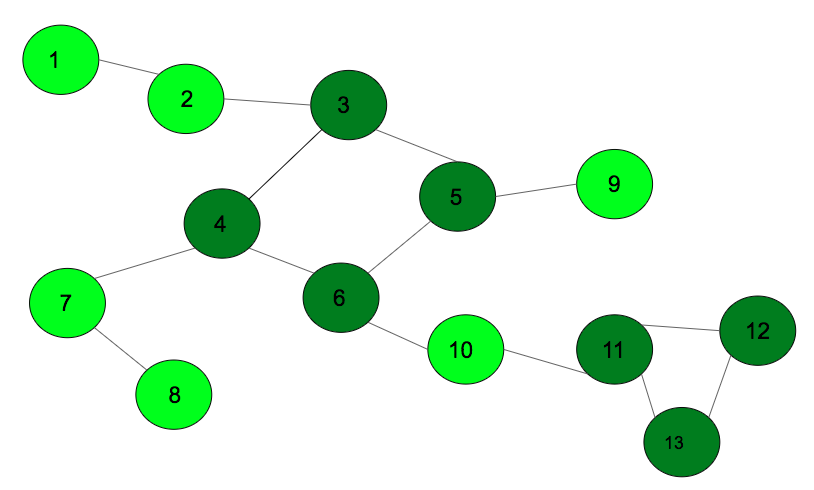
The above graph has two cycles of length 4 and 3, the product of cycle lengths is 12.
Рекомендуется: сначала попробуйте свой подход в {IDE}, прежде чем переходить к решению.
Подход: используя метод раскраски графа, пометьте все вершины различных циклов уникальными номерами. После завершения обхода графа поместите все похожие отмеченные числа в список смежности и распечатайте список смежности соответственно. Ниже приводится алгоритм:
- Вставьте края в список смежности.
- Вызовите функцию DFS, которая использует метод раскраски для отметки вершины.
- Всякий раз, когда есть частично посещенная вершина, возвращайтесь, пока не будет достигнута текущая вершина, и пометьте все их номерами цикла. Как только все вершины будут отмечены, увеличьте номер цикла.
- После завершения Dfs выполните итерацию для ребер и переместите те же отмеченные номера ребер в другой список смежности.
- Итерировать в другом списке смежности и вести подсчет количества вершин в цикле, используя номера карты и цикла.
- Итерируйте для номеров циклов и умножайте длины, чтобы получить конечный продукт, который и будет ответом.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find the// product of lengths of cycle#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int N = 100000; // variables to be used// in both functionsvector<int> graph[N]; // Function to mark the vertex with// different colors for different cyclesvoid dfs_cycle(int u, int p, int color[], int mark[], int par[], int& cyclenumber){ // already (completely) visited vertex. if (color[u] == 2) { return; } // seen vertex, but was not completely // visited -> cycle detected. // backtrack based on parents to find // the complete cycle. if (color[u] == 1) { cyclenumber++; int cur = p; mark[cur] = cyclenumber; // backtrack the vertex which are // in the current cycle thats found while (cur != u) { cur = par[cur]; mark[cur] = cyclenumber; } return; } par[u] = p; // partially visited. color[u] = 1; // simple dfs on graph for (int v : graph[u]) { // if it has not been visited previously if (v == par[u]) { continue; } dfs_cycle(v, u, color, mark, par, cyclenumber); } // completely visited. color[u] = 2;} // add the edges to the graphvoid addEdge(int u, int v){ graph[u].push_back(v); graph[v].push_back(u);} // Function to print the cyclesint productLength(int edges, int mark[], int& cyclenumber){ unordered_map<int, int> mp; // push the edges that into the // cycle adjacency list for (int i = 1; i <= edges; i++) { if (mark[i] != 0) mp[mark[i]]++; } int cnt = 1; // prodcut all the length of cycles for (int i = 1; i <= cyclenumber; i++) { cnt = cnt * mp[i]; } if (cyclenumber == 0) cnt = 0; return cnt;} // Driver Codeint main(){ // add edges addEdge(1, 2); addEdge(2, 3); addEdge(3, 4); addEdge(4, 6); addEdge(4, 7); addEdge(5, 6); addEdge(3, 5); addEdge(7, 8); addEdge(6, 10); addEdge(5, 9); addEdge(10, 11); addEdge(11, 12); addEdge(11, 13); addEdge(12, 13); // arrays required to color the // graph, store the parent of node int color[N]; int par[N]; // mark with unique numbers int mark[N]; // store the numbers of cycle int cyclenumber = 0; int edges = 13; // call DFS to mark the cycles dfs_cycle(1, 0, color, mark, par, cyclenumber); // function to print the cycles cout << productLength(edges, mark, cyclenumber); return 0;} |
Java
// Java program to find the // product of lengths of cycleimport java.io.*;import java.util.*; class GFG { static int N = 100000; static int cyclenumber; // variables to be used // in both functions //@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") static Vector<Integer>[] graph = new Vector[N]; // This static block is used to initialize // array of Vector, otherwise it will throw // NullPointerException static { for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) graph[i] = new Vector<>(); } // Function to mark the vertex with // different colors for different cycles static void dfs_cycle(int u, int p, int[] color, int[] mark, int[] par) { // already (completely) visited vertex. if (color[u] == 2) return; // seen vertex, but was not completely // visited -> cycle detected. // backtrack based on parents to find // the complete cycle. if (color[u] == 1) { cyclenumber++; int cur = p; mark[cur] = cyclenumber; // backtrack the vertex which are // in the current cycle thats found while (cur != u) { cur = par[cur]; mark[cur] = cyclenumber; } return; } par[u] = p; // partially visited. color[u] = 1; // simple dfs on graph for (int v : graph[u]) { // if it has not been visited previously if (v == par[u]) { continue; } dfs_cycle(v, u, color, mark, par); } // completely visited. color[u] = 2; } // add the edges to the graph static void addEdge(int u, int v) { graph[u].add(v); graph[v].add(u); } // Function to print the cycles static int productLength(int edges, int[] mark) { HashMap<Integer, Integer> mp = new HashMap<>(); // push the edges that into the // cycle adjacency list for (int i = 1; i <= edges; i++) { if (mark[i] != 0) { mp.put(mark[i], mp.get(mark[i]) == null ? 1 : mp.get(mark[i]) + 1); } } int cnt = 1; // prodcut all the length of cycles for (int i = 1; i <= cyclenumber; i++) { cnt = cnt * mp.get(i); } if (cyclenumber == 0) cnt = 0; return cnt; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // add edges addEdge(1, 2); addEdge(2, 3); addEdge(3, 4); addEdge(4, 6); addEdge(4, 7); addEdge(5, 6); addEdge(3, 5); addEdge(7, 8); addEdge(6, 10); addEdge(5, 9); addEdge(10, 11); addEdge(11, 12); addEdge(11, 13); addEdge(12, 13); // arrays required to color the // graph, store the parent of node int[] color = new int[N]; int[] par = new int[N]; // mark with unique numbers int[] mark = new int[N]; // store the numbers of cycle cyclenumber = 0; int edges = 13; // call DFS to mark the cycles dfs_cycle(1, 0, color, mark, par); // function to print the cycles System.out.println(productLength(edges, mark)); }} // This code is contributed by// sanjeev2552 |
Python3
# Python3 program to find the# product of lengths of cyclefrom collections import defaultdict # Function to mark the vertex with# different colors for different cyclesdef dfs_cycle(u, p, color, mark, par): global cyclenumber # already (completely) visited vertex. if color[u] == 2: return # seen vertex, but was not completely # visited -> cycle detected. # backtrack based on parents to find # the complete cycle. if color[u] == 1: cyclenumber += 1 cur = p mark[cur] = cyclenumber # backtrack the vertex which are # in the current cycle thats found while cur != u: cur = par[cur] mark[cur] = cyclenumber return par[u] = p # partially visited. color[u] = 1 # simple dfs on graph for v in graph[u]: # if it has not been visited previously if v == par[u]: continue dfs_cycle(v, u, color, mark, par) # completely visited. color[u] = 2 # add the edges to the graphdef addEdge(u, v): graph[u].append(v) graph[v].append(u) # Function to print the cyclesdef productLength(edges, mark, cyclenumber): mp = defaultdict(lambda:0) # push the edges that into the # cycle adjacency list for i in range(1, edges+1): if mark[i] != 0: mp[mark[i]] += 1 cnt = 1 # prodcut all the length of cycles for i in range(1, cyclenumber + 1): cnt = cnt * mp[i] if cyclenumber == 0: cnt = 0 return cnt # Driver Codeif __name__ == "__main__":РЕКОМЕНДУЕМЫЕ СТАТЬИ |