Программа C ++ для циклической сортировки
Cycle sort is an in-place sorting Algorithm, unstable sorting algorithm, a comparison sort that is theoretically optimal in terms of the total number of writes to the original array.
- It is optimal in terms of number of memory writes. It minimizes the number of memory writes to sort (Each value is either written zero times, if it’s already in its correct position, or written one time to its correct position.)
- It is based on the idea that array to be sorted can be divided into cycles. Cycles can be visualized as a graph. We have n nodes and an edge directed from node i to node j if the element at i-th index must be present at j-th index in the sorted array.
Cycle in arr[] = {4, 5, 2, 1, 5}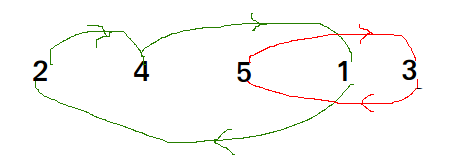
Cycle in arr[] = {4, 3, 2, 1}
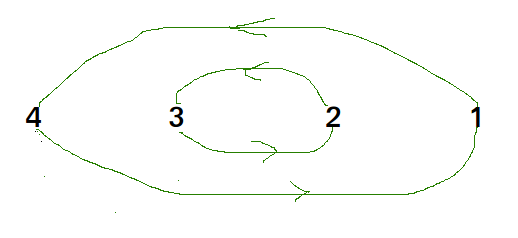
We one by one consider all cycles. We first consider the cycle that includes first element. We find correct position of first element, place it at its correct position, say j. We consider old value of arr[j] and find its correct position, we keep doing this till all elements of current cycle are placed at correct position, i.e., we don’t come back to cycle starting point.
CPP
// C++ program to impleament cycle sort#include <iostream>using namespace std; // Function sort the array using Cycle sortvoid cycleSort (int arr[], int n){ // count number of memory writes int writes = 0; // traverse array elements and put it to on // the right place for (int cycle_start=0; cycle_start<=n-2; cycle_start++) { // initialize item as starting point int item = arr[cycle_start]; // Find position where we put the item. We basically // count all smaller elements on right side of item. int pos = cycle_start; for (int i = cycle_start+1; i<n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos++; // If item is already in correct position if (pos == cycle_start) continue; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (pos != cycle_start) { swap(item, arr[pos]); writes++; } // Rotate rest of the cycle while (pos != cycle_start) { pos = cycle_start; // Find position where we put the element for (int i = cycle_start+1; i<n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos += 1; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (item != arr[pos]) { swap(item, arr[pos]); writes++; } } } // Number of memory writes or swaps // cout << writes << endl ;} // Driver program to test above functionint main(){ int arr[] = {1, 8, 3, 9, 10, 10, 2, 4 }; int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); cycleSort(arr, n) ; cout << "After sort : " <<endl; for (int i =0; i<n; i++) cout << arr[i] << " "; return 0;} |
Output:
After sort : 1 2 3 4 8 9 10 10
Please refer complete article on Cycle Sort for more details!
Attention reader! Don’t stop learning now. Get hold of all the important DSA concepts with the DSA Self Paced Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready. To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more, please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course.
In case you wish to attend live classes with industry experts, please refer Geeks Classes Live and Geeks Classes Live USA
