Очередь приоритетов в обратном порядке в Java
PriorityQueue используется, когда предполагается, что объекты будут обрабатываться на основе приоритета. Известно, что очередь следует алгоритму First-In-First-Out, но иногда элементы очереди необходимо обрабатывать в соответствии с приоритетом, тогда в игру вступает PriorityQueue. PriorityQueue основан на куче приоритетов. Элементы приоритетной очереди упорядочиваются в соответствии с естественным порядком или с помощью компаратора, предоставленного во время построения очереди, в зависимости от того, какой конструктор используется.
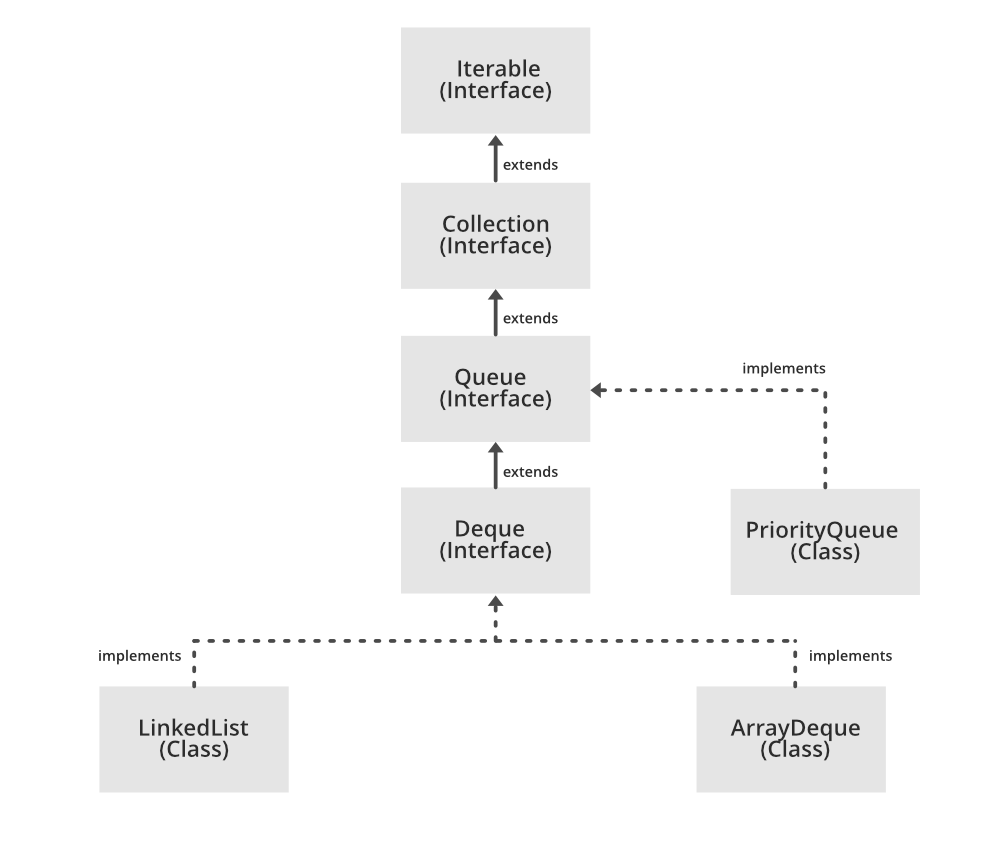
Декларация:
открытый класс PriorityQueue <E> расширяет AbstractQueue <E> реализует Serializable
где E - тип элементов, хранящихся в этой очереди
Типы PriorityQueue
- Очередь с максимальным приоритетом
- Очередь с минимальным приоритетом
Example of Default Priority Queue
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the// working of default PriorityQueueimport java.util.*; class PriorityQueueDemo { // Main Method public static void main(String args[]) { // Creating empty priority queue PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(); // Adding items to the pQueue using add() pQueue.add(10); pQueue.add(20); pQueue.add(15); pQueue.add(5); // Printing the top element of PriorityQueue System.out.println(pQueue.peek()); // Printing the top element and removing it // from the PriorityQueue container System.out.println(pQueue.poll()); // Printing the top element again System.out.println(pQueue.peek()); }} |
5 5 10
В Java Priority Queue по умолчанию реализует min Priority Queue. Если нам нужно изменить порядок Priority Queue с min на max Priority Queue, мы используем следующие методы:
- Использование по умолчанию Comparator Collections.reverseOrder ()
- Использование настраиваемого компаратора
- Использование лямбда-выражения
Метод 1. Использование по умолчанию Comparator Collections.reverseOrder ()
Метод Collections.reverseOrder () используется , чтобы получить обратное поведение компаратора по умолчанию. Это компаратор по умолчанию в пакет java.util .
Example:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the// working of PriorityQueue in revers orderimport java.util.*; class PriorityQueueDemo { // Main Method public static void main(String args[]) { // Creating empty priority queue PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>( Collections.reverseOrder()); // Adding items to the pQueue using add() pQueue.add(10); pQueue.add(20); pQueue.add(15); pQueue.add(5); // Printing the top element of PriorityQueue System.out.println(pQueue.peek()); // Printing the top element and removing it // from the PriorityQueue container System.out.println(pQueue.poll()); // Printing the top element again System.out.println(pQueue.peek()); }} |
20 20 15
Метод 2: использование настраиваемого компаратора
Метод java.util.PriorityQueue.comparator () разделяет важную функцию установки и возврата компаратора, который можно использовать для упорядочивания элементов в PriorityQueue. Метод возвращает нулевое значение, если очередь следует естественному шаблону упорядочения элементов.
Example:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the// working of PriorityQueue in revers order import java.util.*; public class PriorityQueueDemo { // Main Method public static void main(String[] args) { // Creating empty priority queue // with custom Comparator PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>( new Comparator<Integer>() { // Compare method for place element in // revers order public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) { if (a < b) return 1; if (a > b) return -1; return 0; } }); // Adding items to the pQueue using add() pQueue.add(10); pQueue.add(15); pQueue.add(20); pQueue.add(5); // Printing the top element of PriorityQueue System.out.println(pQueue.peek()); // Printing the top element and removing it // from the PriorityQueue container System.out.println(pQueue.poll()); // Printing the top element again System.out.println(pQueue.peek()); }} |
20 20 15
Метод 3: использование лямбда-выражения
Лямбда-выражение, начиная с Java 8, лямбда-функция называет свои входные параметры a и b и возвращает (ba), что в основном и делает класс компаратора int, за исключением того, что он возвращает ab.
Example:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate the// working of PriorityQueue in revers orderimport java.util.*; class PriorityQueueDemo { // Main Method public static void main(String args[]) { // Creating empty priority queue PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>((a, b) -> b - a); // Adding items to the pQueue using add() pQueue.add(10); pQueue.add(20); pQueue.add(15); pQueue.add(5); // Printing the top element of PriorityQueue System.out.println(pQueue.peek()); // Printing the top element and removing it // from the PriorityQueue container System.out.println(pQueue.poll()); // Printing the top element again System.out.println(pQueue.peek()); }} |
20 20 15
Вниманию читателя! Не переставай учиться сейчас. Ознакомьтесь со всеми важными концепциями Java Foundation и коллекций с помощью курса "Основы Java и Java Collections" по доступной для студентов цене и будьте готовы к работе в отрасли. Чтобы завершить подготовку от изучения языка к DS Algo и многому другому, см. Полный курс подготовки к собеседованию .