Найдите все углы данного треугольника
Зная координаты всех трех вершин треугольника в 2D-плоскости, задача состоит в том, чтобы найти все три угла.
Пример:
Ввод: A = (0, 0),
В = (0, 1),
С = (1, 0)
Выход: 90, 45, 45
Рекомендуется: сначала попробуйте свой подход в {IDE}, прежде чем переходить к решению.
Чтобы решить эту проблему, мы используем приведенный ниже Закон косинусов.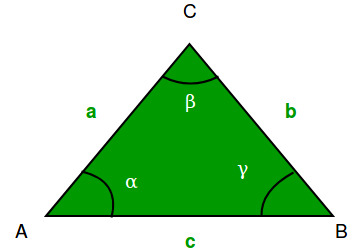
с ^ 2 = а ^ 2 + Ь ^ 2-2 (а) (б) (соз бета)
После перестановки
beta = acos( ( a^2 + b^2 - c^2 ) / (2ab) )
В тригонометрии закон косинусов (также известный как формула косинуса или правило косинуса) связывает длины сторон треугольника с косинусом одного из его углов.
Сначала рассчитайте длину всех сторон. Затем примените формулу выше, чтобы получить все углы в радиан. Затем преобразуйте углы из радиан в градусов.
Below is implementation of above steps.
C++
// Code to find all three angles// of a triangle given coordinate// of all three vertices#include <iostream>#include <utility> // for pair#include <cmath> // for math functionsusing namespace std; #define PI 3.1415926535 // returns square of distance b/w two pointsint lengthSquare(pair<int,int> X, pair<int,int> Y){ int xDiff = X.first - Y.first; int yDiff = X.second - Y.second; return xDiff*xDiff + yDiff*yDiff;} void printAngle(pair<int,int> A, pair<int,int> B, pair<int,int> C){ // Square of lengths be a2, b2, c2 int a2 = lengthSquare(B,C); int b2 = lengthSquare(A,C); int c2 = lengthSquare(A,B); // length of sides be a, b, c float a = sqrt(a2); float b = sqrt(b2); float c = sqrt(c2); // From Cosine law float alpha = acos((b2 + c2 - a2)/(2*b*c)); float betta = acos((a2 + c2 - b2)/(2*a*c)); float gamma = acos((a2 + b2 - c2)/(2*a*b)); // Converting to degree alpha = alpha * 180 / PI; betta = betta * 180 / PI; gamma = gamma * 180 / PI; // printing all the angles cout << "alpha : " << alpha << endl; cout << "betta : " << betta << endl; cout << "gamma : " << gamma << endl;} // Driver codeint main(){ pair<int,int> A = make_pair(0,0); pair<int,int> B = make_pair(0,1); pair<int,int> C = make_pair(1,0); printAngle(A,B,C); return 0;} |
Java
// Java Code to find all three angles// of a triangle given coordinate// of all three vertices import java.awt.Point;import static java.lang.Math.PI;import static java.lang.Math.sqrt;import static java.lang.Math.acos; class Test{ // returns square of distance b/w two points static int lengthSquare(Point p1, Point p2) { int xDiff = p1.x- p2.x; int yDiff = p1.y- p2.y; return xDiff*xDiff + yDiff*yDiff; } static void printAngle(Point A, Point B, Point C) { // Square of lengths be a2, b2, c2 int a2 = lengthSquare(B,C); int b2 = lengthSquare(A,C); int c2 = lengthSquare(A,B); // length of sides be a, b, c float a = (float)sqrt(a2); float b = (float)sqrt(b2); float c = (float)sqrt(c2); // From Cosine law float alpha = (float) acos((b2 + c2 - a2)/(2*b*c)); float betta = (float) acos((a2 + c2 - b2)/(2*a*c)); float gamma = (float) acos((a2 + b2 - c2)/(2*a*b)); // Converting to degree alpha = (float) (alpha * 180 / PI); betta = (float) (betta * 180 / PI); gamma = (float) (gamma * 180 / PI); // printing all the angles System.out.println("alpha : " + alpha); System.out.println("betta : " + betta); System.out.println("gamma : " + gamma); } // Driver method public static void main(String[] args) { Point A = new Point(0,0); Point B = new Point(0,1); Point C = new Point(1,0); printAngle(A,B,C); }} |
Python3
# Python3 code to find all three angles # of a triangle given coordinate # of all three vertices import math # returns square of distance b/w two points def lengthSquare(X, Y): xDiff = X[0] - Y[0] yDiff = X[1] - Y[1] return xDiff * xDiff + yDiff * yDiff def printAngle(A, B, C): # Square of lengths be a2, b2, c2 a2 = lengthSquare(B, C) b2 = lengthSquare(A, C) c2 = lengthSquare(A, B) # length of sides be a, b, c a = math.sqrt(a2); b = math.sqrt(b2); c = math.sqrt(c2); # From Cosine law alpha = math.acos((b2 + c2 - a2) / (2 * b * c)); betta = math.acos((a2 + c2 - b2) / (2 * a * c)); gamma = math.acos((a2 + b2 - c2) / (2 * a * b)); # Converting to degree alpha = alpha * 180 / math.pi; betta = betta * 180 / math.pi; gamma = gamma * 180 / math.pi; # printing all the angles print("alpha : %f" %(alpha)) print("betta : %f" %(betta)) print("gamma : %f" %(gamma)) # Driver codeA = (0, 0)B = (0, 1) C = (1, 0) printAngle(A, B, C); # This code is contributed # by ApurvaRaj |
C#
// C# Code to find all three angles// of a triangle given coordinate// of all three verticesusing System; class GFG{ class Point { public int x, y; public Point(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } } // returns square of distance b/w two points static int lengthSquare(Point p1, Point p2) { int xDiff = p1.x - p2.x; int yDiff = p1.y - p2.y; return xDiff * xDiff + yDiff * yDiff; } static void printAngle(Point A, Point B, Point C) { // Square of lengths be a2, b2, c2 int a2 = lengthSquare(B, C); int b2 = lengthSquare(A, C); int c2 = lengthSquare(A, B); // length of sides be a, b, c float a = (float)Math.Sqrt(a2); float b = (float)Math.Sqrt(b2); float c = (float)Math.Sqrt(c2); // From Cosine law float alpha = (float) Math.Acos((b2 + c2 - a2) / (2 * b * c)); float betta = (float) Math.Acos((a2 + c2 - b2) / (2 * a * c)); float gamma = (float) Math.Acos((a2 + b2 - c2) / (2 * a * b)); // Converting to degree alpha = (float) (alpha * 180 / Math.PI); betta = (float) (betta * 180 / Math.PI); gamma = (float) (gamma * 180 / Math.PI); // printing all the angles Console.WriteLine("alpha : " + alpha); Console.WriteLine("betta : " + betta); Console.WriteLine("gamma : " + gamma); } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { Point A = new Point(0, 0); Point B = new Point(0, 1); Point C = new Point(1, 0); printAngle(A, B, C); }} // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji |
Output:
alpha : 90 betta : 45 gamma : 45
Ссылка :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Law_of_cosines
Эта статья предоставлена Pratik Chhajer. Если вам нравится GeeksforGeeks, и вы хотели бы внести свой вклад, вы также можете написать статью на сайте deposit.geeksforgeeks.org или отправить свою статью по электронной почте: grant@geeksforgeeks.org. Посмотрите, как ваша статья появляется на главной странице GeeksforGeeks, и помогите другим гикам.
Пожалуйста, напишите комментарии, если вы обнаружите что-то неправильное, или вы хотите поделиться дополнительной информацией по теме, обсужденной выше.
Вниманию читателя! Не прекращайте учиться сейчас. Освойте все важные концепции DSA с помощью самостоятельного курса DSA по приемлемой для студентов цене и будьте готовы к работе в отрасли. Чтобы завершить подготовку от изучения языка к DS Algo и многому другому, см. Полный курс подготовки к собеседованию .
Если вы хотите посещать живые занятия с отраслевыми экспертами, пожалуйста, обращайтесь к Geeks Classes Live и Geeks Classes Live USA.