Matplotlib.pyplot.broken_barh () в Python
Matplotlib - один из самых популярных пакетов Python, используемых для визуализации данных. Это кроссплатформенная библиотека для создания 2D-графиков из данных в массивах. Pyplot - это набор функций командного стиля, которые заставляют matplotlib работать как MATLAB.
matplotlib.pyplot.broken_barh ()
Функция broken_barh () используется для построения горизонтальной последовательности прямоугольников. Прямоугольник рисуется для каждого компонента xranges, который состоит из последовательности кортежей. Все прямоугольники имеют одинаковое вертикальное положение и оценку, характеризующуюся диапазоном значений.
Syntax: matplotlib.pyplot.broken_barh(xranges, yrange, *, data=None, **kwargs)
Parameters:
- xranges : sequence of tuples (xmin, xwidth)
Each tuples gives the position(xmin) of the rectangle and it’s horizontal extension(xwidth) from that position.- yranges : (ymin, ymax)
In the above attribute, ymin gives the position of the rectangle and ymax gives the vertical extension from ymin.Returns:
- BrokenBarHCollection: A collection of horizontal bars spanning yrange with a sequence of xranges.
Examples to illustrate the matplotlib.pyplot.broken_barh() function are as follows:
Example 1:
# importing moduleimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Adding title to the plotplt.title("GEEKSFORGEEKS - EXAMPLE") # adding x axis label to the plotplt.xlabel("x-label") # label for y axis for the plotplt.ylabel("y-label") x_1 = [(1, 4), (10, 7)]y_1 = (2, 2) # Plotting the chartplt.broken_barh(x_1, y_1, facecolors ="green") x_2 = [(10, 1), (15, 4), (25, 6)]y_2 = (6, 2) # Plotting the chartplt.broken_barh(x_2, y_2, facecolors ="cyan") plt.show() |
Выход :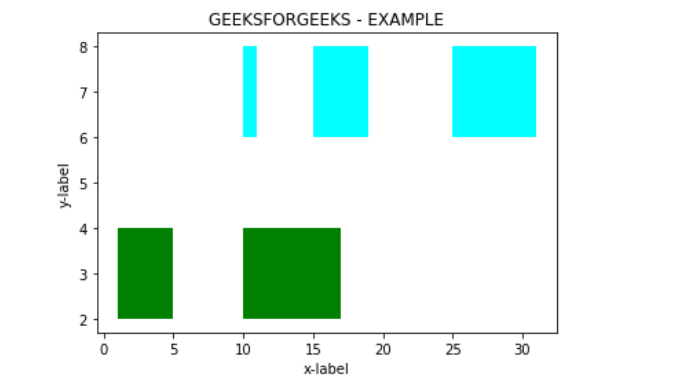
Example 2:
# importing moduleimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt # Adding title to the plotplt.title("GEEKSFORGEEKS - EXAMPLE") # adding x axis label to the plotplt.xlabel("Number of Cars") # label for y axis for the plotplt.ylabel("Average Speed") x_1 = [(10, 3), (15, 4)]y_1 = (50, 10) # Plotting the chartplt.broken_barh(x_1, y_1, facecolors ="cyan") x_2 = [(1, 4), (10, 1), (15, 4), (25, 6)]y_2 = (70, 10) # Plotting the chartplt.broken_barh(x_2, y_2, facecolors ="green") x_3 = [(5, 3), (11, 2), (18, 5)]y_3 = (90, 10) # Plotting the chartplt.broken_barh(x_3, y_3, facecolors ="blue") plt.show() |
Выход :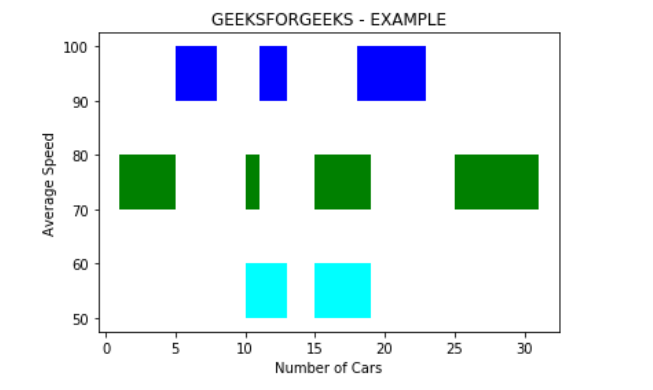
Внимание компьютерщик! Укрепите свои основы с помощью базового курса программирования Python и изучите основы.
Для начала подготовьтесь к собеседованию. Расширьте свои концепции структур данных с помощью курса Python DS. А чтобы начать свое путешествие по машинному обучению, присоединяйтесь к курсу Машинное обучение - базовый уровень.