Django ModelForm - Создание формы из моделей
Django ModelForm - это класс, который используется для прямого преобразования модели в форму Django. Если вы создаете приложение на основе базы данных, скорее всего, у вас будут формы, которые близко соответствуют моделям Django. Например, модель и форма регистрации пользователя будут иметь одинаковое качество и количество полей модели и полей формы. Поэтому вместо создания избыточного кода, чтобы сначала создать форму, а затем сопоставить ее с моделью в представлении, мы можем напрямую использовать ModelForm. Он принимает в качестве аргумента имя модели и преобразует его в форму Django. Не только это, ModelForm предлагает множество методов и функций, которые автоматизируют весь процесс и помогают устранить избыточность кода.
Как преобразовать модель в форму Django?
Чтобы объяснить работу проекта, мы будем использовать проект geeksforgeeks , создать модель и сопоставить ее с формами Django.
Refer to the following articles to check how to create a project and an app in Django.
- How to Create a Basic Project using MVT in Django?
- How to Create an App in Django ?
Now when we have our project ready, create a model in geeks/models.py,
# import the standard Django Model# from built-in libraryfrom django.db import models # declare a new model with a name "GeeksModel"class GeeksModel(models.Model): # fields of the model title = models.CharField(max_length = 200) description = models.TextField() last_modified = models.DateTimeField(auto_now_add = True) img = models.ImageField(upload_to = "images/") # renames the instances of the model # with their title name def __str__(self): return self.title |
Now, run following commands to create the model,
Python manage.py makemigrations Python manage.py migrate
We can check that model has been successfully created at http://127.0.0.1:8000/admin/geeks/geeksmodel/add/,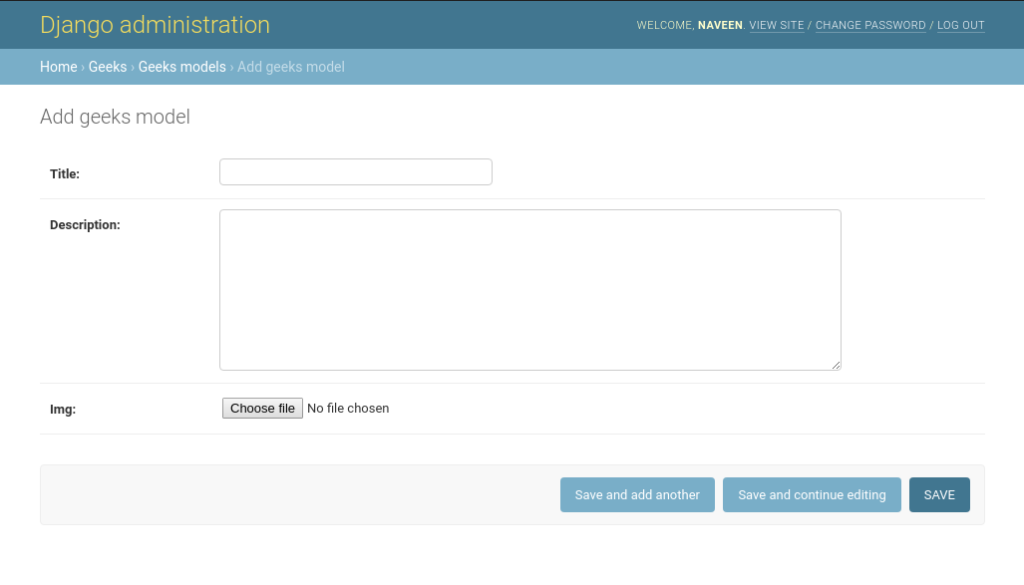
To create a form directly for this model, dive into geeks/forms.py and Enter following code,
# import form class from djangofrom django import forms # import GeeksModel from models.pyfrom .models import GeeksModel # create a ModelFormclass GeeksForm(forms.ModelForm): # specify the name of model to use class Meta: model = GeeksModel fields = "__all__" |
This form takes two arguments fields or exclude.
- fields – It is strongly recommended that you explicitly set all fields that should be edited in the form using the fields attribute. Failure to do so can easily lead to security problems when a form unexpectedly allows a user to set certain fields, especially when new fields are added to a model. Depending on how the form is rendered, the problem may not even be visible on the web page. Set the fields attribute to the special value ‘__all__’ to indicate that all fields in the model should be used.
- exclude – Set the exclude attribute of the ModelForm’s inner Meta class to a list of fields to be excluded from the form.
For example:class PartialAuthorForm(ModelForm): class Meta: model = Author exclude = ["title"]
Finally, to complete our MVT structure, create a view that would render the form and directly save it to the database. In geeks/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import renderfrom .forms import GeeksForm def home_view(request): context ={} # create object of form form = GeeksForm(request.POST or None, request.FILES or None) # check if form data is valid if form.is_valid(): # save the form data to model form.save() context["form"]= form return render(request, "home.html", context) |
Everything set, Now visit http://127.0.0.1:8000/,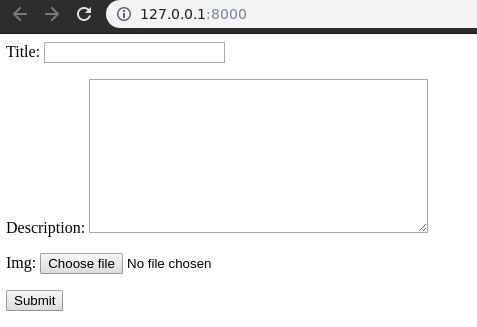
Now you can see that every model field is mapped into a form field and displayed correspondingly. Field mappings are discussed later in this article. So now let’s try entering data into form and check if it gets saved into the database.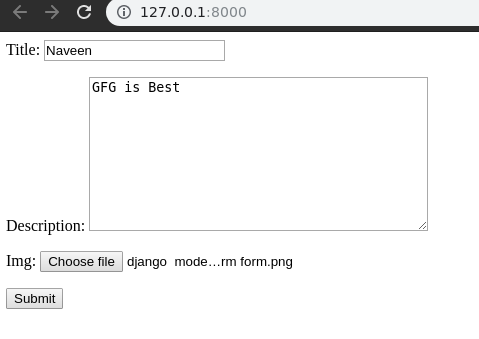
Hit submit and Bingo the form gets saved automatically to database. We can verify it at http://localhost:8000/admin/geeks/geeksmodel/.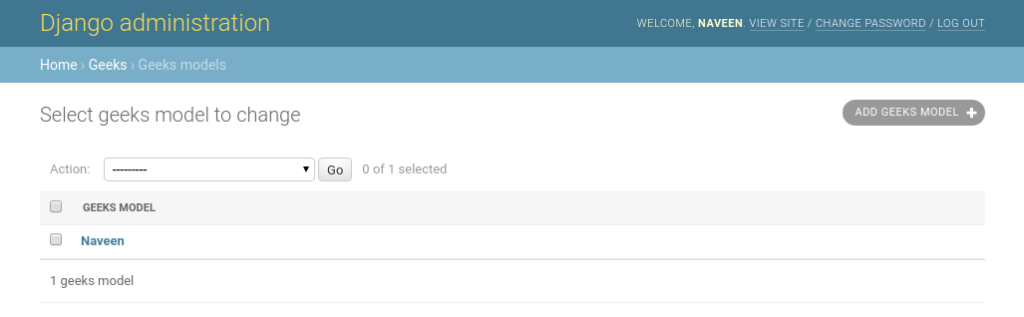
Field types
The generated Form class will have a form field for every model field specified, in the order specified in the fields attribute. Each model field has a corresponding default form field. For example, a CharField on a model is represented as a CharField on a form. A model ManyToManyField is represented as a MultipleChoiceField. Here is the full list of conversions:
| Model Field | Form Field |
|---|---|
| AutoField | Not represented in the form |
| BigAutoField | Not represented in the form |
| BigIntegerField | IntegerField with min_value set to -9223372036854775808 and max_value set to 9223372036854775807. |
| BinaryField | CharField, if editable is set to True on the model field, otherwise not represented in the form. |
| BooleanField | BooleanField, or NullBooleanField if null=True. |
| CharField | CharField with max_length set to the model field’s max_length and empty_value set to None if null=True. |
| DateField | DateField |
| DateTimeField | DateTimeField |
| DecimalField | DecimalField |
| DurationField | DurationField |
| EmailField | EmailField |
| FileField | FileField |
| FilePathField | FilePathField |
| FloatField | FloatField |
| ForeignKey | ModelChoiceField |
| ImageField | ImageField |
| IntegerField | IntegerField |
| IPAddressField | IPAddressField |
| GenericIPAddressField | GenericIPAddressField |
| ManyToManyField | ModelMultipleChoiceField |
| NullBooleanField | NullBooleanField |
| PositiveIntegerField | IntegerField |
| PositiveSmallIntegerField | IntegerField |
| SlugField | SlugField |
| SmallAutoField | Not represented in the form |
| TextField | CharField with widget=forms.Textarea |
| TimeField | TimeField |
| URLField | URLField |
Attention geek! Strengthen your foundations with the Python Programming Foundation Course and learn the basics.
To begin with, your interview preparations Enhance your Data Structures concepts with the Python DS Course. And to begin with your Machine Learning Journey, join the Machine Learning – Basic Level Course