Django CRUD (создание, получение, обновление, удаление) Представления на основе функций
Django - это веб-фреймворк на основе Python, который позволяет быстро создавать веб-приложения без всех проблем с установкой или зависимостями, которые обычно возникают с другими фреймворками. Django основан на архитектуре MVT (шаблон представления модели) и вращается вокруг операций CRUD (создание, получение, обновление, удаление). CRUD лучше всего можно объяснить как подход к созданию веб-приложения Django. В общем случае CRUD означает выполнение операций Create, Retrieve, Update и Delete над таблицей в базе данных. Давайте обсудим, что на самом деле означает CRUD,
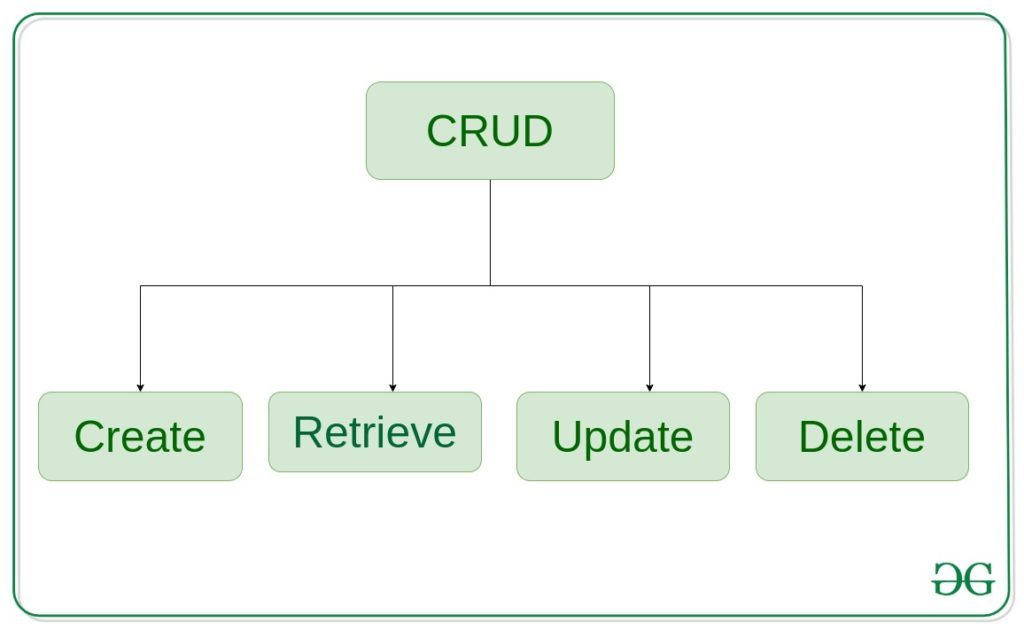
Создать - создать или добавить новые записи в таблицу в базе данных.
Получить - читать, извлекать, искать или просматривать существующие записи в виде списка (представление списка) или извлекать конкретную запись в деталях (подробное представление)
Обновить - обновить или отредактировать существующие записи в таблице в базе данных.
Удалить - удалить, деактивировать или удалить существующие записи в таблице в базе данных.
Django CRUD (создание, получение, обновление, удаление) представлений на основе функций
Illustration of How to create and use CRUD view using an Example. Consider a project named geeksforgeeks having an app named geeks.
Refer to the following articles to check how to create a project and an app in Django.
- How to Create a Basic Project using MVT in Django?
- How to Create an App in Django ?
After you have a project and an app, let’s create a model of which we will be creating instances through our view. In geeks/models.py,
# import the standard Django Model# from built-in libraryfrom django.db import models # declare a new model with a name "GeeksModel"class GeeksModel(models.Model): # fields of the model title = models.CharField(max_length = 200) description = models.TextField() # renames the instances of the model # with their title name def __str__(self): return self.title |
After creating this model, we need to run two commands in order to create Database for the same.
Python manage.py makemigrations Python manage.py migrate
Now we will create a Django ModelForm for this model. Refer this article for more on modelform – Django ModelForm – Create form from Models. create a file forms.py in geeks folder,
from django import formsfrom .models import GeeksModel # creating a formclass GeeksForm(forms.ModelForm): # create meta class class Meta: # specify model to be used model = GeeksModel # specify fields to be used fields = [ "title", "description", ] |
Create View
Create View refers to a view (logic) to create an instance of a table in the database. It is just like taking an input from a user and storing it in a specified table.
In geeks/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import render # relative import of formsfrom .models import GeeksModelfrom .forms import GeeksForm def create_view(request): # dictionary for initial data with # field names as keys context ={} # add the dictionary during initialization form = GeeksForm(request.POST or None) if form.is_valid(): form.save() context["form"]= form return render(request, "create_view.html", context) |
Create a template in templates/create_view.html,
<form method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <!-- Security token --> {% csrf_token %} <!-- Using the formset --> {{ form.as_p }} <input type="submit" value="Submit"></form> |
Now visit http://localhost:8000/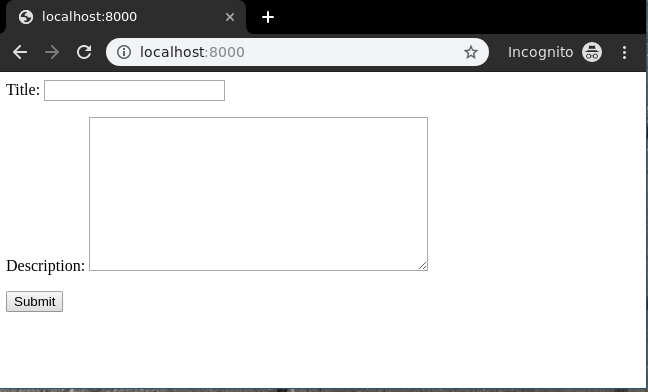
To check complete implementation of Function based Create View, visit Create View – Function based Views Django.
Retrieve View
Retrieve view is basically divided into two types of views Detail View and List View.
List View
List View refers to a view (logic) to list all or particular instances of a table from the database in a particular order. It is used to display multiple types of data on a single page or view, for example, products on an eCommerce page.
In geeks/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import render # relative import of formsfrom .models import GeeksModel def list_view(request): # dictionary for initial data with # field names as keys context ={} # add the dictionary during initialization context["dataset"] = GeeksModel.objects.all() return render(request, "list_view.html", context) |
Create a template in templates/list_view.html,
<div class="main"> {% for data in dataset %}. {{ data.title }}<br/> {{ data.description }}<br/> <hr/> {% endfor %} </div> |
Now visit http://localhost:8000/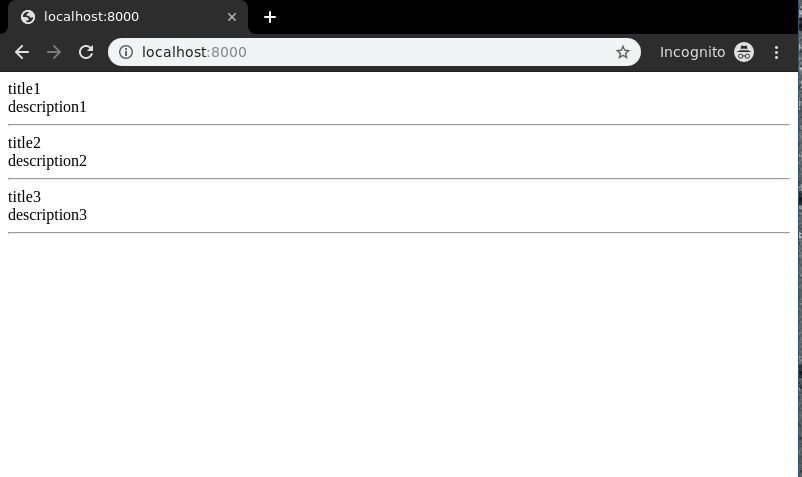
To check complete implementation of Function based List View, visit List View – Function based Views Django
Detail View
Detail View refers to a view (logic) to display a particular instnace of a table from the database with all the necessary details. It is used to display multiple types of data on a single page or view, for example, profile of a user.
In geeks/views.py,
from django.urls import path # importing views from views..pyfrom .views import detail_view urlpatterns = [ path("<id>", detail_view ),] |
Let’s create a view and template for the same. In geeks/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import render # relative import of formsfrom .models import GeeksModel # pass id attribute from urlsdef detail_view(request, id): # dictionary for initial data with # field names as keys context ={} # add the dictionary during initialization context["data"] = GeeksModel.objects.get(id = id) return render(request, "detail_view.html", context) |
Create a template in templates/Detail_view.html,
<div class="main"> <!-- Specify fields to be displayed --> {{ data.title }}<br/> {{ data.description }}<br/> </div> |
Let’s check what is there on http://localhost:8000/1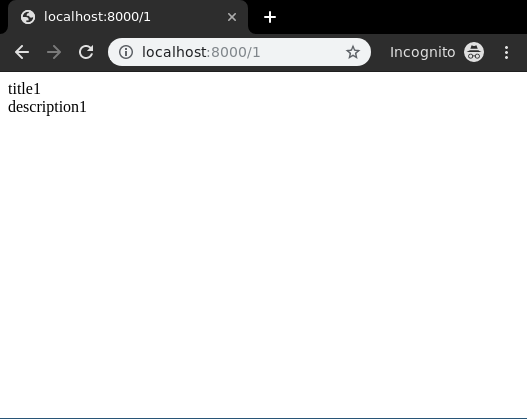
To check complete implementation of Function based Detail View, visit Detail View – Function based Views Django
Update View
Update View refers to a view (logic) to update a particular instance of a table from the database with some extra details. It is used to update enteries in the database for example, updating an article at geeksforgeeks.
In geeks/views.py,
from django.shortcuts import (get_object_or_404, render, HttpResponseRedirect) # relative import of formsfrom .models import GeeksModelfrom .forms import GeeksForm # after updating it will redirect to detail_Viewdef detail_view(request, id): # dictionary for initial data with # field names as keys context ={} # add the dictionary during initialization context["data"] = GeeksModel.objects.get(id = id) return render(request, "detail_view.html", context) # update view for detailsdef update_view(request, id): # dictionary for initial data with # field names as keys context ={} # fetch the object related to passed id obj = get_object_or_404(GeeksModel, id = id) # pass the object as instance in form form = GeeksForm(request.POST or None, instance = obj) # save the data from the form and # redirect to detail_view if form.is_valid(): form.save() return HttpResponseRedirect("/"+id) # add form dictionary to context context["form"] = form return render(request, "update_view.html", context) |
Now create following templates in templates folder,
In geeks/templates/update_view.html,
<div class="main"> <!-- Create a Form --> <form method="POST"> <!-- Security token by Django --> {% csrf_token %} <!-- form as paragraph --> {{ form.as_p }} <input type="submit" value="Update"> </form> </div> |
In geeks/templates/detail_view.html,
<div class="main"> <!-- Display attributes of instance --> {{ data.title }} <br/> {{ data.description }}</div> |
Let’s check if everything is working, visithttp://localhost:8000/1/update.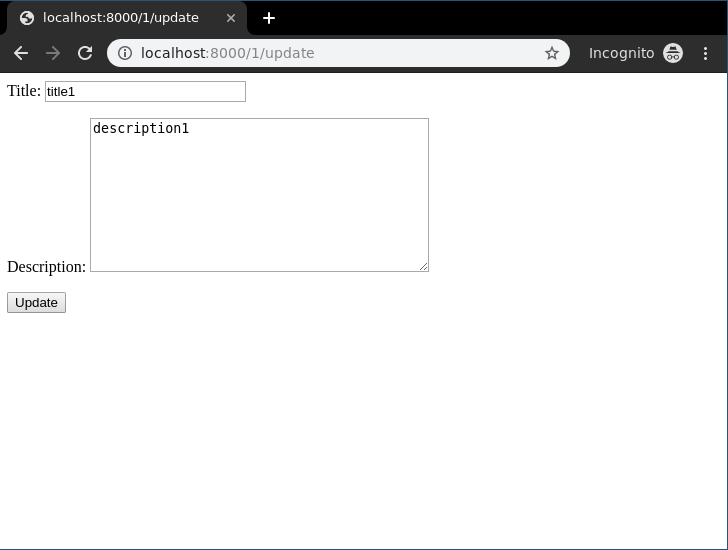
To check complete implementation of Function based update View, visit Update View – Function based Views Django
Delete View
Delete View refers to a view (logic) to delete a particular instance of a table from the database. It is used to delete entries in the database for example, deleting an article at geeksforgeeks.
In geeks/views.py
from django.shortcuts import (get_object_or_404, render, HttpResponseRedirect) from .models import GeeksModel # delete view for detailsdef delete_view(request, id): # dictionary for initial data with # field names as keys context ={} # fetch the object related to passed id obj = get_object_or_404(GeeksModel, id = id) if request.method =="POST": # delete object obj.delete() # after deleting redirect to # home page return HttpResponseRedirect("/") return render(request, "delete_view.html", context) |
Now a url mapping to this view with a regular expression of id,
In geeks/urls.py
from django.urls import path # importing views from views..pyfrom .views import delete_viewurlpatterns = [ path("<id>/delete", delete_view ),] |
Template for delete view includes a simple form confirming whether user wants to delete the instance or not. In geeks/templates/delete_view.html,
<div class="main"> <!-- Create a Form --> <form method="POST"> <!-- Security token by Django --> {% csrf_token %} Are you want to delete this item ? <input type="submit" value="Yes" /> <a href="/">Cancel </a> </form></div> |
Everything ready, now let’s check if it is working or not, visit http://localhost:8000/2/delete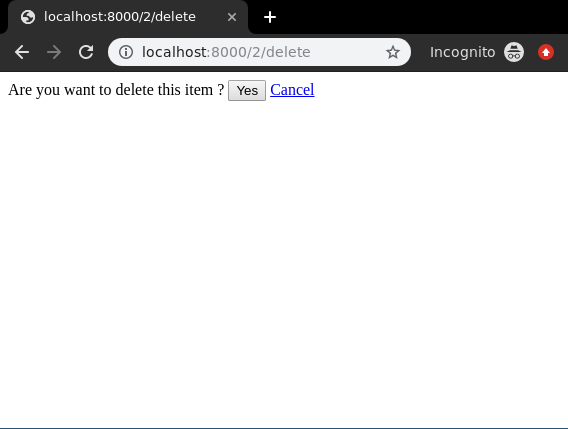
To check complete implementation of Function based Delete View, visit Delete View – Function based Views Django
Attention geek! Strengthen your foundations with the Python Programming Foundation Course and learn the basics.
To begin with, your interview preparations Enhance your Data Structures concepts with the Python DS Course. And to begin with your Machine Learning Journey, join the Machine Learning – Basic Level Course