Динамическое программирование на деревьях | Комплект 2
Для дерева с N узлами и N-1 ребрами найдите максимальную высоту дерева, когда любой узел в дереве считается корнем дерева.
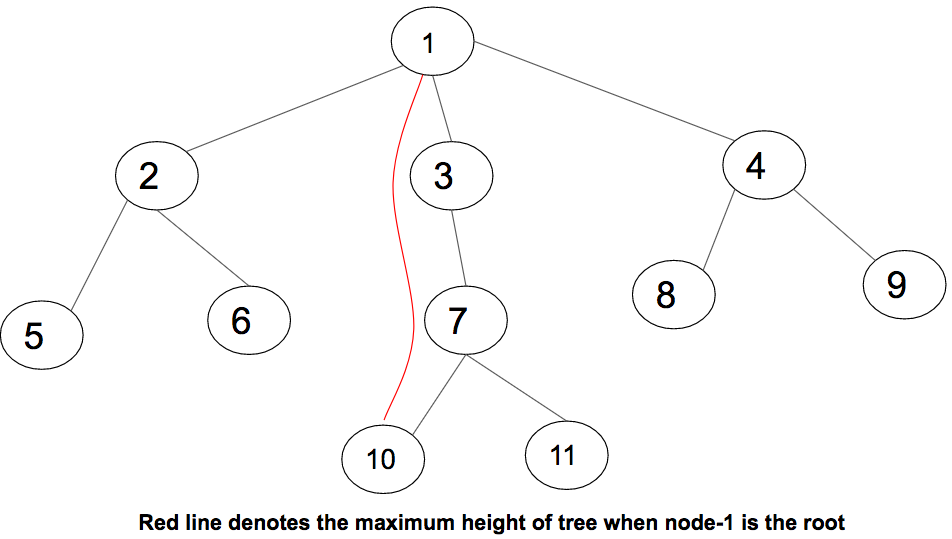
На приведенной выше диаграмме представлено дерево с 11 узлами и 10 ребрами, а также путь, который дает нам максимальную высоту, когда узел 1 рассматривается как корень. Максимальная высота 3.
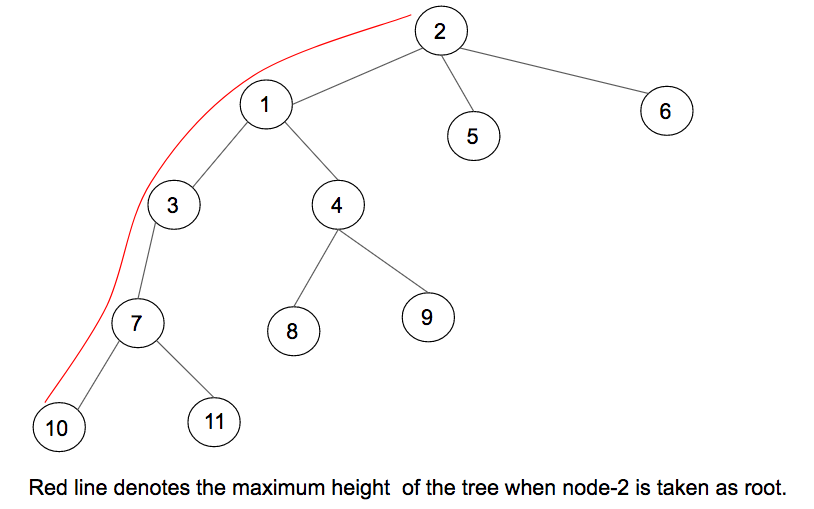
На приведенной выше диаграмме, когда 2 рассматривается как корень, самый длинный найденный путь имеет КРАСНЫЙ цвет. Наивный подход заключался бы в обходе дерева с использованием обхода DFS для каждого узла и вычислении максимальной высоты, когда узел рассматривается как корень дерева. Временная сложность обхода дерева с помощью DFS составляет O (N). Общая временная сложность DFS для всех N узлов будет O (N) * N, то есть O (N 2 ) .
Вышеупомянутую проблему можно решить с помощью динамического программирования на деревьях. Чтобы решить эту проблему, предварительно рассчитайте две вещи для каждого узла. Одна будет максимальной высотой при движении вниз по ветвям к листьям. В то время как другой будет максимальной высотой при перемещении вверх через своего родителя к любому из листьев.
Оптимальная основа:
Когда узел i рассматривается как корень,
in [i] - максимальная высота дерева, когда мы движемся вниз через его поддеревья и листья.
Кроме того, out [i] - максимальная высота дерева при движении вверх через его родителя.
The maximum height of a tree when node i is
considered as a root will be max(in[i], out[i]).
Расчет in [i]:
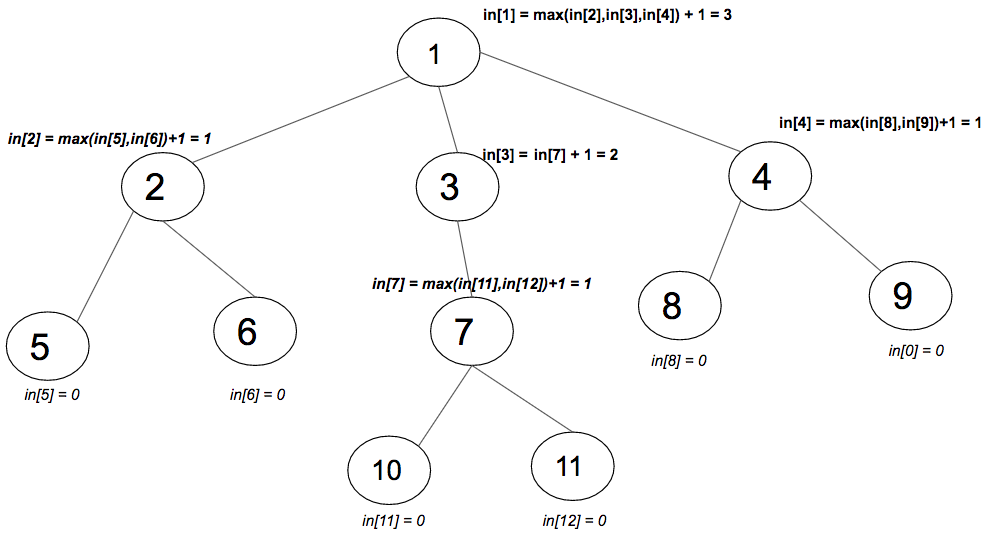
На изображении выше значения в [i] были вычислены для каждого узла i. Берется максимум каждого поддерева и добавляется 1 к родительскому элементу этого поддерева. Добавьте 1 для границы между родительским деревом и поддеревом. Пройдите по дереву с помощью DFS и вычислите в [i] как max (в [i], 1 + в [child]) для каждого узла.
Расчет out [i]:
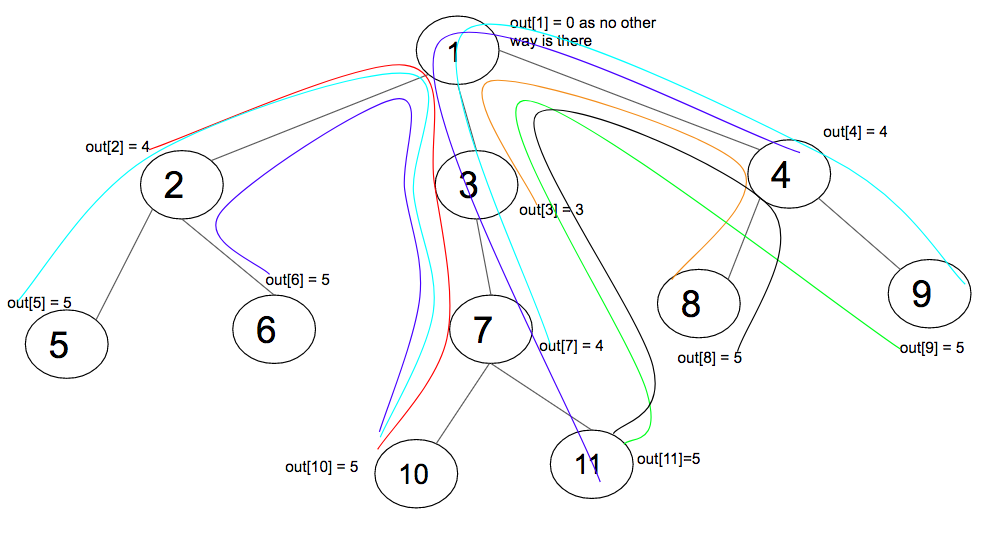
На приведенной выше диаграмме показаны все значения out [i] и путь. Для вычисления out [i] переместитесь вверх к родительскому узлу i. Из родителя узла i можно перейти двумя способами: один будет во всех ветвях родительского узла. Другое направление - перейти к родительскому (назовите его parent2, чтобы избежать путаницы) родительского (назовите его parent1) узла i. Максимальная высота вверх через parent2 равна самому [parent1] . Как правило, out [node i] как 1 + max (out [i], 1 + max всех ветвей). Добавьте 1 для ребер между узлом и родителем.
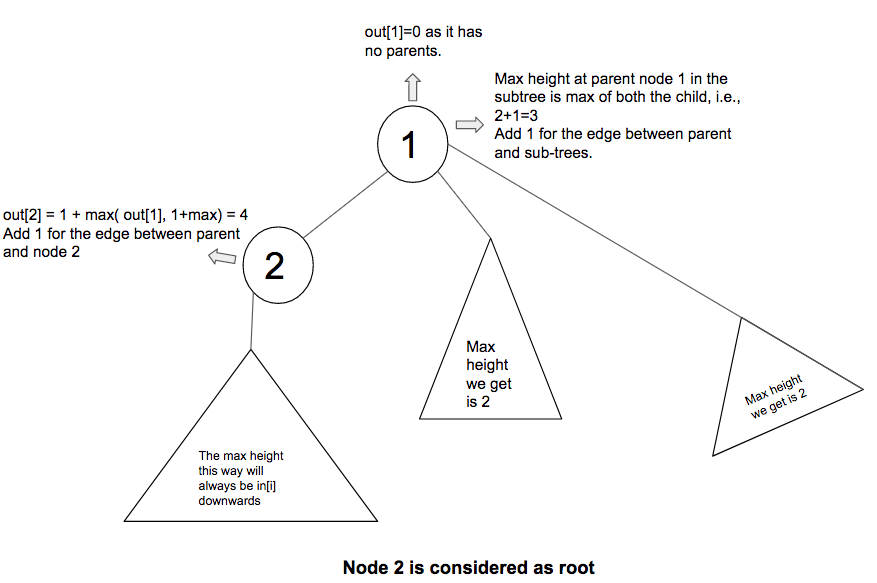
Приведенная выше диаграмма объясняет вычисление out [i], когда 2 рассматривается как корень дерева. Ветви узла 2 не учитываются, поскольку максимальная высота по этому пути уже вычислена и сохранена в i [2]. В этом случае при движении вверх родительский элемент 2, т. Е. 1, не имеет родителя. Таким образом, при расчете максимума учитываются ветви, кроме той, в которой есть узел.
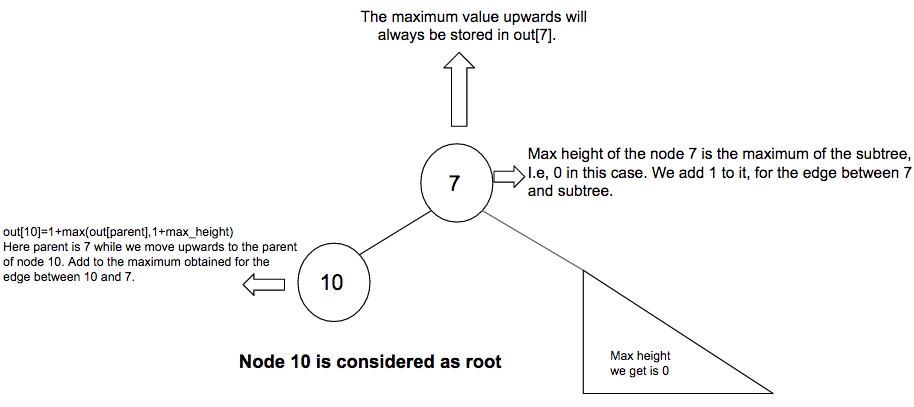
На приведенной выше диаграмме поясняется расчет out [10]. Родитель узла 10, т. Е. 7, имеет родителя и ветвь (в данном случае именно дочерний элемент). Таким образом, максимальная высота обоих была принята для подсчета в тех случаях, когда существуют родительский элемент и ветви.
В случае нескольких ветвей родительского элемента, возьмите для подсчета самую длинную из них (исключая ветвь, в которой находится узел).
Расчет максимальной высоты всех ветвей, связанных с родительским:
in [i] сохраняет максимальную высоту при движении вниз. Нет необходимости хранить ветки по всей длине. Только первая и вторая максимальная длина среди всех ветвей дадут ответ. Поскольку используемый алгоритм основан на DFS, будут рассмотрены все ветви, связанные с родительским узлом, включая ветвь с узлом. Если полученный таким образом первый максимальный путь такой же, как в [i], то maximum1 - это длина ветви, в которой лежит узел i. В этом случае наш самый длинный путь будет максимум2.
Отношение повторения in [i] и out [i]:
in[i] = max(in[i], 1 + in[child])
out[i] = 1 + max(out[parent of i], 1 + longest path of all branches of parent of i)
Below is the implementation of the above idea:
C++
// C++ code to find the maximum path length// considering any node as root#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std;const int MAX_NODES = 100;int in[MAX_NODES];int out[MAX_NODES];// function to pre-calculate the array in[]// which stores the maximum height when travelled// via branchesvoid dfs1(vector<int> v[], int u, int parent){ // initially every node has 0 height in[u] = 0; // traverse in the subtree of u for (int child : v[u]) { // if child is same as parent if (child == parent) continue; // dfs called dfs1(v, child, u); // recursively calculate the max height in[u] = max(in[u], 1 + in[child]); }}// function to pre-calculate the array ouut[]// which stores the maximum height when traveled// via parentvoid dfs2(vector<int> v[], int u, int parent){ // stores the longest and second // longest branches int mx1 = -1, mx2 = -1; // traverse in the subtress of u for (int child : v[u]) { if (child == parent) continue; // compare and store the longest // and second longest if (in[child] >= mx1) { mx2 = mx1; mx1 = in[child]; } else if (in[child] > mx2) mx2 = in[child]; } // traverse in the subtree of u for (int child : v[u]) { if (child == parent) continue; int longest = mx1; // if longest branch has the node, then // consider the second longest branch if (mx1 == in[child]) longest = mx2; // recursively calculate out[i] out[child] = 1 + max(out[u], 1 + longest); // dfs function call dfs2(v, child, u); }}// function to print all the maximum heights// from every nodevoid printHeights(vector<int> v[], int n){ // traversal to calculate in[] array dfs1(v, 1, 0); // traversal to calculate out[] array dfs2(v, 1, 0); // print all maximum heights for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cout << "The maximum height when node " << i << " is considered as root" << " is " << max(in[i], out[i]) << "
";}// Driver Codeint main(){ int n = 11; vector<int> v[n + 1]; // initialize the tree given in the diagram v[1].push_back(2), v[2].push_back(1); v[1].push_back(3), v[3].push_back(1); v[1].push_back(4), v[4].push_back(1); v[2].push_back(5), v[5].push_back(2); v[2].push_back(6), v[6].push_back(2); v[3].push_back(7), v[7].push_back(3); v[7].push_back(10), v[10].push_back(7); v[7].push_back(11), v[11].push_back(7); v[4].push_back(8), v[8].push_back(4); v[4].push_back(9), v[9].push_back(4); // function to print the maximum height from every node printHeights(v, n); return 0;} |
Java
// Java code to find the maximum path length// considering any node as rootimport java.io.*;import java.util.*;class GFG{static final int MAX_NODES = 100;static int in[] = new int[MAX_NODES];static int out[] = new int[MAX_NODES];// Function to pre-calculate the array in[]// which stores the maximum height when travelled// via branchesstatic void dfs1(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> v, int u, int parent){ // Initially every node has 0 height in[u] = 0; // Traverse in the subtree of u for(int j = 0; j < v.get(u).size(); j++) { int child = v.get(u).get(j); // If child is same as parent if (child == parent) continue; // dfs called dfs1(v, child, u); // Recursively calculate the max height in[u] = Math.max(in[u], 1 + in[child]); }}// Function to pre-calculate the array ouut[]// which stores the maximum height when traveled// via parentstatic void dfs2(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> v, int u, int parent){ // Stores the longest and second // longest branches int mx1 = -1, mx2 = -1; // Traverse in the subtress of u for(int j = 0; j < v.get(u).size(); j++) { int child = v.get(u).get(j); if (child == parent) continue; // Compare and store the longest // and second longest if (in[child] >= mx1) { mx2 = mx1; mx1 = in[child]; } else if (in[child] > mx2) mx2 = in[child]; } // Traverse in the subtree of u for(int j = 0; j < v.get(u).size(); j++) { int child = v.get(u).get(j); if (child == parent) continue; int longest = mx1; // If longest branch has the node, then // consider the second longest branch if (mx1 == in[child]) longest = mx2; // Recursively calculate out[i] out[child] = 1 + Math.max(out[u], 1 + longest); // dfs function call dfs2(v, child, u); }}static void addEdge(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, int u, int v){ adj.get(u).add(v); adj.get(v).add(u);}// Function to print all the maximum heights// from every nodestatic void printHeights(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> v, int n){ // Traversal to calculate in[] array dfs1(v, 1, 0); // Traversal to calculate out[] array dfs2(v, 1, 0); // Print all maximum heights for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) System.out.println( "The maximum height when node " + i + " is considered as root is " + Math.max(in[i], out[i]));}// Driver Codepublic static void main(String[] args){ // Creating a graph with 11 vertices int V = 12; ArrayList<ArrayList< Integer>> adj = new ArrayList<ArrayList< Integer>>(V + 1); for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) adj.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); // Initialize the tree given in the diagram addEdge(adj, 1, 2); addEdge(adj, 1, 3); addEdge(adj, 1, 4); addEdge(adj, 2, 5); addEdge(adj, 2, 6); addEdge(adj, 3, 7); addEdge(adj, 7, 10); addEdge(adj, 7, 11); addEdge(adj, 4, 8); addEdge(adj, 4, 9); // Function to print the maximum height // from every node printHeights(adj, V);}}// This code is contributed by decoding |
Python3
# Python3 code to find the maximum path length# considering any node as rootinn = [0] * 100out = [0] * 100# function to pre-calculate the array inn[]# which stores the maximum height when travelled# via branchesdef dfs1(v, u, parent): global inn, out # initially every node has 0 height inn[u] = 0 # traverse in the subtree of u for child in v[u]: # if child is same as parent if (child == parent): continue # dfs called dfs1(v, child, u) # recursively calculate the max height inn[u] = max(inn[u], 1 + inn[child])# function to pre-calculate the array ouut[]# which stores the maximum height when traveled# via parentdef dfs2(v, u, parent): global inn, out # stores the longest and second # longest branches mx1, mx2 = -1, -1 # traverse in the subtress of u for child in v[u]: if (child == parent): continue # compare and store the longest # and second longest if (inn[child] >= mx1): mx2 = mx1 mx1 = inn[child] elif (inn[child] > mx2): mx2 = inn[child] # traverse in the subtree of u for child in v[u]: if (child == parent): continue longest = mx1 # if longest branch has the node, then # consider the second longest branch if (mx1 == inn[child]): longest = mx2 # recursively calculate out[i] out[child] = 1 + max(out[u], 1 + longest) # dfs function call dfs2(v, child, u)# function to prall the maximum heights# from every nodedef printHeights(v, n): global inn, out # traversal to calculate inn[] array dfs1(v, 1, 0) # traversal to calculate out[] array dfs2(v, 1, 0) # prall maximum heights for i in range(1, n + 1): print("The maximum height when node", i, "is considered as root is", max(inn[i], out[i]))# Driver Codeif __name__ == "__main__": n = 11 v = [[] for i in range(n + 1)] # initialize the tree given in the diagram v[1].append(2)
|