Цикл сортировки
Опубликовано: 20 Января, 2022
Циклическая сортировка - это алгоритм сортировки на месте, алгоритм нестабильной сортировки, сортировка сравнения, которая теоретически оптимальна с точки зрения общего количества записей в исходный массив.
- Оптимален по количеству операций записи в память. Он минимизирует количество операций записи в память для сортировки (каждое значение либо записывается ноль раз, если оно уже находится в правильной позиции, либо записывается один раз в правильную позицию).
- В его основе лежит идея о том, что сортируемый массив можно разбить на циклы. Циклы можно визуализировать в виде графика. У нас есть n узлов и ребро, направленное от узла i к узлу j, если элемент с i-м индексом должен присутствовать в j-м индексе в отсортированном массиве.
Цикл в arr [] = {2, 4, 5, 1, 3}
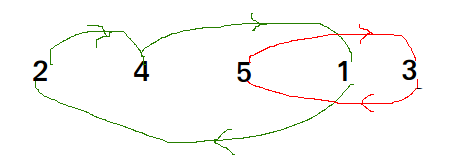
- Цикл в arr [] = {4, 3, 2, 1}
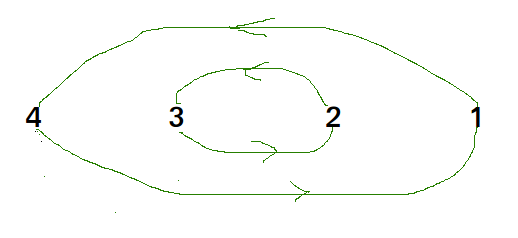
Мы по порядку рассматриваем все циклы. Сначала рассмотрим цикл, который включает в себя первый элемент. Мы находим правильное положение первого элемента, помещаем его в правильное положение, скажем j. Мы рассматриваем старое значение arr [j] и находим его правильное положение, продолжаем делать это до тех пор, пока все элементы текущего цикла не будут помещены в правильное положение, т.е. мы не вернемся к начальной точке цикла.
Рекомендуется: сначала попробуйте свой подход в {IDE}, прежде чем переходить к решению.
Объяснение :
arr[] = {10, 5, 2, 3}
index = 0 1 2 3
cycle_start = 0
item = 10 = arr[0]
Find position where we put the item
pos = cycle_start
i=pos+1
while(i<n)
if (arr[i] < item)
pos++;
We put 10 at arr[3] and change item to
old value of arr[3].
arr[] = {10, 5, 2, 10}
item = 3
Again rotate rest cycle that start with index "0"
Find position where we put the item = 3
we swap item with element at arr[1] now
arr[] = {10, 3, 2, 10}
item = 5
Again rotate rest cycle that start with index "0" and item = 5
we swap item with element at arr[2].
arr[] = {10, 3, 5, 10 }
item = 2
Again rotate rest cycle that start with index "0" and item = 2
arr[] = {2, 3, 5, 10}
Above is one iteration for cycle_stat = 0.
Repeat above steps for cycle_start = 1, 2, ..n-2
CPP
// C++ program to implement cycle sort#include <iostream>using namespace std;// Function sort the array using Cycle sortvoid cycleSort(int arr[], int n){ // count number of memory writes int writes = 0; // traverse array elements and put it to on // the right place for (int cycle_start = 0; cycle_start <= n - 2; cycle_start++) { // initialize item as starting point int item = arr[cycle_start]; // Find position where we put the item. We basically // count all smaller elements on right side of item. int pos = cycle_start; for (int i = cycle_start + 1; i < n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos++; // If item is already in correct position if (pos == cycle_start) continue; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (pos != cycle_start) { swap(item, arr[pos]); writes++; } // Rotate rest of the cycle while (pos != cycle_start) { pos = cycle_start; // Find position where we put the element for (int i = cycle_start + 1; i < n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos += 1; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (item != arr[pos]) { swap(item, arr[pos]); writes++; } } } // Number of memory writes or swaps // cout << writes << endl ;}// Driver program to test above functionint main(){ int arr[] = { 1, 8, 3, 9, 10, 10, 2, 4 }; int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]); cycleSort(arr, n); cout << "After sort : " << endl; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) cout << arr[i] << " "; return 0;} |
Java
// Java program to implement cycle sortimport java.util.*;import java.lang.*;class GFG { // Function sort the array using Cycle sort public static void cycleSort(int arr[], int n) { // count number of memory writes int writes = 0; // traverse array elements and put it to on // the right place for (int cycle_start = 0; cycle_start <= n - 2; cycle_start++) { // initialize item as starting point int item = arr[cycle_start]; // Find position where we put the item. We basically // count all smaller elements on right side of item. int pos = cycle_start; for (int i = cycle_start + 1; i < n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos++; // If item is already in correct position if (pos == cycle_start) continue; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (pos != cycle_start) { int temp = item; item = arr[pos]; arr[pos] = temp; writes++; } // Rotate rest of the cycle while (pos != cycle_start) { pos = cycle_start; // Find position where we put the element for (int i = cycle_start + 1; i < n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos += 1; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (item != arr[pos]) { int temp = item; item = arr[pos]; arr[pos] = temp; writes++; } } } } // Driver program to test above function public static void main(String[] args) { int arr[] = { 1, 8, 3, 9, 10, 10, 2, 4 }; int n = arr.length; cycleSort(arr, n); System.out.println("After sort : "); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) System.out.print(arr[i] + " "); }}// Code Contributed by Mohit Gupta_OMG <(0_o)> |
Python3
# Python program to implement cycle sortdef cycleSort(array): writes = 0 # Loop through the array to find cycles to rotate. for cycleStart in range(0, len(array) - 1): item = array[cycleStart] # Find where to put the item. pos = cycleStart for i in range(cycleStart + 1, len(array)): if array[i] < item: pos += 1 # If the item is already there, this is not a cycle. if pos == cycleStart: continue # Otherwise, put the item there or right after any duplicates. while item == array[pos]: pos += 1 array[pos], item = item, array[pos] writes += 1 # Rotate the rest of the cycle. while pos != cycleStart: # Find where to put the item. pos = cycleStart for i in range(cycleStart + 1, len(array)): if array[i] < item: pos += 1 # Put the item there or right after any duplicates. while item == array[pos]: pos += 1 array[pos], item = item, array[pos] writes += 1 return writes # driver codearr = [1, 8, 3, 9, 10, 10, 2, 4 ]n = len(arr)cycleSort(arr)print("After sort : ")for i in range(0, n) : print(arr[i], end = " ")# Code Contributed by Mohit Gupta_OMG <(0_o)> |
C#
// C# program to implement cycle sortusing System;class GFG { // Function sort the array using Cycle sort public static void cycleSort(int[] arr, int n) { // count number of memory writes int writes = 0; // traverse array elements and // put it to on the right place for (int cycle_start = 0; cycle_start <= n - 2; cycle_start++) { // initialize item as starting point int item = arr[cycle_start]; // Find position where we put the item. // We basically count all smaller elements // on right side of item. int pos = cycle_start; for (int i = cycle_start + 1; i < n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos++; // If item is already in correct position if (pos == cycle_start) continue; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (pos != cycle_start) { int temp = item; item = arr[pos]; arr[pos] = temp; writes++; } // Rotate rest of the cycle while (pos != cycle_start) { pos = cycle_start; // Find position where we put the element for (int i = cycle_start + 1; i < n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos += 1; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (item != arr[pos]) { int temp = item; item = arr[pos]; arr[pos] = temp; writes++; } } } } // Driver program to test above function public static void Main() { int[] arr = { 1, 8, 3, 9, 10, 10, 2, 4 }; int n = arr.Length; // Function calling cycleSort(arr, n); Console.Write("After sort : "); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) Console.Write(arr[i] + " "); }}// This code is contributed by Nitin Mittal |
Javascript
<script>// Javascript program to implement cycle sort // Function sort the array using Cycle sort function cycleSort(arr, n) { // count number of memory writes let writes = 0; // traverse array elements and put it to on // the right place for (let cycle_start = 0; cycle_start <= n - 2; cycle_start++) { // initialize item as starting point let item = arr[cycle_start]; // Find position where we put the item. We basically // count all smaller elements on right side of item. let pos = cycle_start; for (let i = cycle_start + 1; i < n; i++) if (arr[i] < item) pos++; // If item is already in correct position if (pos == cycle_start) continue; // ignore all duplicate elements while (item == arr[pos]) pos += 1; // put the item to it"s right position if (pos != cycle_start) { let temp = item; &
РЕКОМЕНДУЕМЫЕ СТАТЬИ |