2D преобразование | Вращение объектов
Мы должны повернуть объект на заданный угол вокруг заданной точки поворота и распечатать новые координаты.
Примеры:
Ввод: {(100, 100), (150, 200), (200, 200),
(200, 150)} нужно повернуть вокруг
(0, 0) на 90 градусов
Выход: (-100, 100), (-200, 150), (-200, 200), (-150, 200)
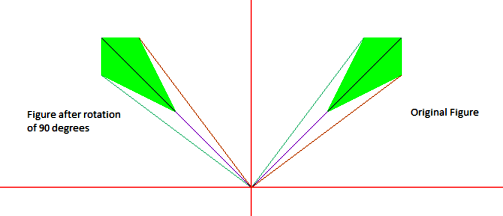
Ввод: {(100, 100), (100, 200), (200, 200)}
должен быть повернут примерно на (50, -50) на
-45 градусов
Выход: (191.421, 20.7107), (262.132, 91.4214),
(332,843, 20,7107)

Чтобы повернуть объект, нам нужно повернуть каждую вершину фигуры индивидуально.
Поворачивая точку P (x, y) на угол A относительно начала координат, мы получаем точку P '(x', y '). Значения x 'и y' можно рассчитать следующим образом:

Мы знаем это,
х = rcosB, y = rsinB
x '= rcos (A + B) = r (cosAcosB - sinAsinB) = rcosB cosA - rsinB sinA = xcosA - ysinA
y '= rsin (A + B) = r (sinAcosB + cosAsinB) = rcosB sinA + rsinB cosA = xsinA + ycosA
Уравнение матрицы вращения: -
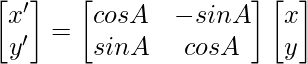
C
// C program to rotate an object by// a given angle about a given point#include <math.h>#include <stdio.h>// Using macros to convert degree to radian// and call sin() and cos() as these functions// take input in radians#define SIN(x) sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)#define COS(x) cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)// To rotate an objectvoid rotate(float a[][2], int n, int x_pivot, int y_pivot, int angle){ int i = 0; while (i < n) { // Shifting the pivot point to the origin // and the given points accordingly int x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot; int y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot; // Calculating the rotated point co-ordinates // and shifting it back a[i][0] = x_pivot + (x_shifted * COS(angle) - y_shifted * SIN(angle)); a[i][1] = y_pivot + (x_shifted * SIN(angle) + y_shifted * COS(angle)); printf("(%f, %f) ", a[i][0], a[i][1]); i++; }}// Driver Codeint main(){ // 1st Example // The following figure is to be // rotated about (0, 0) by 90 degrees int size1 = 4; // No. of vertices // Vertex co-ordinates must be in order float points_list1[][2] = { { 100, 100 }, { 150, 200 }, { 200, 200 }, { 200, 150 } }; rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90); // 2nd Example // The following figure is to be // rotated about (50, -50) by -45 degrees /*int size2 = 3;//No. of vertices float points_list2[][2] = {{100, 100}, {100, 200}, {200, 200}}; rotate(points_list2, size2, 50, -50, -45);*/ return 0;} |
CPP
// C++ program to rotate an object by// a given angle about a given point#include <iostream>#include <math.h>using namespace std;// Using macros to convert degree to radian// and call sin() and cos() as these functions// take input in radians#define SIN(x) sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)#define COS(x) cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)// To rotate an object given as order set of points in a[]// (x_pivot, y_pivot)void rotate(float a[][2], int n, int x_pivot, int y_pivot, int angle){ int i = 0; while (i < n) { // Shifting the pivot point to the origin // and the given points accordingly int x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot; int y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot; // Calculating the rotated point co-ordinates // and shifting it back a[i][0] = x_pivot + (x_shifted * COS(angle) - y_shifted * SIN(angle)); a[i][1] = y_pivot + (x_shifted * SIN(angle) + y_shifted * COS(angle)); cout << "(" << a[i][0] << ", " << a[i][1] << ") "; i++; }}// Driver Codeint main(){ // 1st Example // The following figure is to be // rotated about (0, 0) by 90 degrees int size1 = 4; // No. of vertices // Vertex co-ordinates must be in order float points_list1[][2] = { { 100, 100 }, { 150, 200 }, { 200, 200 }, { 200, 150 } }; rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90); // 2nd Example // The following figure is to be // rotated about (50, -50) by -45 degrees /*int size2 = 3;//No. of vertices float points_list2[][2] = {{100, 100}, {100, 200}, {200, 200}}; rotate(points_list2, size2, 50, -50, -45);*/ return 0;} |
Выход:
(-100, 100), (-200, 150), (-200, 200), (-150, 200)
Ссылки: матрица вращения
Эта статья предоставлена Набанитом Роем . Если вам нравится GeeksforGeeks, и вы хотели бы внести свой вклад, вы также можете написать статью на сайте deposit.geeksforgeeks.org или отправить свою статью по электронной почте: grant@geeksforgeeks.org. Посмотрите, как ваша статья появляется на главной странице GeeksforGeeks, и помогите другим гикам.
Пожалуйста, напишите комментарии, если вы обнаружите что-то неправильное, или вы хотите поделиться дополнительной информацией по теме, обсужденной выше.
Вниманию читателя! Не прекращайте учиться сейчас. Освойте все важные концепции DSA с помощью самостоятельного курса DSA по приемлемой для студентов цене и будьте готовы к работе в отрасли. Чтобы завершить подготовку от изучения языка к DS Algo и многому другому, см. Полный курс подготовки к собеседованию .
Если вы хотите посещать живые занятия с отраслевыми экспертами, пожалуйста, обращайтесь к Geeks Classes Live и Geeks Classes Live USA.